Description
1. Introduction
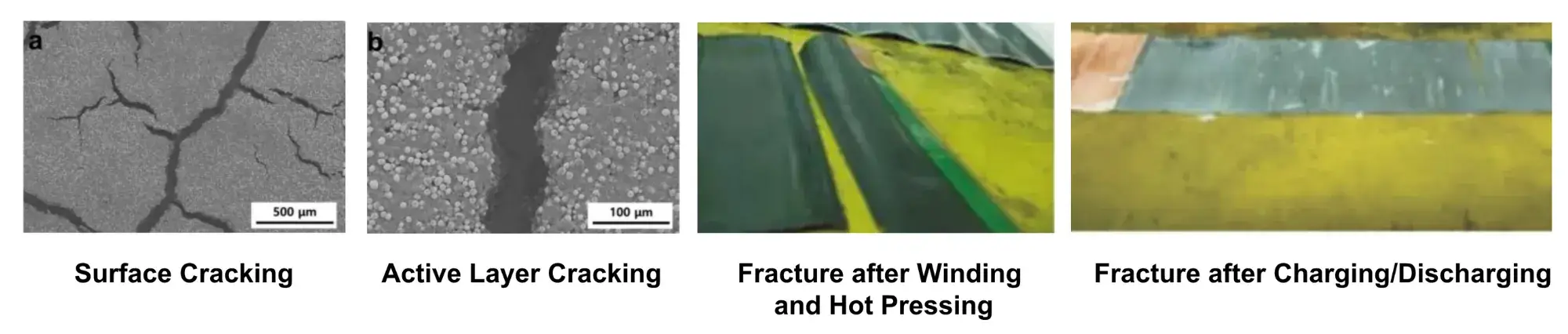
The of lithium-ion battery electrode flexibility is a crucial parameter in the battery manufacturing process. During the winding process, if the electrodes have poor flexibility, the innermost layers of the wound core are prone to fracture. This can generate particles, burrs, and sharp edges on the electrodes, leading to cell performance degradation and posing safety risks such as internal short circuits. Therefore, monitoring electrode flexibility is particularly important.
