-
iestinstrument
Tesla 4680 Battery VS. BYD Blade Battery: Study Reveals Different Battery Cell Technologies
Tesla 4680 battery technology is reshaping the electric vehicle (EV) market, competing directly with the BYD Blade battery through fundamentally different design philosophies. A collaborative teardown study conducted by Fraunhofer IKTS, MEET at the University of Münster, and PEM of RWTH Aachen University—published in Cell Reports Physical Science—provides a detailed comparison of the BYD Blade battery vs Tesla 4680 battery, highlighting differences in design, materials, manufacturing methods, and market positioning.
Tesla leverages its 4680 battery cells to maximize energy density and overall performance, while BYD emphasizes cost efficiency and safety with its prismatic Blade cells. This divergence underscores the contrasting strategies between high-performance EVs and mass-market affordability, setting the stage for the growing EV battery market bifurcation.

Figure 1. Tesla 4680 Battery VS. BYD Blade Battery
1. Structural and Material Contrasts
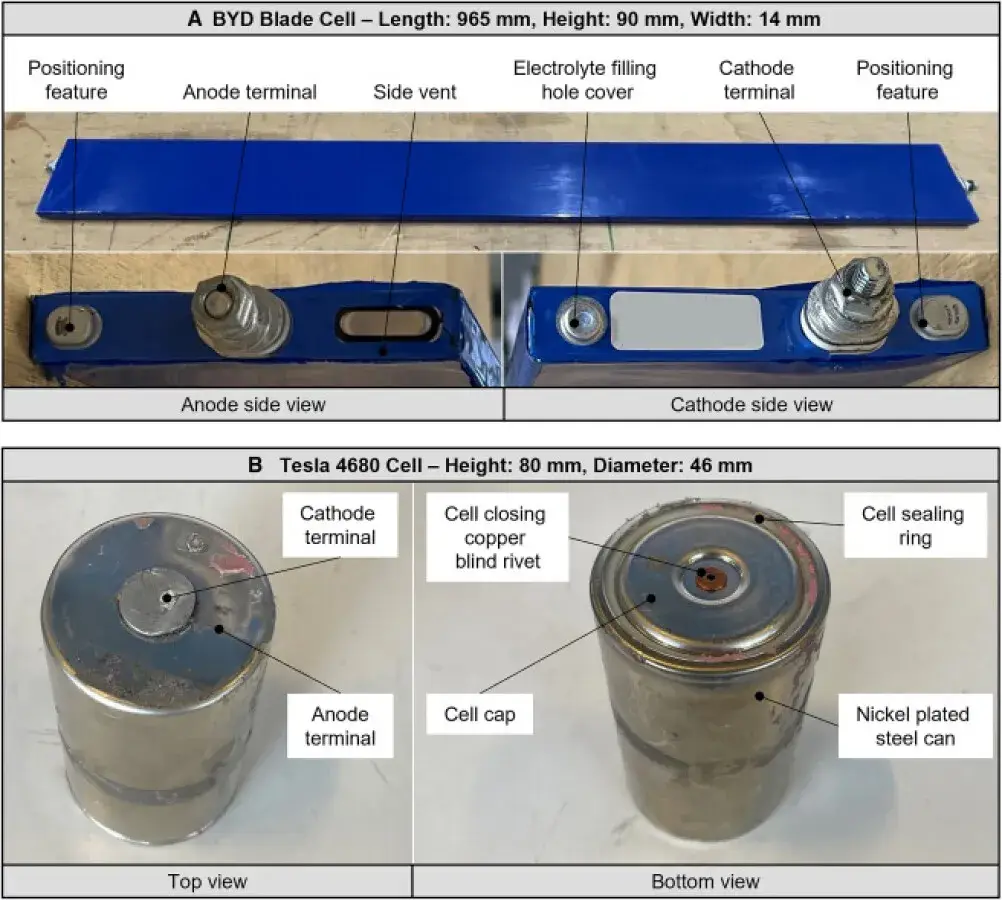
Tesla 4680 battery cells employs a tabless design with nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM811) cathode chemistry, optimized for high energy density (241 Wh/kg gravimetric, 643.3 Wh/L volumetric). Its jelly-roll electrode configuration, laser-welded for inter-electrode connections, minimizes internal resistance and enhances current collection efficiency.
In the contrast, BYD Cells Battery adopts lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistry, prioritizing thermal stability and cost efficiency. Its elongated, flat design integrates stacked electrodes secured via hybrid laser and ultrasonic welding, ensuring mechanical robustness and simplified thermal management.
