-
iestinstrument
Solid-state Electrolytes Testing Method for Electrochemical Properties
1. Preface
The conductivity of the solid-state electrolyte and its overall cycle performance are greatly influenced by factors such as density, roughness, and integrity of the pressed solid electrolyte sheet. Moreover, stable and consistent pressure during testing is vital for ensuring accurate test results. Hence, having production and testing systems capable of applying stable and standardized pressure is critical for the advancement of solid-state electrolytes and their lithium-metal batteries.
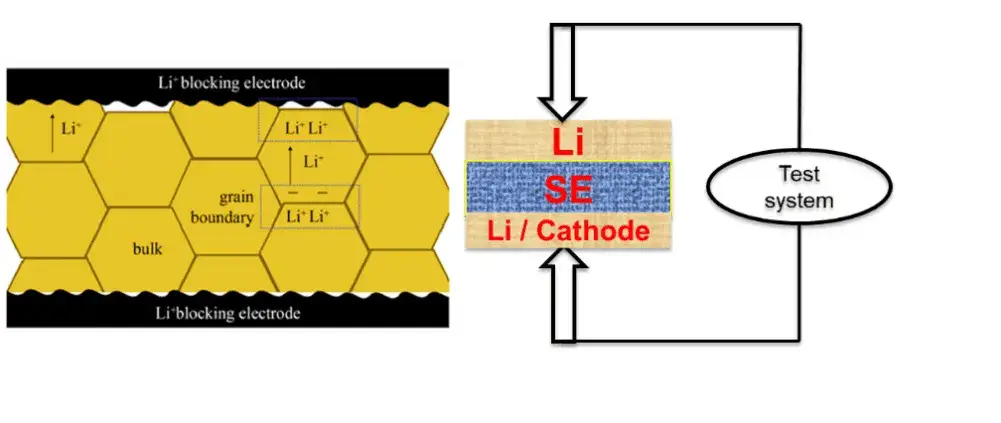 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the testing of solid-state electrolytes
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the testing of solid-state electrolytes
2. Testing Instrument
Solid-state electrolyte test system SEMS1100 (jointly developed by IEST and Xiamen University), is a multi-functional test dedicated to solid-state electrolyte samples, integrating pressure plate, testing, calculation of the automatic chemical performance of solid-state electrolyte measurement equipment. The system adopts an integrated structure design, including pressurized module, electrochemical test module, density measurement module, ceramic sheet pressing and clamping module, etc., which is suitable for the testing of various oxides, sulfide, polymer and other solid-state electrolytes.
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the solid-state electrolyte test system equipment
3. Application Cases
3.1 Powder Production
To evaluate the electrochemical properties of solid-state electrolyte powder, And the samples with poor interface contact also need to spray a conductive metal on the surface as an ion blocking electrode, The force application and uniformity will greatly affect the integrity of the prepared ceramic sheet, Figure 3 shows a macro picture of ceramic pieces obtained from different pressing devices, The uniform force application of SEMS1100 equipment is used to prepare the solid-state electrolyte ceramic sheet, Complete and uniform samples in different pressure ranges, Reduce the risk of sample destruction, Improve the yield and test efficiency.
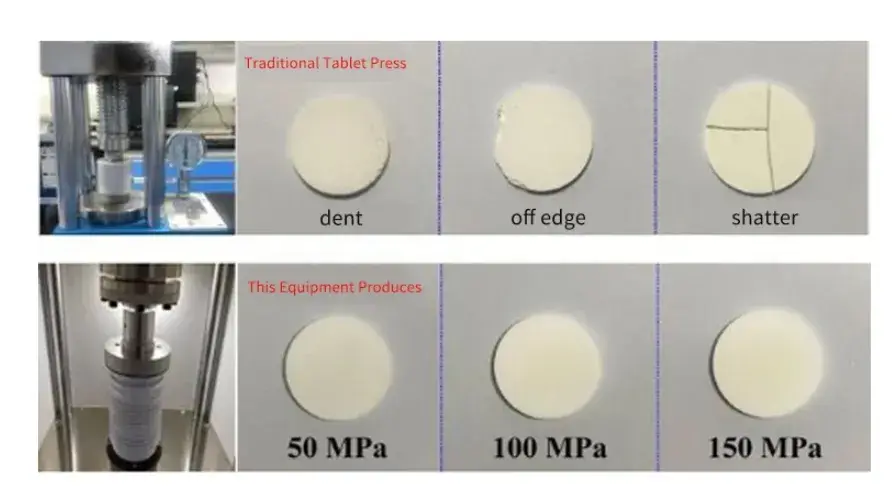
Figure 3. Comparison of the production results of different devices
3.2 Lon Electrical Conductivity
The two different solid-state electrolyte materials Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7 (PO4) 3 (LATP) and Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 (LLZO) and their electrochemical impedance spectrum and ionic conductivity change, as shown in Figure 4, by applying different quantitative pressure to the sandwich ceramic tablets and measuring their electrochemical impedance spectrum, the test pressure can affect their ionic conductivity to varying degrees, which indicates the necessity to test the electrochemical properties of the solid-state electrolyte by applying stable quantified pressure.
