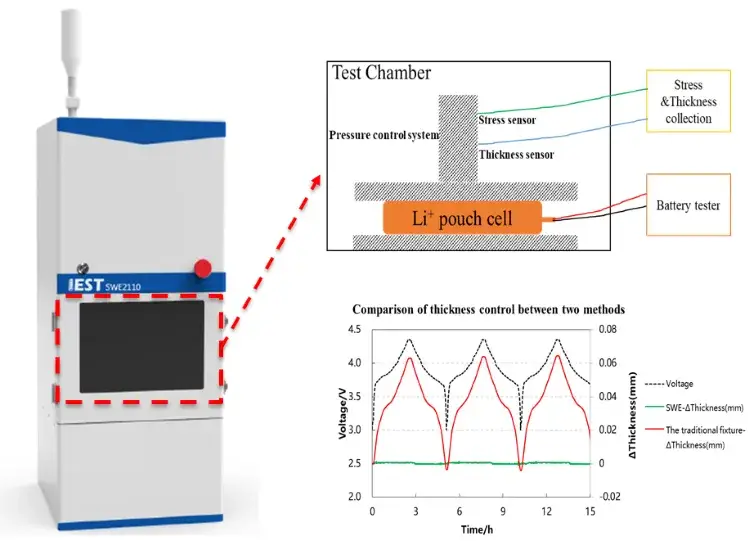
-
iestinstrument
Lithium Metal Batteries With Zero Volume Expansion Composite Anode For High Energy Density and Stability

1. Abstract
A roll-to-roll process was developed to fabricate a composite lithium metal batteriesthat exhibits near-zero volume expansion during cycling. The anode uses a sandwich architecture—an electronic-insulating top layer, a porous middle host that accommodates plated lithium, and a lithiophilic bottom layer—combined with a Cu-coated carbon-fiber current collector and an ultrathin Li–Mg alloy foil. The results show that full cells pairing these zero-volume-expansion anodes with NCM₈₁₁ or LCO cathodes achieve high area and volumetric energy densities while retaining mechanical flexibility and durable cycling. Notably, a reported single-layer cell reaches 22.7 mWh·cm⁻² area energy and a multilayer flexible cell reaches ~375 Wh·L⁻¹ volumetric energy; the flexible stacks maintain ~75% capacity after 3,000 bending cycles. This article summarizes the materials, methods, electrochemical/mechanical performance and practical implications for lithium metal batteries and lithium metal anode development.
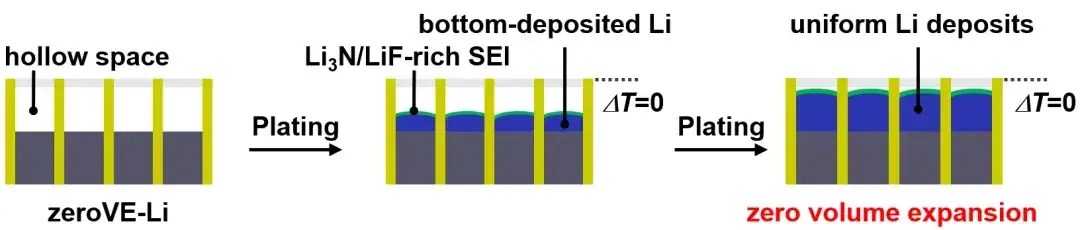
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of lithium intercalation of zero volume expansion anode
2. Introduction: A New Paradigm for Lithium Metal Anodes
The pursuit of higher energy density in lithium metal batteries is often hampered by the intrinsic challenges of the lithium metal anode. Uncontrolled dendrite growth and significant volume fluctuations during cycling lead to safety risks, rapid capacity fade, and mechanical failure—particularly problematic for flexible battery applications. In a significant 2022 advancement, a collaborative team from Southern University of Science and Technology and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University developed a novel solution: a roll-to-roll fabricated, zero-volume-expansion (zeroVE) lithium composite anode. This innovative design promises to dramatically improve the energy density, cycling stability, and mechanical flexibility of lithium metal batteries.
3. Test Plan
- Construct lithium composite anode and lithium metal batteries.
- Structural characterization: morphology characterization FE-SEM, surface chemical structure XPS, swelling behavior SWE2100 (IEST).
- Electrochemical performance characterization: cycle performance of deduction and soft pack.