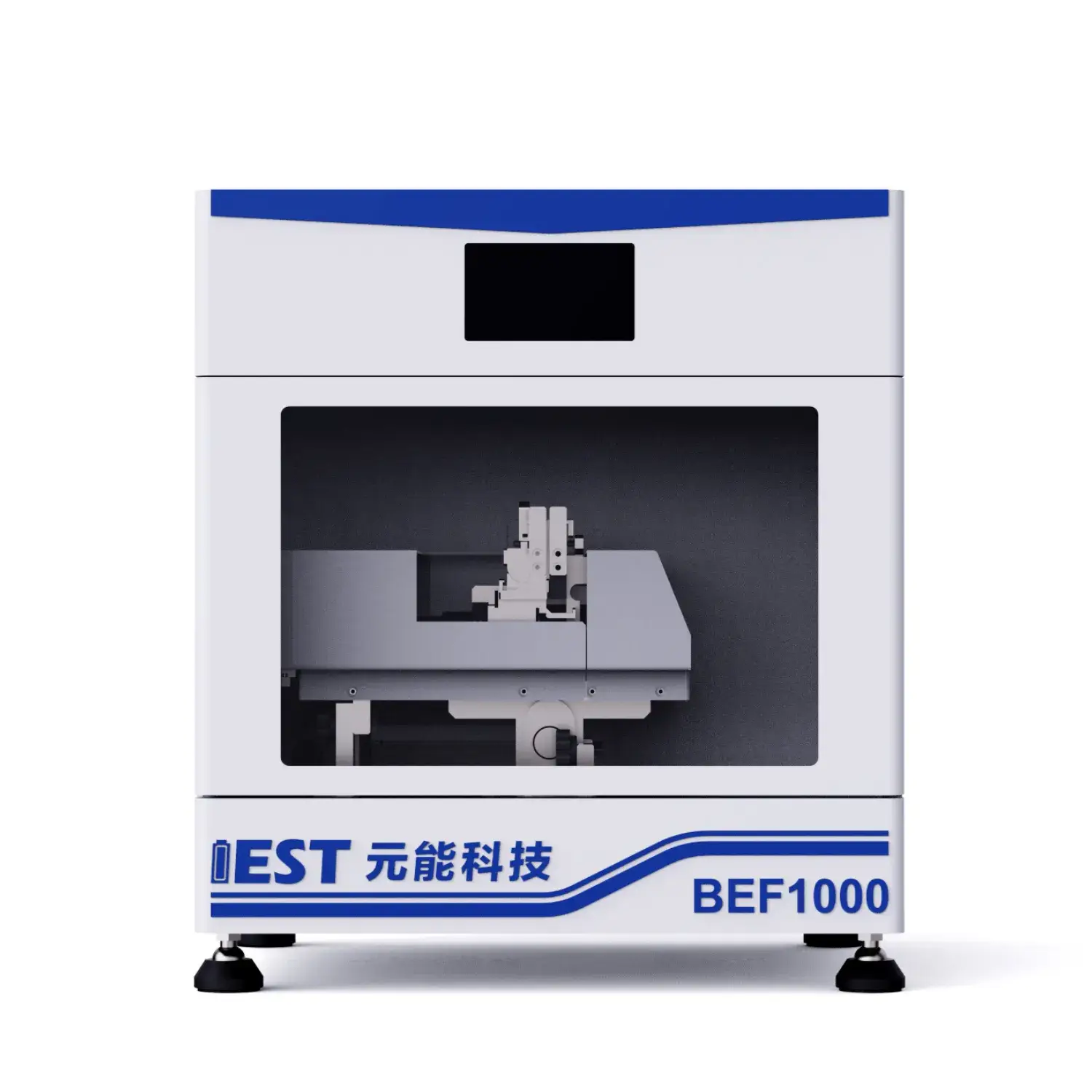
2. Battery Electrode Flexibility Testing System
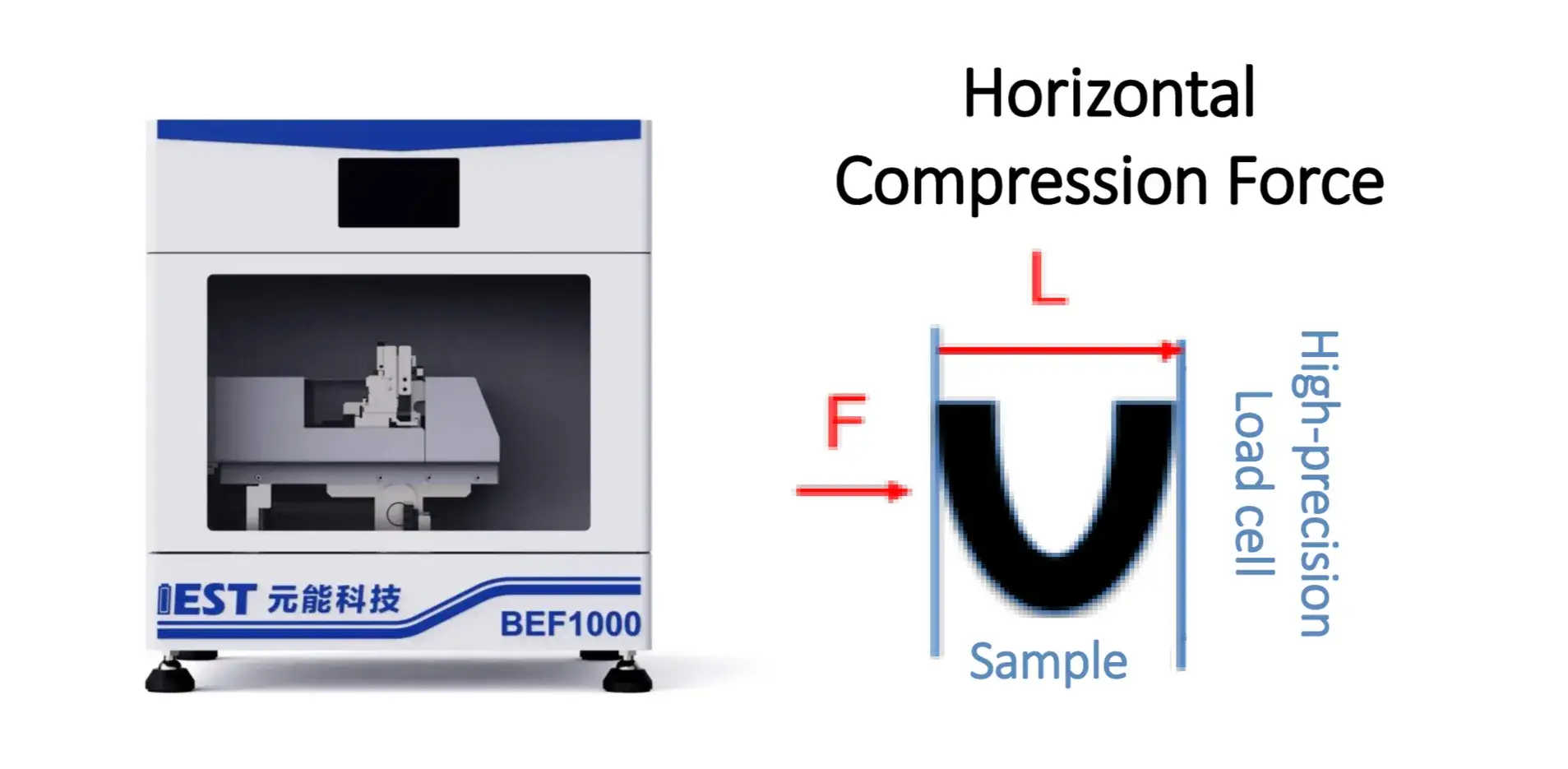
The Battery Electrode Flexibility Testing System(BEF1000) adopts the fundamental testingmethod for electrode stress-strain curves: after bending the electrode at a specificangle and mounting it on the testing device, displacement is applied to induce defor-mation, and the stress and strain (stress-displacement relationship) of the electrodeunder different deformation degrees are measured to evaluate its flexibility.