2. Performance and Thermal Trade-offs
While the Tesla 4680 battery achieves superior energy storage, it produces 2.3× more heat per volume under 1C loads compared to the Blade cells, requiring advanced cooling systems. The BYD cells battery, although lower in energy density (160 Wh/kg, 355 Wh/L), offers exceptional thermal stability and long cycle life, reflecting its safety-first strategy.
This BYD cells battery vs Tesla battery comparison highlights Tesla’s focus on high-performance applications versus BYD’s mass-market approach centered on affordability and reliability.
3. Divergent Manufacturing Approaches
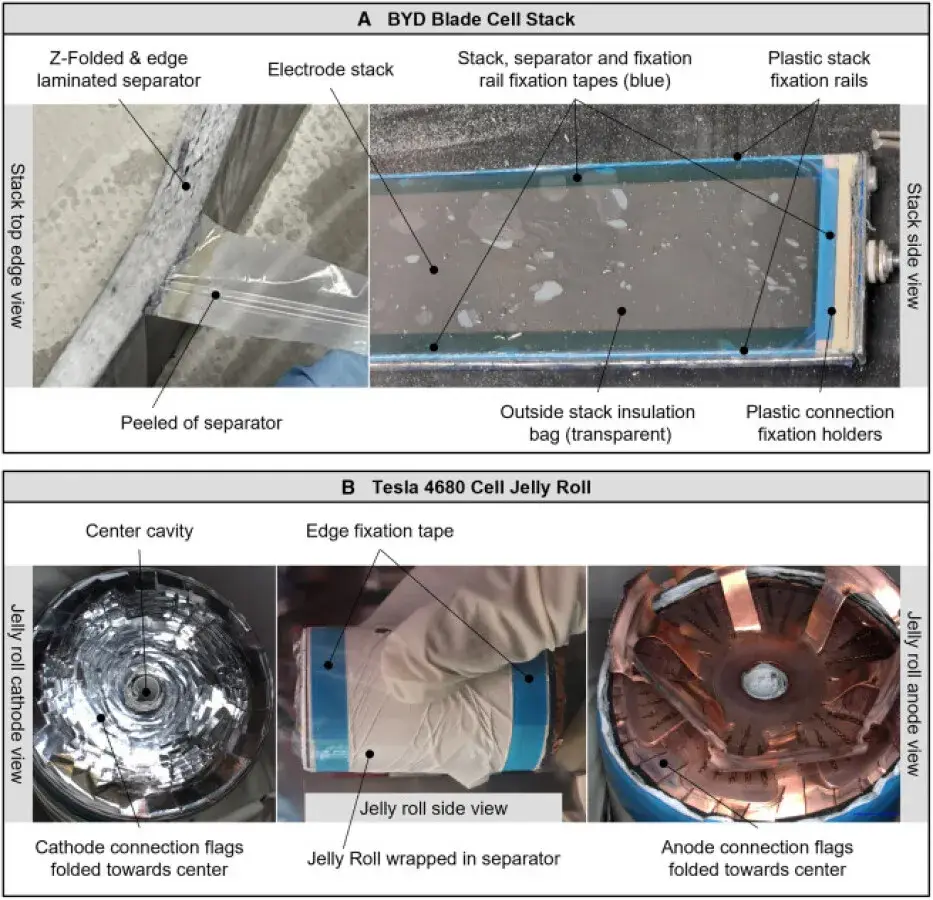
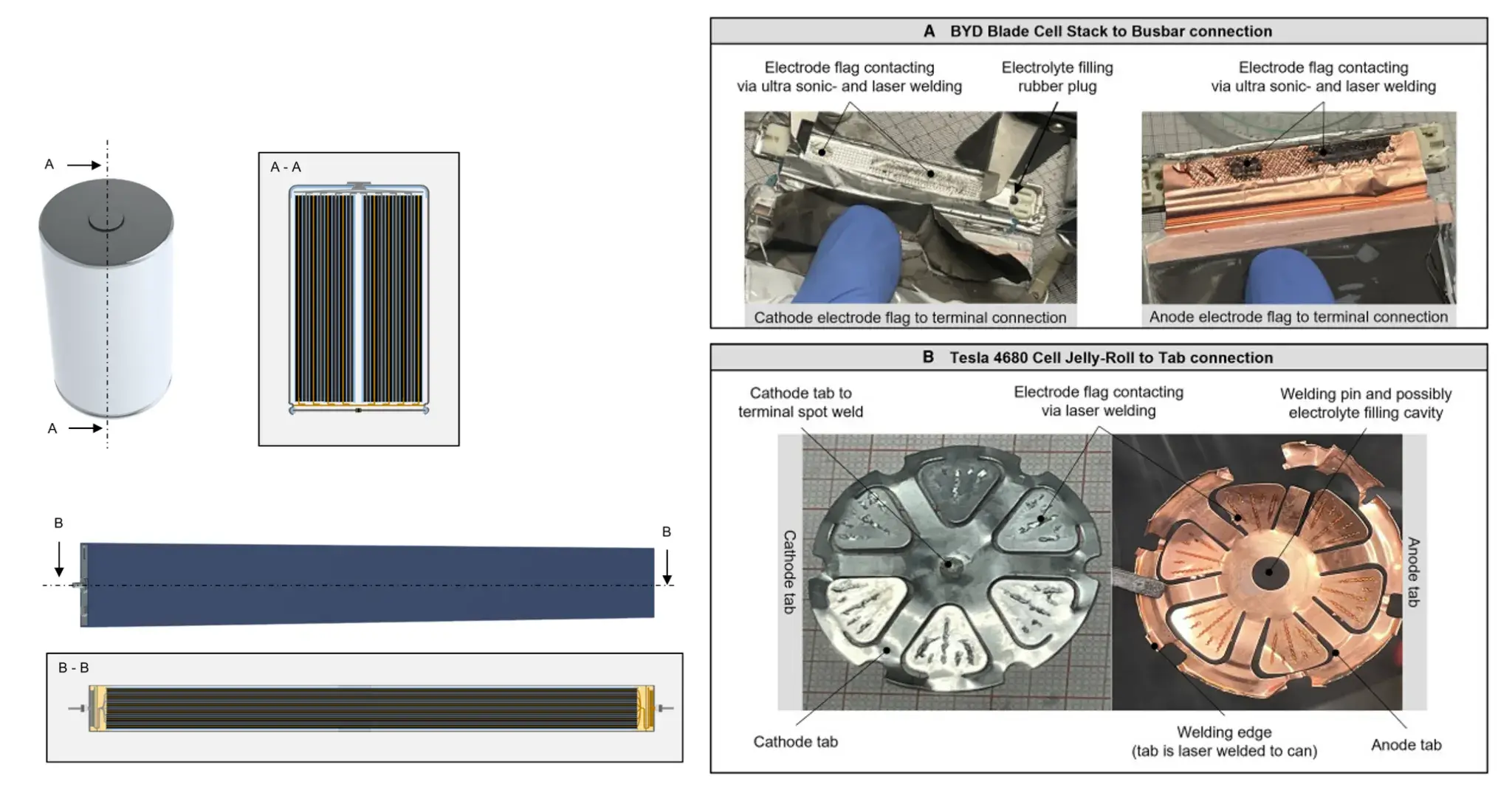
Beyond chemistry and energy density, the manufacturing methodologies exhibit stark contrasts. Tesla employs a tabless electrode design to improve electrical flow and minimize resistance. The 4680 cell utilizes laser welding for electrode connections and a continuous coating process to enhance production efficiency. In contrast, BYD leverages a proprietary lamination process to ensure precise electrode stacking, enabling the creation of exceptionally large electrode assemblies. The company also adopts a hybrid laser and ultrasonic welding strategy, an innovative contacting approach that optimizes spatial efficiency for electrode-to-terminal connections. Cost remains a critical differentiator: According to the study, BYD cells battery achieves a material cost advantage of approximately €10/kWh compared to Tesla 4680 battery cell, positioning it as an attractive option for automakers prioritizing cost reduction.
Both companies use graphite anode electrodes, but Tesla also uses polyacrylic acid (PAA) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) as binders, which may have a certain impact on long-term durability; while BYD uses carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) as binders.
4. Strategic Market Positioning
5. Future Implications
The study highlights an industry bifurcation: NCM-based systems for performance-driven segments versus LFP for cost-sensitive markets. As EV adoption grows, next-generation batteries must balance energy density, thermal management, and cost. Tesla’s advancements in cell efficiency and BYD’s manufacturing innovations exemplify the critical role of tailored solutions in addressing diverse market needs. Ultimately, the EV revolution will hinge not on a singular technological pathway but on strategic optimization of these trade-offs to drive sustainable electrification.
6. References
7. Lithium Battery Testing Solutions Recommend:IEST Instrument
IEST Instrument is a high-tech enterprise focusing on R&D and production of lithium ion battery tester. Dedicated to providing efficient and cutting-edge testing solutions for global electrochemical energy storage, the company supports customers in achieving successful R&D outcomes and quality enhancement. Its core team consists of seasoned experts in materials science, electrochemistry, and automation, and has secured over 100 authorized patents. The testing equipment is widely used in power batteries, energy storage, and materials science, serving customers in more than 20 countries and regions—including China, Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia—and providing world-leading innovative testing solutions to over 900 customers worldwide, earning widespread recognition.
Contact Us
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details, please leave a message here, we will reply you as soon as we can.