- Mechanical performance characterization: bending performance of electrodes and pouch cells.
4. Design and Fabrication: A Sandwiched Structure for Stability
The core innovation is a meticulously engineered three-layer (sandwich) structure for the lithium metal anode:
-
A top electron-insulating (EI) layer.
-
A middle porous layer designed to accommodate lithium deposition.
-
A bottom lithiophilic layer.
The researchers constructed this anode by laminating an EI film, a copper-clad carbon matrix (CuCM), and an ultrathin LiMg alloy foil using a roll-pressing process. This method creates a hollow, composite structure. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and elemental mapping confirmed the successful fabrication and distinct layers of this architecture.
5. Validation: In-Situ Expansion Analysis Confirms Zero Volume Change
Proving the “zero-volume-expansion” claim is critical. The team assembled single-layer pouch cells pairing the zeroVE-Li anode with an NCM811 cathode. Using the IEST in-situ expansion analysis system (SWE2100), they simultaneously monitored thickness and force changes during cycling.
The results, shown in Figure 2, were conclusive. While a conventional lithium metal anode exhibited significant thickness and stress variations during charge/discharge, the zeroVE-Li anode showed almost no detectable change. This direct experimental evidence validates the design’s ability to fully contain deposition-induced expansion within its internal porous layer, a major breakthrough for cell dimensional stability.
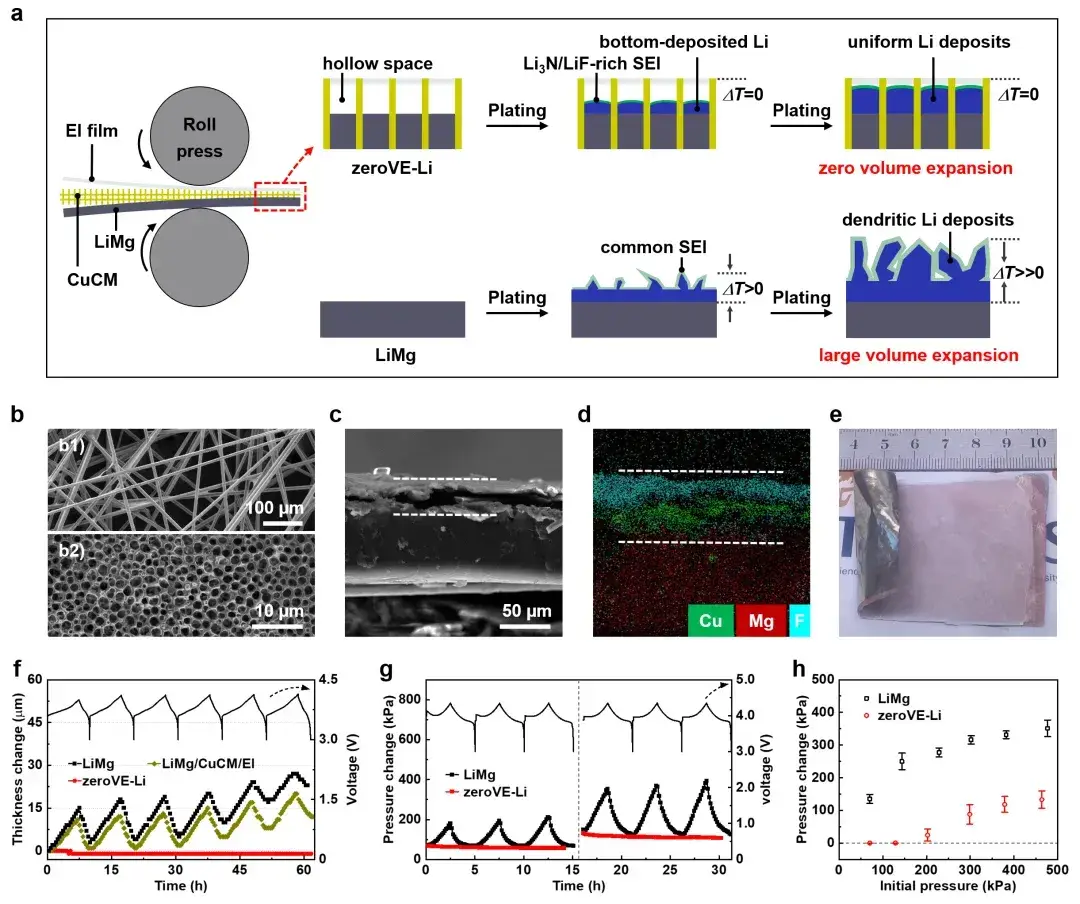
Figure 2. Design principle and volume expansion behavior of Li metal anode with zero volume expansion
6. Performance: Electrochemical and Mechanical Excellence
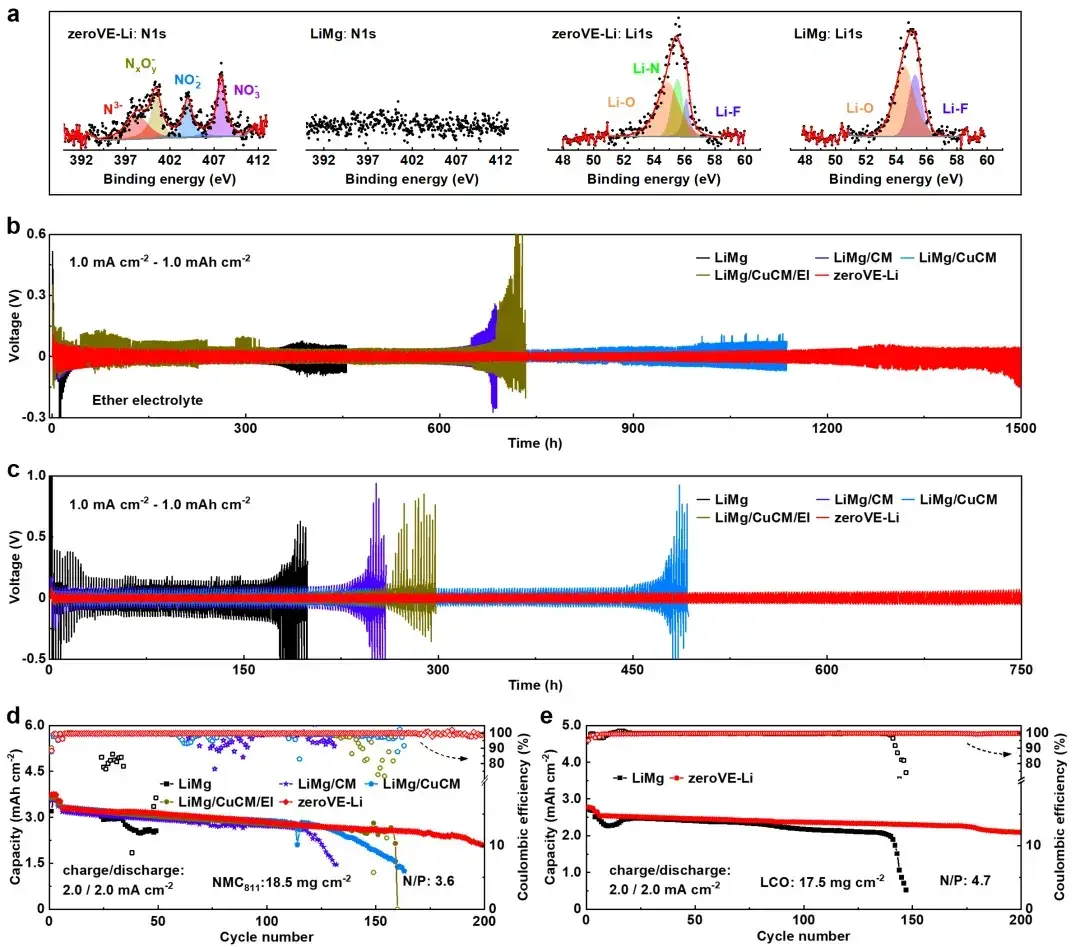
Figure 3. SEI and cycle stability analysis of the lithium metal anode with zero volume expansion
6.1 Enhanced SEI and Cycling
The change of the lithium metal interface brought by the upper insulating functional layer in the new lithium metal anode was characterized by XPS, which proved that the SEI contains the inorganic layers Li3N and LiF with the best inhibition effect on lithium dendrites. And by assembling two kinds of batteries whose positive electrodes are NCM811 and LCO respectively, it can be clearly compared that the cell has the highest cycle capacity retention rate when zeroVE-Li is used as the negative electrode.