3. Innovation Solutions
- Enhance battery performance and consistency
- Optimize manufacturing processes, improving production efficiency and first-pass yield
- Ensure battery safety and reliability
- Support the R&D of new materials and processes
- Meet industry standards and market demands
Systematic flexibility testing enables comprehensive optimization of electrode sheet performance, driving advancements in battery technology and providing crucial support for the growth of the new energy industry.
4. Applications

5. Equipment Functions
- Cyclic Testing: Enables single-pressure application or multiple reciprocating tests.
- Inspection: Equipped with third-party calibrated standard thickness blocks and weights for regular equipment spot checks.
5.1 Displacement Force Precision Testing
Precise displacement control, combined with high-precision pressure sensors, Real-time recording of displacement pressure curves
5.2 Flip mechanism Bi-directional Testing
The test meachaism is capable of rotated 90°, supporting horizontal pressing and vertical pressing. testing scenarios.
5.3 Detachable Electrode Fixture
Ensures consistent clamping of the electrodes, prevents twisting damage to the electrodes, facilitates operation for testing personnel.
6. Methods of Analysis
6.1 Bendability
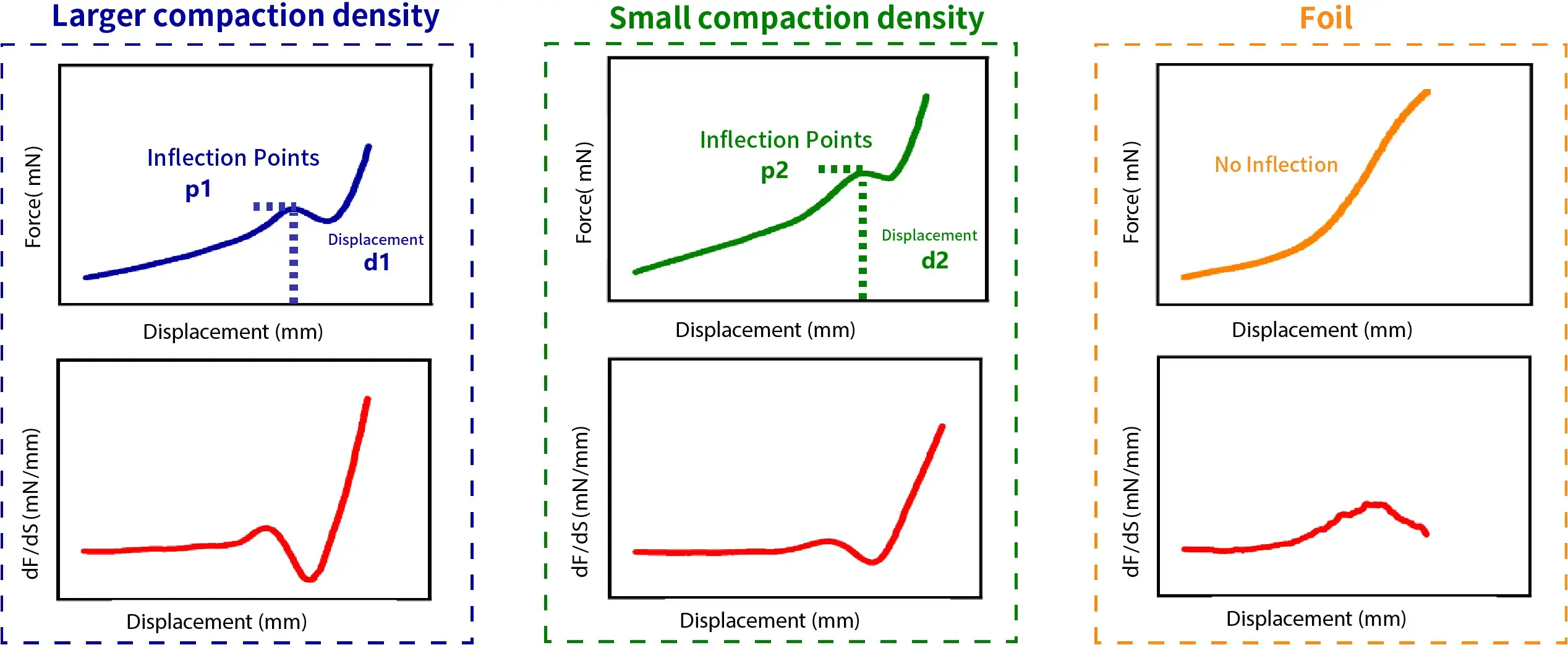
-
Analyzing the Fracture Point: Electrodes with a larger compression displacement at the fracture point generally exhibit better flexibility.