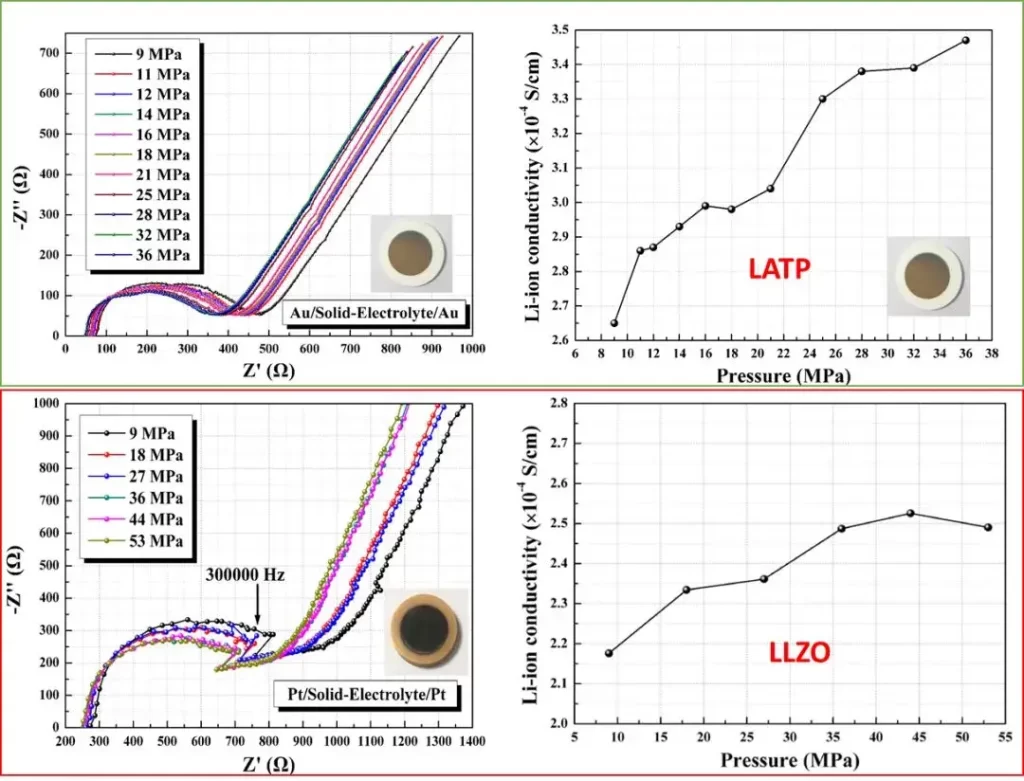
Figure 4. Electrochemical impedance spectra of two solid-state electrolytes and their ionic conductivity to pressure
3.3 Electron Conductivity & Compaction Density
Through the SEMS 1100 equipment, the electronic conductivity and compaction density of the LATP powder can be tested simultaneously during the lampressing process, and it is found that the compaction density ranges from the initial 1.7g / cm with the increase of the applied pressure3 Increase it to 2.1g / cm3 However, the electron conductivity is stable at around 50MPa, that is, the density and electron conductivity trend of the solid-state electrolyte materials are not completely consistent, indicating that under different pressure conditions, different tests are necessary to synchronize the characteristics of the solid-state electrolyte to obtain comprehensive and accurate measurement results.