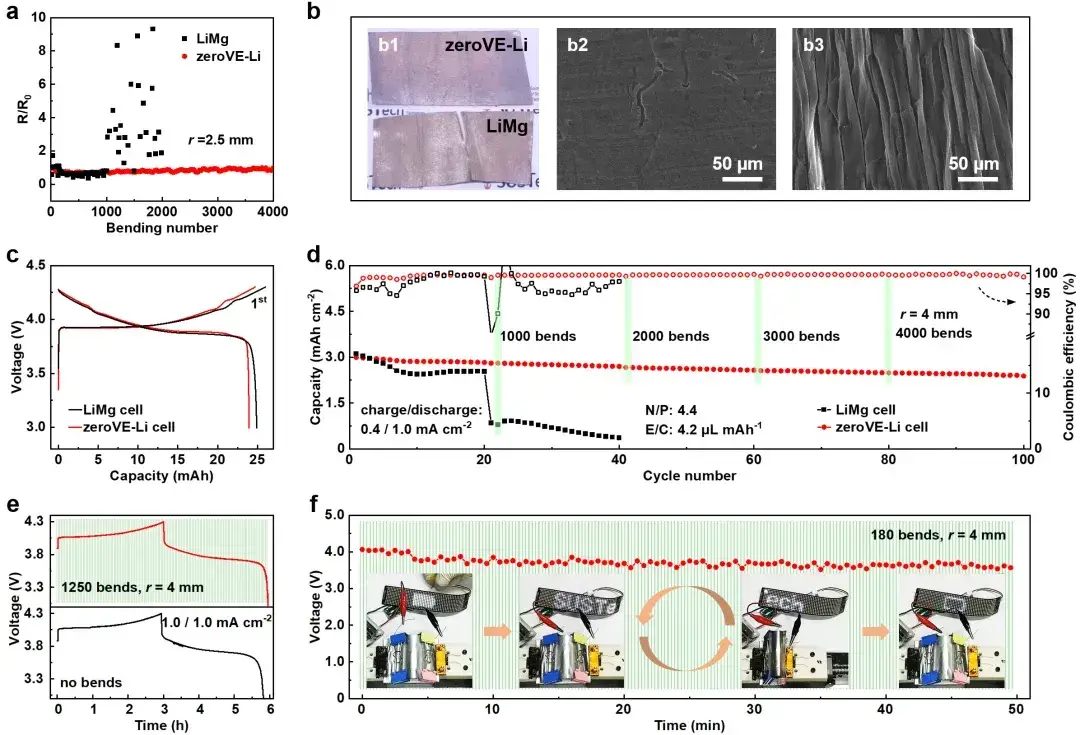
Figure 4. Electrochemical and mechanical stability of single-layer lithium metal batteries
6.2 Exceptional Flexibility
Through dynamic bending and resistance test, the author found that after 4000 bending experiments, the resistance and morphology of zeroVE Li did not change significantly, showing excellent flexibility. The zeroVE Li electrode was matched with a high surface loaded flexible positive electrode to assemble a flexible battery. From the aspects of electrochemical cycle stability and mechanical stability, the zero volume expansion negative electrode showed high coulomb efficiency, high cycle capacity retention rate and good bendability.