-
Observing the First Derivative: Poorer electrode flexibility may show higher peaks or abrupt changes in the derivative.
-
Curve Shape: Higher electrode flexibility tend to exhibit smoother curves without significant sudden changes or inflection points.
-
Curve Slope: Good electrode flexibility demonstrate a smaller slope in the force-displacement curve, indicating greater deformation under the same applied force.
6.2 Recoverability
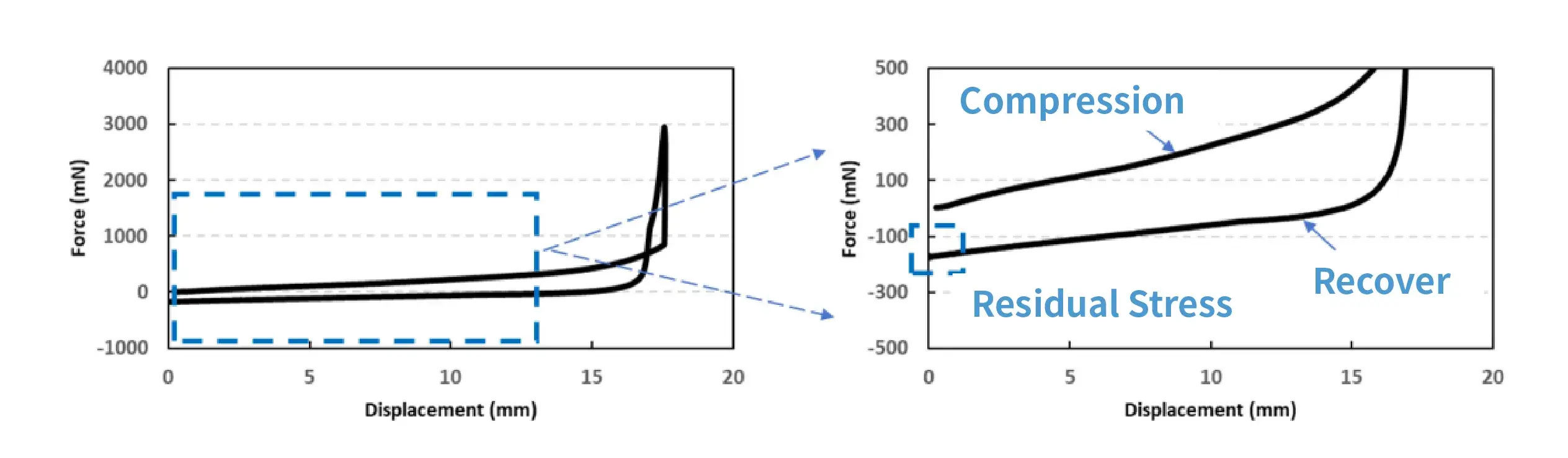
- Curve Shape: The stress- strain curve has no obvious inflection points, and for electrode sheets with higher flexibility, the absolute value of their residual stress is smaller.
- Fatigue Test: Evaluate the recovery ability and long-term stability after deformation during multiple bending processes by analyzing residual stress.