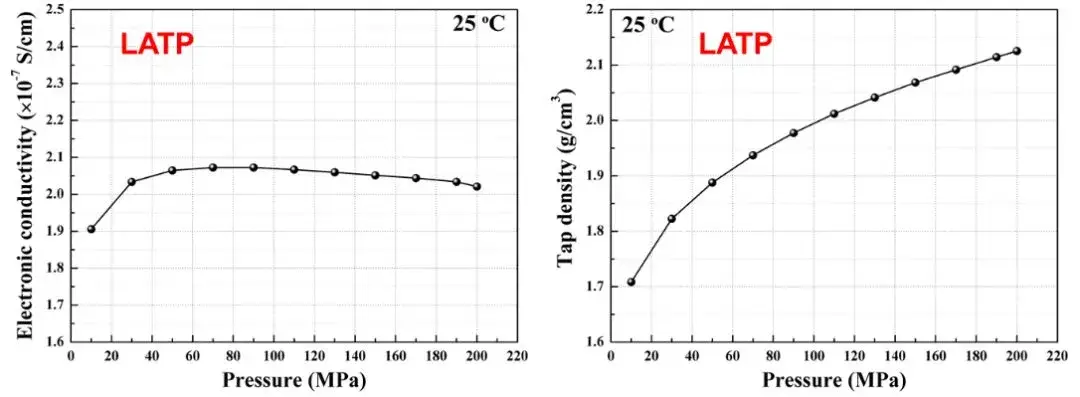
Figure 5. LATP Change of electron conductivity and compaction density of solid-state electrolyte
3.4 Recycling Performance of Solid-state Lithium Metal Battery
Li-SE-Li symmetrical battery is assembled in the SEMS 1100 matching sealing device, apply different pressure respectively, test the circulating deposition of lithium metal, measure the potential change of symmetrical battery, you can see that when the applied pressure drops from 120MPa to 110MPa, the overpotential of the battery increases significantly, which shows that the deposition behavior of lithium metal battery is relatively sensitive to the pressure change, and it is important to evaluate the interface stability of solid-state electrolyte by changing the applied pressure.
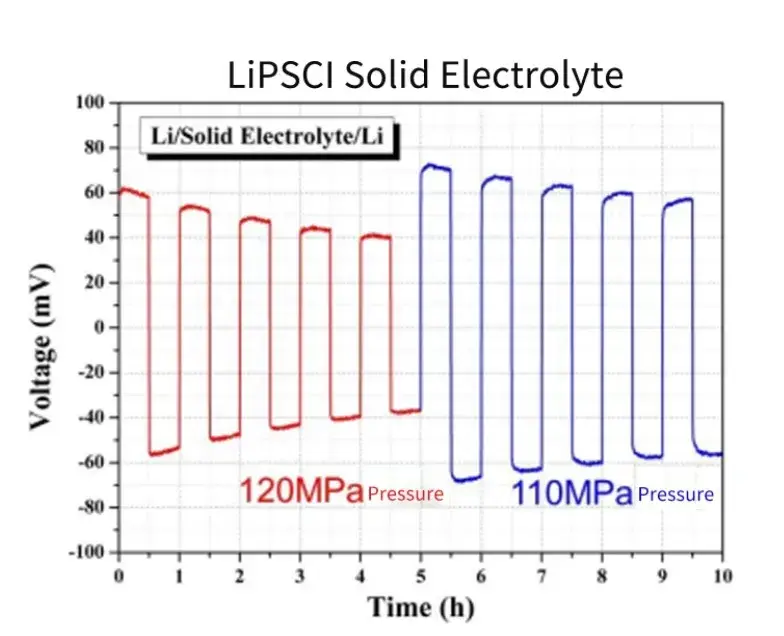
Figure 6. Cycle charge and discharge test of a symmetrical battery
3.5 Electrochemical Stabilization Window
The Li-SE-stainless steel battery is assembled in the SEMS 1100 matching sealing device, and the cyclic voltammetry tests its redox potential. It can be seen that when the overpotential rises to 3V, the oxidative current density of the battery is only about 1.2 A cm-2 this shows that the solid electrolyte is relatively stable in a voltage window of 0~3V, that is, the pressurization and sealing electrochemical test of different solid electrolyte materials and their lithium metal batteries can be realized through the SEMS 1100 equipment.