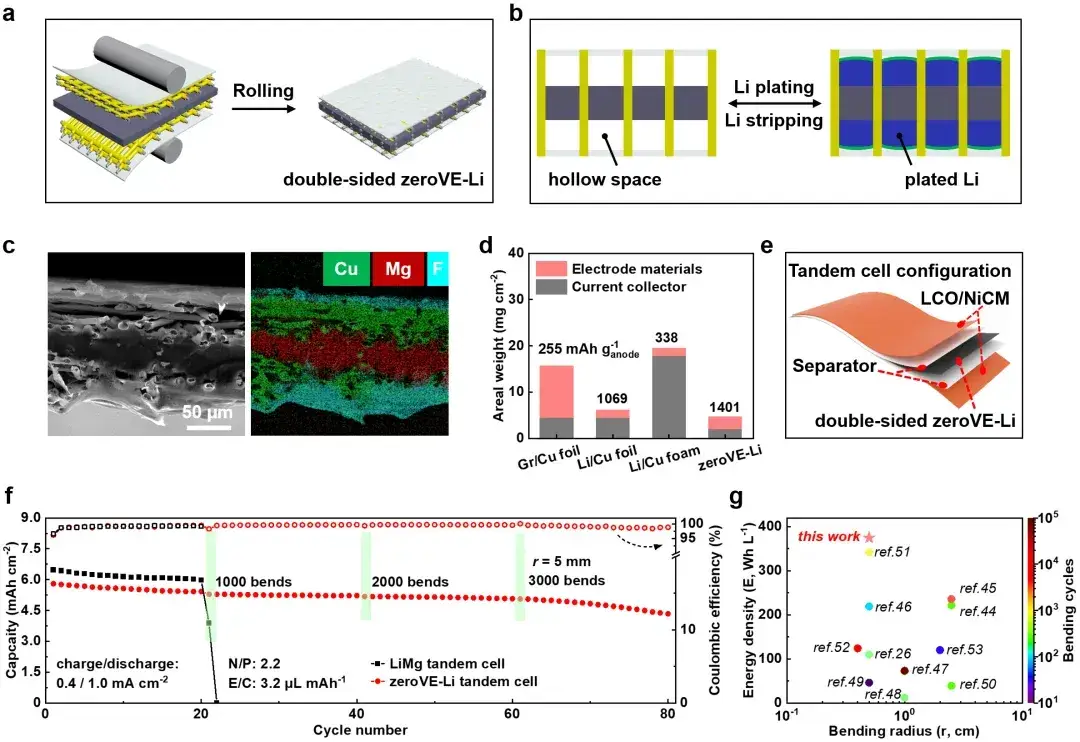
Figure 5. Electrochemical and mechanical stability of multilayer lithium metal batteries
6.3 Record-High Energy Density for Flexible Cells
The author continues to prepare double-sided zero volume expansion anode and finds that it has higher mass specific capacity than commercial anode materials. The assembled multilayer flexible lithium metal battery has high weight energy density and volume energy density, and can still maintain 75% capacity retention after 3000 cycles of bending test. By comparing the energy density values of flexible lithium based batteries in other relevant documents, the flexible lithium metal batteries developed in this work based on zero volume expansion lithium composite anode has a very high surface energy density (22.7 mWh cm-2), a practical volume energy density (375 Wh L-1, based on the volume of positive and negative electrodes, diaphragms and packaging materials) and a record flexible quality factor (FOM, 45.6).
7. Summary
In this paper, a roll-to-roll method was developed to synthesize a lithium composite anode with zero volume swelling, which has excellent electrochemical performance and mechanical flexibility, and can significantly improve the energy density of lithium metal batteries. The negative electrode has a sandwich structure: it includes an electronic insulating layer on the top, a lithiophilic layer on the bottom, and a porous layer in the middle that absorbs volume expansion. By matching NCM and LCO anode electrodes, the author further verified the excellent flexibility of the corresponding flexible lithium metal batteries, properties such as energy density and cycle retention. The zero volume expansion design provides a new idea for the practical application of lithium metal batteries. The roll-to-roll manufacturing process also shows its potential for large-scale production. In principle, this zero volume expansion design is also applicable to construct other metal battery anodes (such as sodium, potassium, and zinc metal batteries, etc.) to improve energy density, cycling, and structural stability.
8. Original Literature
Chao Luo, Hong Hu, Tian Zhang, Shujing Wen, Ruo Wang, Yanan An, Shang-Sen Chi, Jun Wang, Chaoyang Wang, Jian Chang*, Zijian Zheng*, and Yonghong Deng*. Roll-to-roll Fabrication of Zero-Volume-Expansion Lithium Composite Anodes to Realize High-Energy-Density Flexible and Stable Lithium Metal Batteries. [Advanced Materials]
6. Recommendation of Test Equipment Related to IEST
Key data in this groundbreaking study was generated using the SWE2100 system from IEST. SWE series using a highly stable and reliable automation platform, equipped with high-precision thickness measurement sensors, it can measure the thickness change and change rate of the entire charge discharge process of the electric core, and can achieve the following functions:
1.Test the battery expansion thickness curve under constant pressure.
2.Test the battery expansion force curve under the condition of constant gap.
3.Battery compression performance test: stress-strain curve compression modulus.d
4.Step by step test of battery expansion force.
5.Different temperature control: – 20~80 ℃.
Contact Us
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details, please leave a message here, we will reply you as soon as we can.