7. Multifunctional Analysis Software
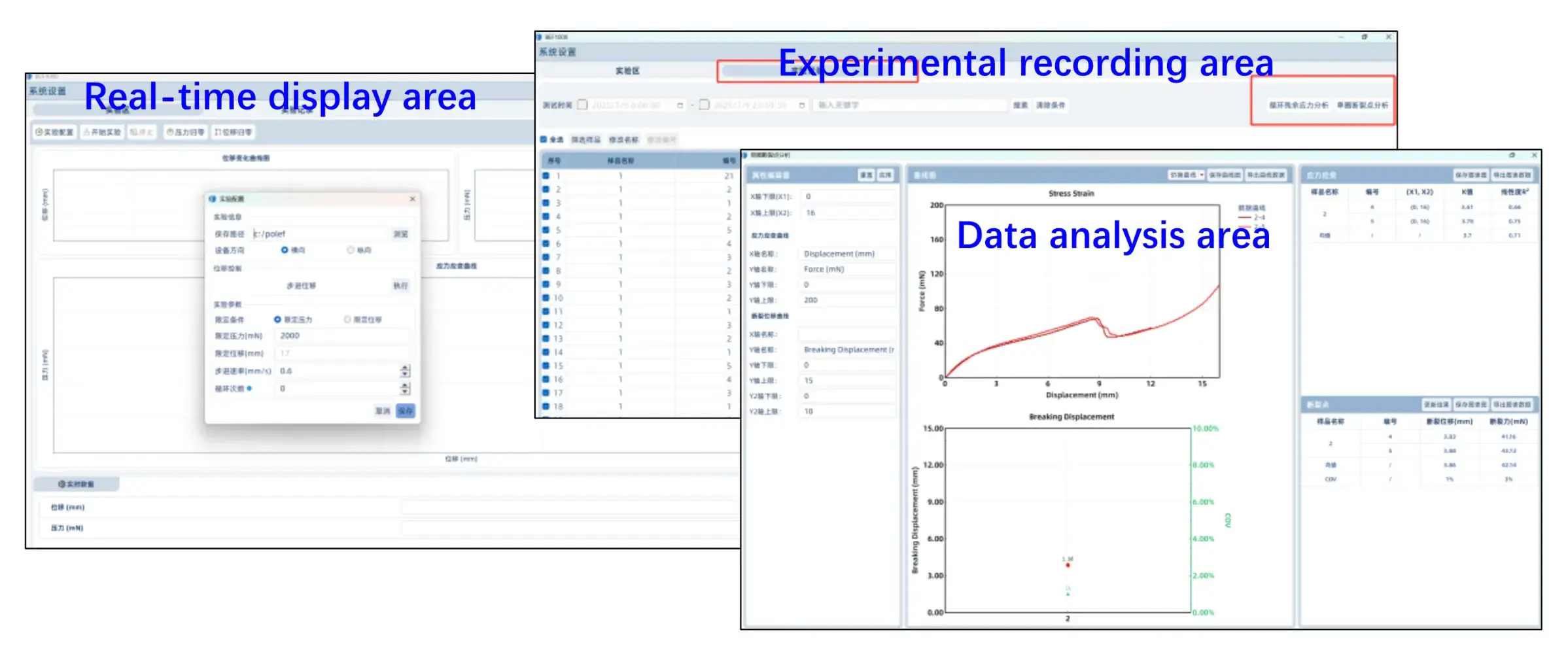
- Records stress-strain data during compression/return cycles in real-time and automatically plots the curves.
- Allows setting either compression distance to measure pressure or target pressure to measure displacement.
- Displays the slope of the F-S curve (dF/dS).
- Shows historical test data and enables export of F-S curves for multi-sample comparison.
- Automatically identifies the fracture point in single-cycle compression and residual stress in multi-cycle tests.
