-
iestinstrument
Influence of High Intensive Dry Mixing and Calendaring on Relative Electrode Resistivity Determined Via An Advanced Two Point Approach
Literature appreciation: Influence of High Intensive Dry Mixing and Calendaring on Relative Electrode Resistivity Determined Via An Advanced Two Point Approach
1. Author Information and Article Abstract
Bastian Georg Westphal from the Technical University of Braunschweig, Germany, introduced a fast and simple two-point method (ATPM) to test the relative size of the electrode resistivity in the battery preparation process. Explored some factors that affect the test results, including test pressure, loading current, surface finish of electrode sheet, rolling conditions, dry mixing strength, etc. Providing strong support for lithium battery technology researchers to further understand electrode sheet technology and monitor process stability.
2. Measuring Principle
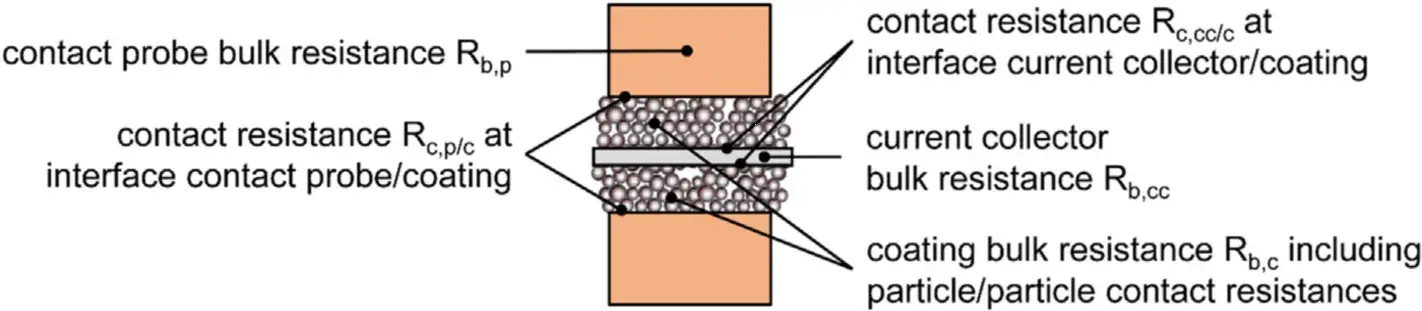
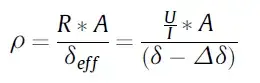
3. Measure Sample Information
The samples tested in this article are all single-sided electrode sheets coated in the laboratory according to a certain formula and process. The information is shown in the table below.
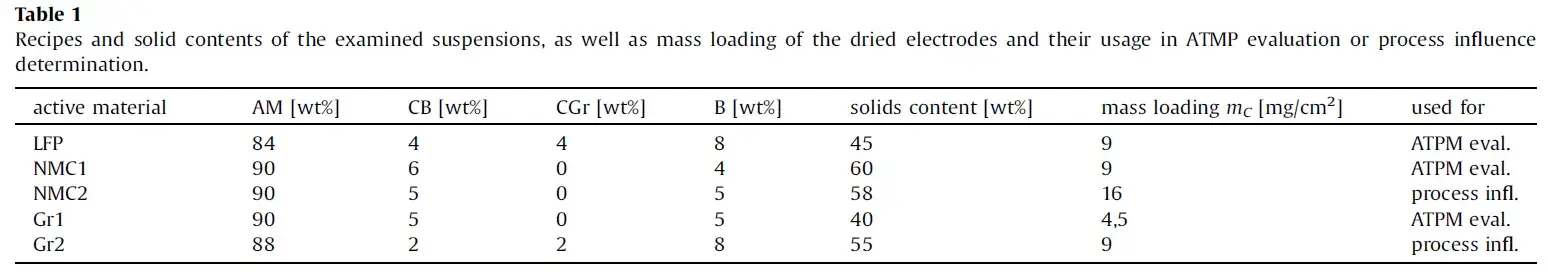
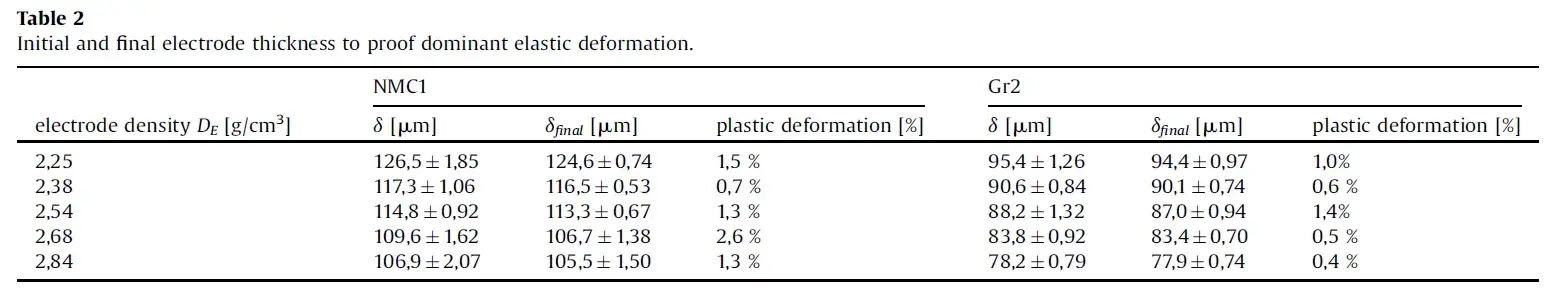
4. Result Analysis