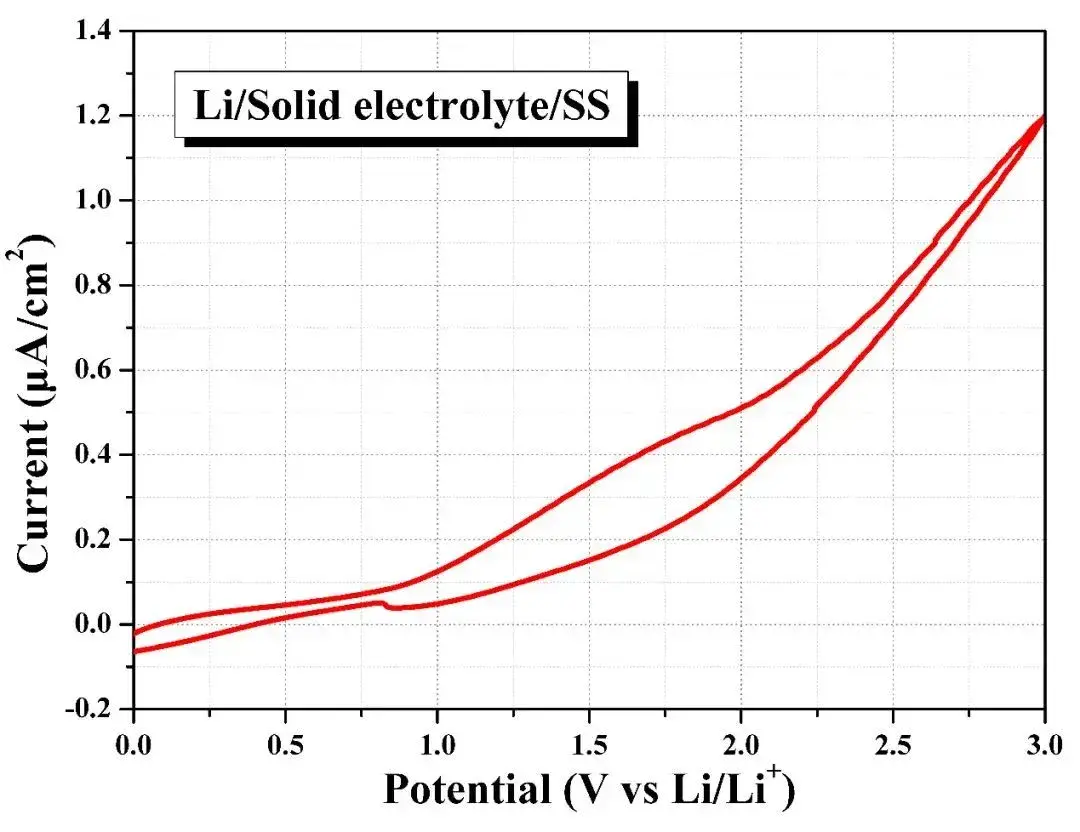
Figure 7. Electrochemical Window Test of Solid-state Electrolytes
4. Summary
This paper using solid-state electrolyte integrated test system SEMS1100, for all kinds of solid-state electrolyte materials, plate and electrochemical performance test, can be accurately evaluated under different quantitative pressure conditions on the solid-state electrolyte ion conductivity, electron conductivity, compaction density, electrochemical window, and lithium metal battery interface stability and cycle performance, for researchers to understand and develop solid electrolyte material, to accelerate the solid electrolyte research.
5. References
[1] Huang Xiao, Wu Linbin, Huang Zhen, et al. Characterization and testing of key electrical and electrochemical properties of lithium-ion solid electrolytes, Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020,9 (2): 479-500.
[2] Yong-Gun Lee, Satoshi Fujiki, Changhoon Jung, et al.High-energy long -cycling all-solid-state lithium metal batteries enabled by silver–carbon composite anodes.2020, 4(5): 299-308.
[3] Nicholas Williard a, Chris Hendricks a, Jaesik Chung, et al. Effects of external pressure on phase stability and diffusion rate in lithium-ion cells.Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 895, 115400.
[4] T / SPSTS 019- -2021; Performance Requirements and Test Methods of Solid State Electrolytes for Solid State Lithium Battery; Inorganic oxide; Solid State Electrolytes for Solid State Electrolytes.
Subscribe Us
Contact Us
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details, please leave a message here, we will reply you as soon as we can.