Applications
1. Anode & Cathode Electrode
Analysis:
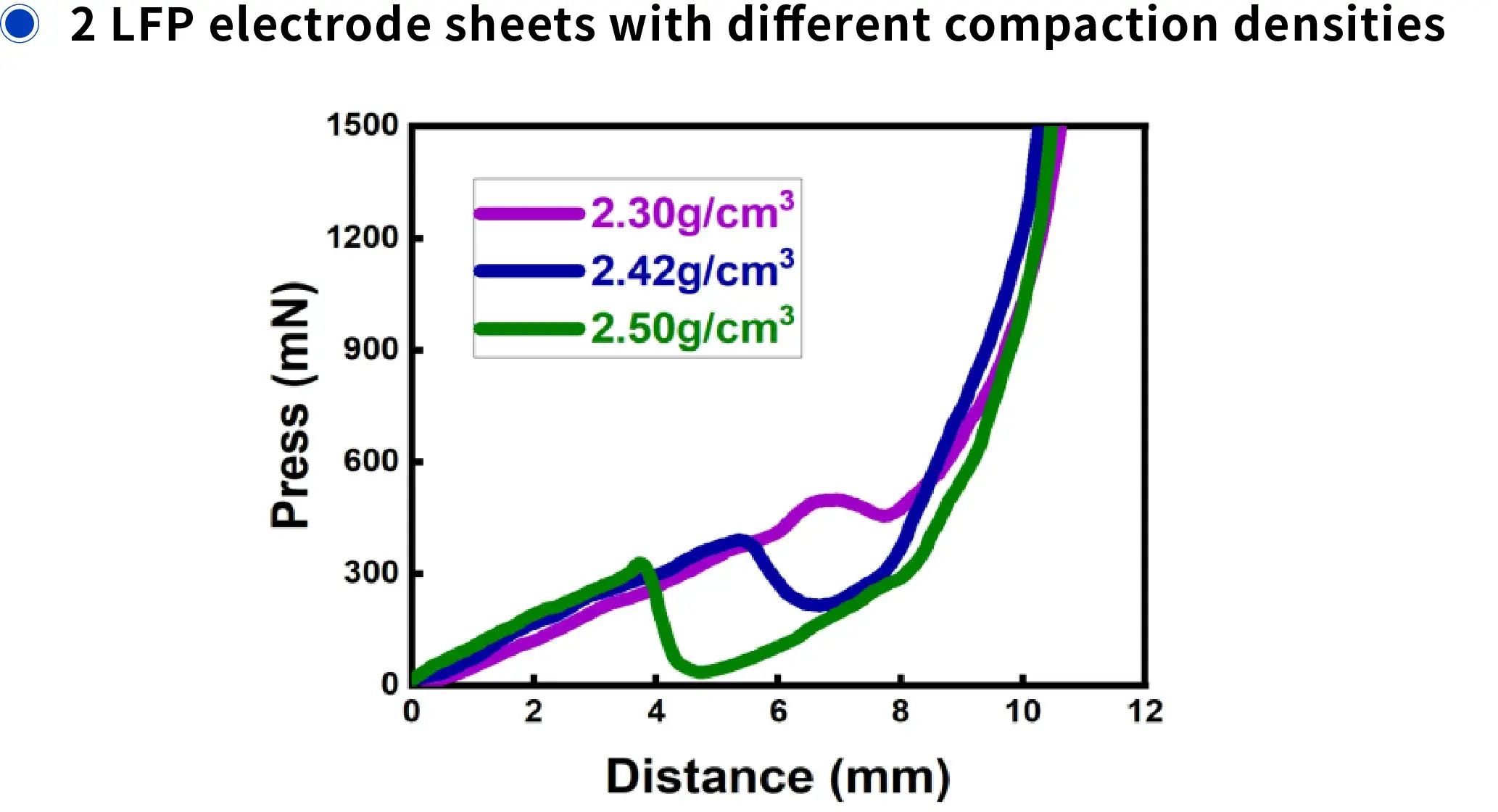
- Three groups of electrode sheets with different compacted densities underwent compression testing.
- As the compacted density increased, the compressive fracture stress and corresponding displacement both decreased, indicating progressive deterioration of flexibility.
Analysis:
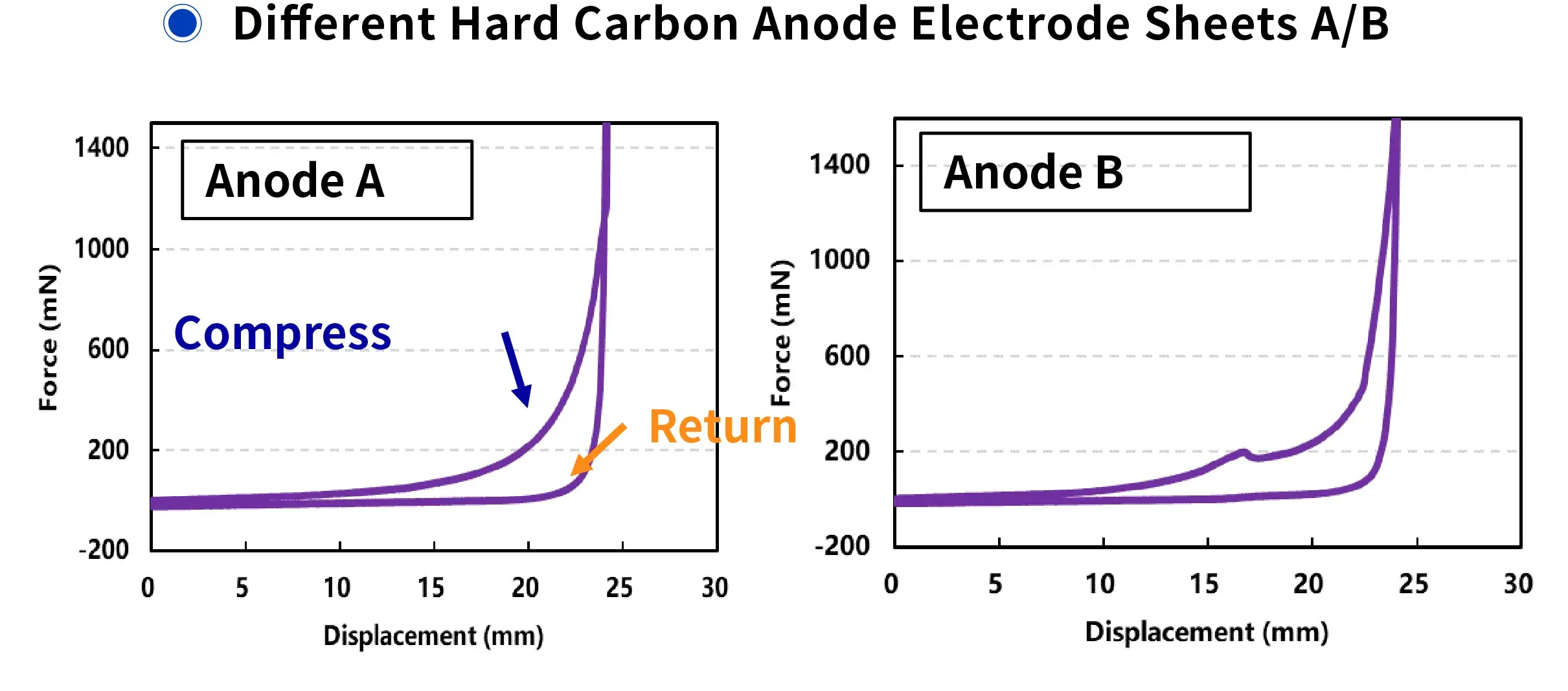
- Compression and decompression cyclic experiments were conducted on two sets of electrode sheets to compare their flexibility.
- An inflection point appeared in the curve for Electrode B, indicating a clear stress decay process, suggesting that B has slightly poorer flexibility than A.
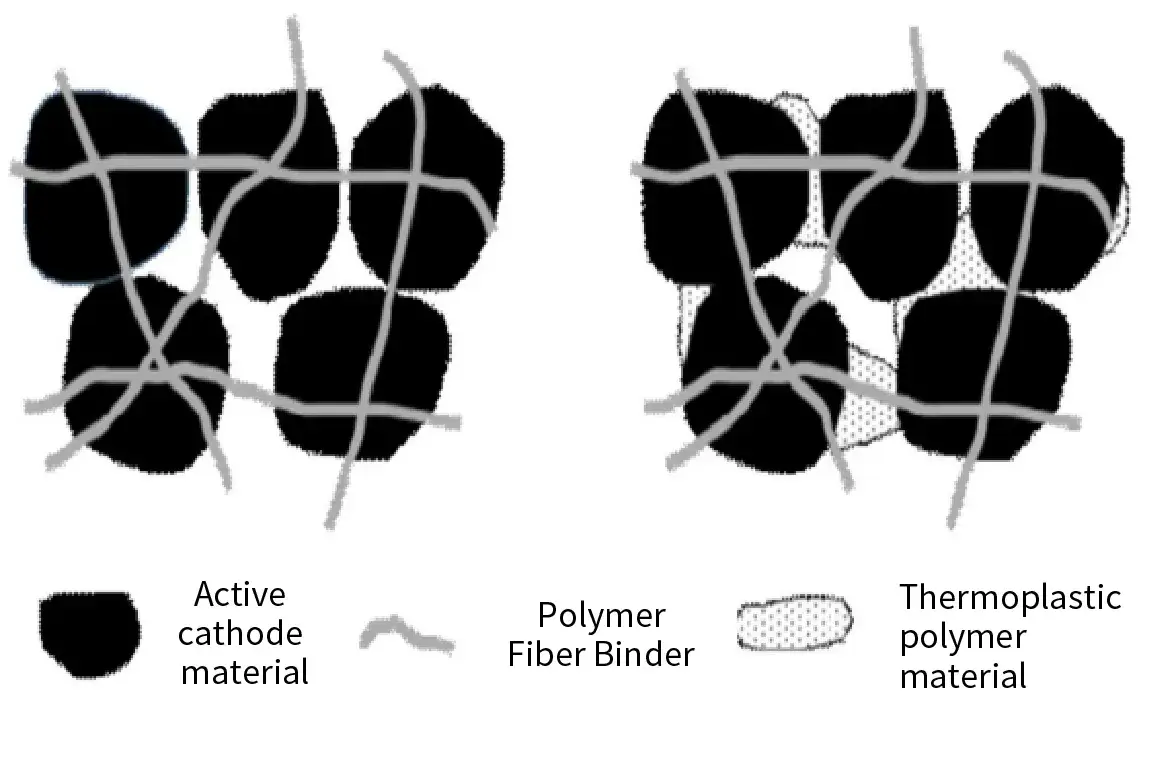
2. Fibrous Binder