4.1 The Influence of Test Parameters
When testing the the electrode resistivity, the current and pressure applied at both ends of the electrode will affect the absolute value of the resistivity. When a current of 0.1/1/10/20mA is applied to three different types of electrode sheets, the LFP electrode resistivity basically remains unchanged, the NCM1 electrode resistivity is basically unchanged when the current is above 1mA, the resistivity of the Gr1 electrode sheet needs to be kept constant when the current is above 10mA, the resistivity trend of the three electrode sheets is consistent with the resistivity trend of the three materials reported in the literature. Graphite electrode sheets are greatly affected by current mainly because the low resistivity of graphite itself will set off higher parasitic resistivity, so a larger current is required to reduce the impact of interface voltage drop. Based on the above factors, the author believes that 10mA is a suitable test current for all three types of electrode sheets.
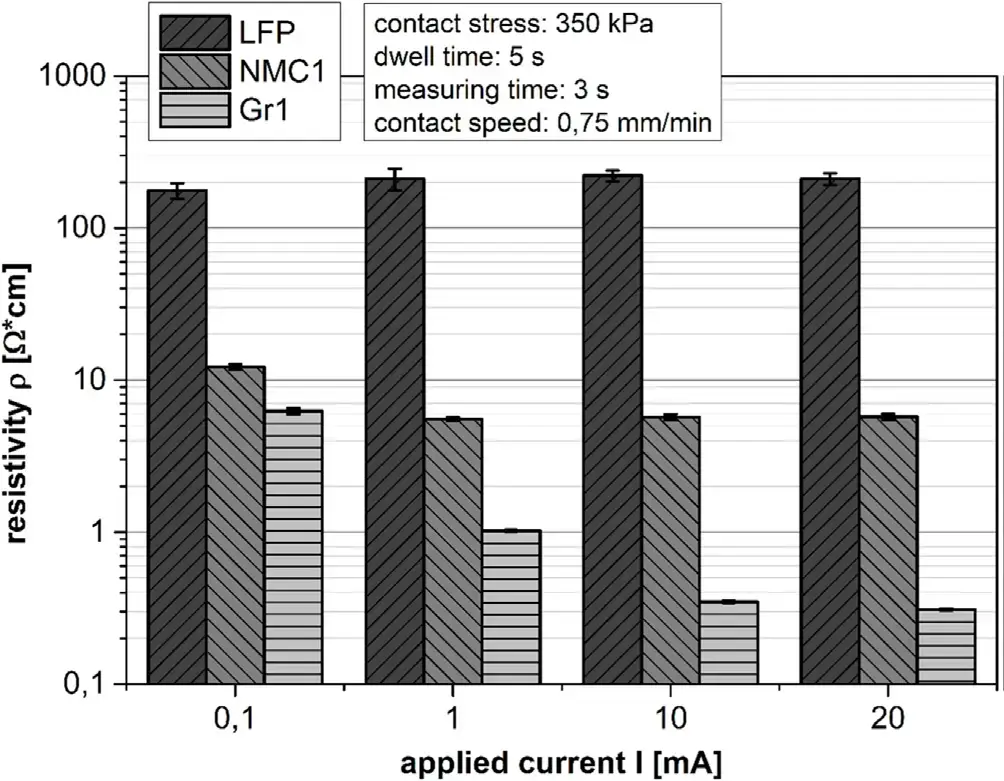
Figure 2. The effect of loading current on the electrode resistivity
The applied pressure will also affect the electrode resistivity. With the increase of the applied pressure, it can be seen that the conductivity of NMC1 and Gr1 decrease with the increase of the applied pressure. This is because the increase in pressure reduces the interface contact resistance between the probe and the coating. On the other hand, the application of pressure reduces the thickness of the electrode and shortens the conductive path. Therefore, the test pressure should be as small as possible without considering changing the conductive path of the electrode itself. In summary, the author believes that 350kPa is an appropriate applied pressure.
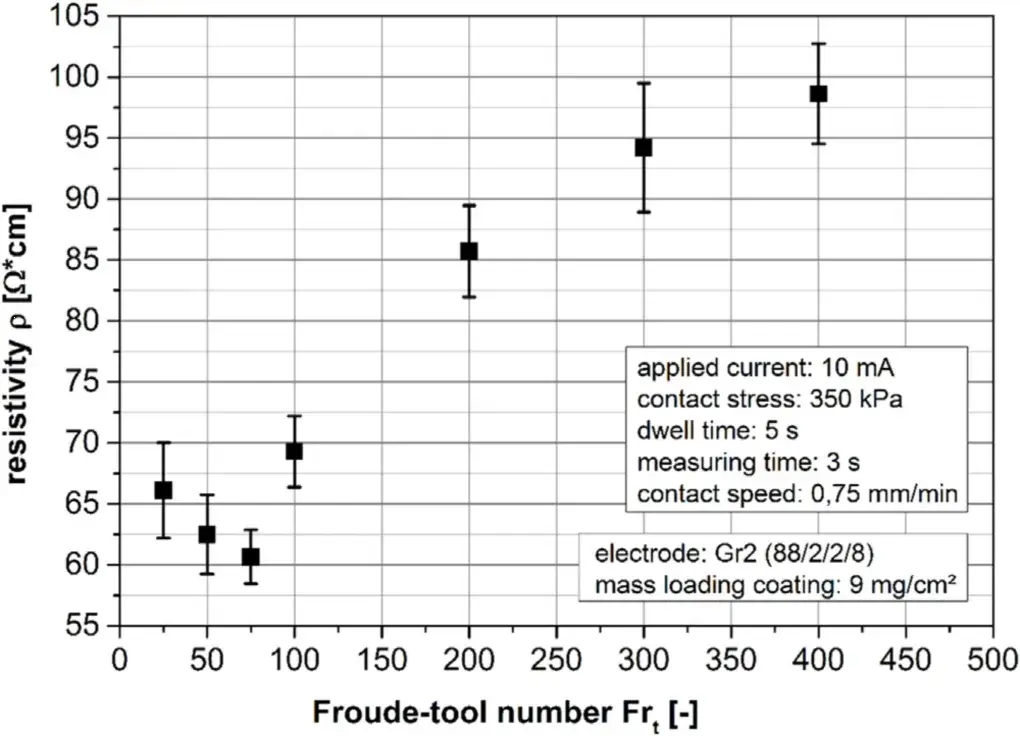
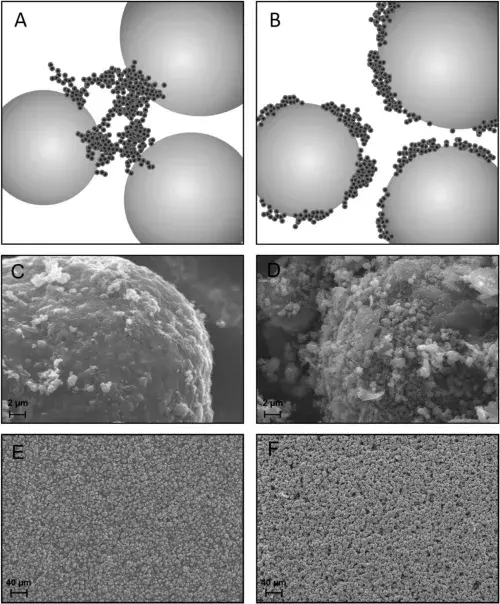
Figure 3. The influence of different dry mixing strengths on the electrode resistivity
5. Summary
The two-point method proposed in this paper is a simpler and faster method to evaluate the process performance of the electrode from the perspective of practical application. It is more suitable for testing the electrode resistance of the lithium ion battery than the four-probe method. Test pressure, loading current, rolling pressure, dry mixing strength, etc. will all affect the absolute value of resistivity. Therefore, it is necessary to select appropriate parameters to obtain stable test results to guide process development.
6. IEST Related Test Equipment Recommendation
BER Series Multi-function Battery Electrode Resistance Instrument(IEST): The double-planar, controlled-voltage disc electrode resistance method has the following characteristics: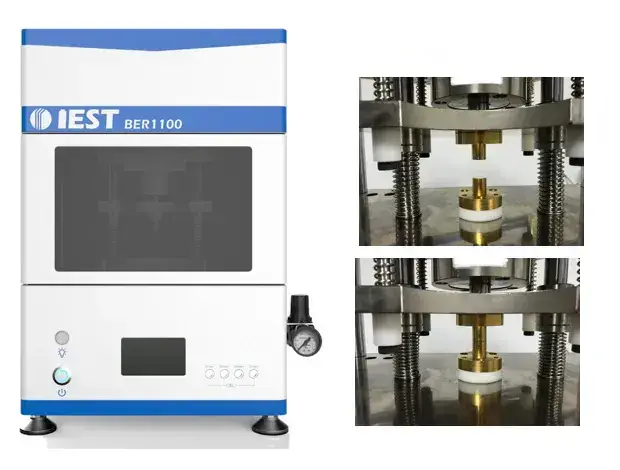
- Separate the voltage and current lines, eliminate the influence of inductance on voltage measurement, and improve the detection accuracy.
- The 14mm diameter disc electrode ensures a relatively large contact area with the sample and reduces the test error.
- Directly measure the longitudinal penetration resistance of the real electrode, that is, the sum of the coating resistance, the contact resistance between the coating and the current collector, and the current collector resistance.
- It can monitor the change of electrode resistance, electrode thickness and electrode compaction with pressure in real time.
- The applied pressure can be accurately controlled to ensure the consistency of the test data.
The battery electrode sheet resistance tester(BER Series) can better evaluate the performance of the electronic conductive network or the uniformity of the electrode microstructure in the electrode production process, and help to research and improve the electrode formulation and the control parameters of the mixing, coating and rolling process.
7. Reference
Subscribe Us
Contact Us
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details, please leave a message here, we will reply you as soon as we can.