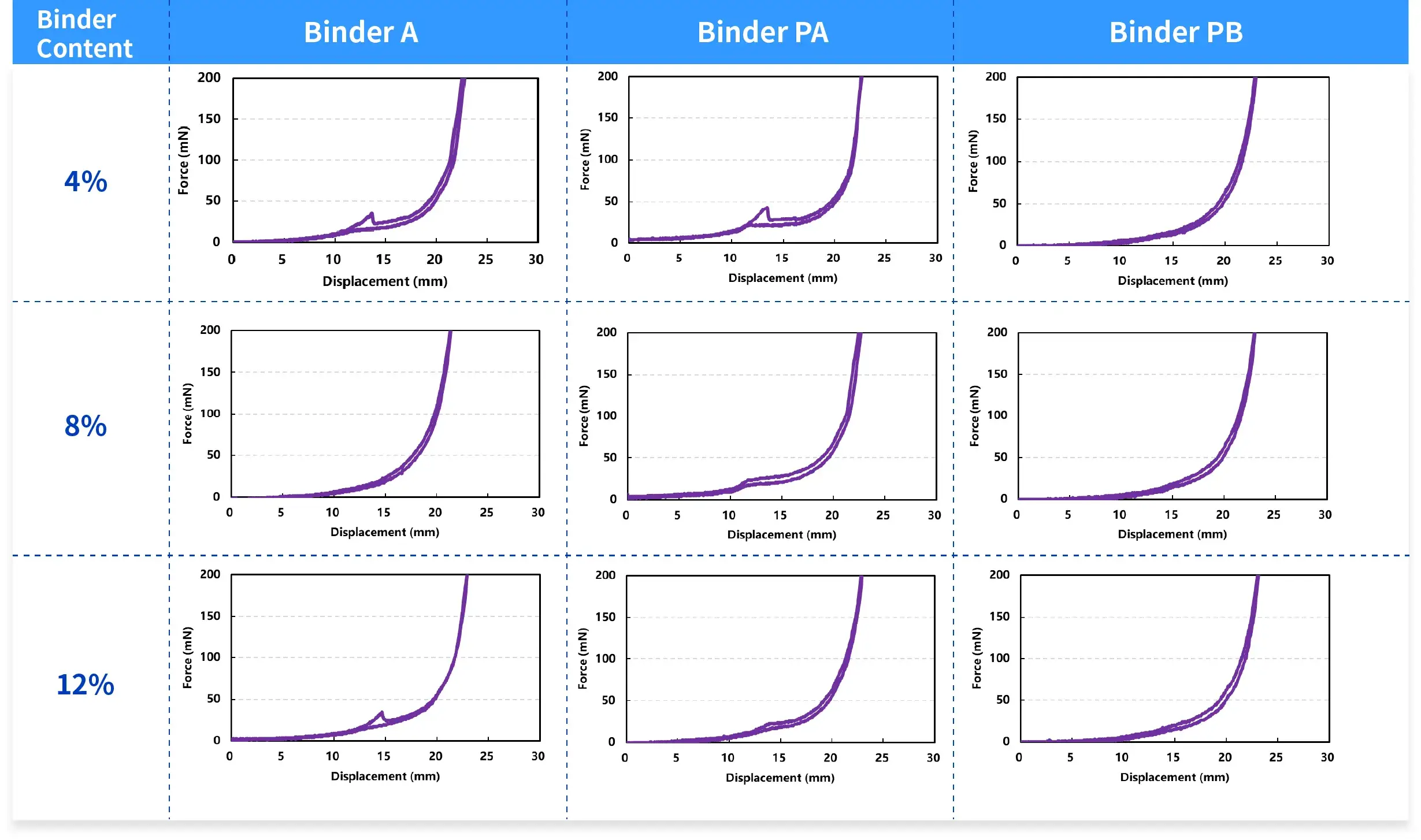
Analysis:
- Evaluating the impact of varying binder types in the electrode sheets to evaluate their flexibility during compression.
- At the same content, the flexibility of binders A and PA is inferior to that of PB; and an 8% content might be a relatively suitable proportion for all three types of binders.
3. Product Application Analysis
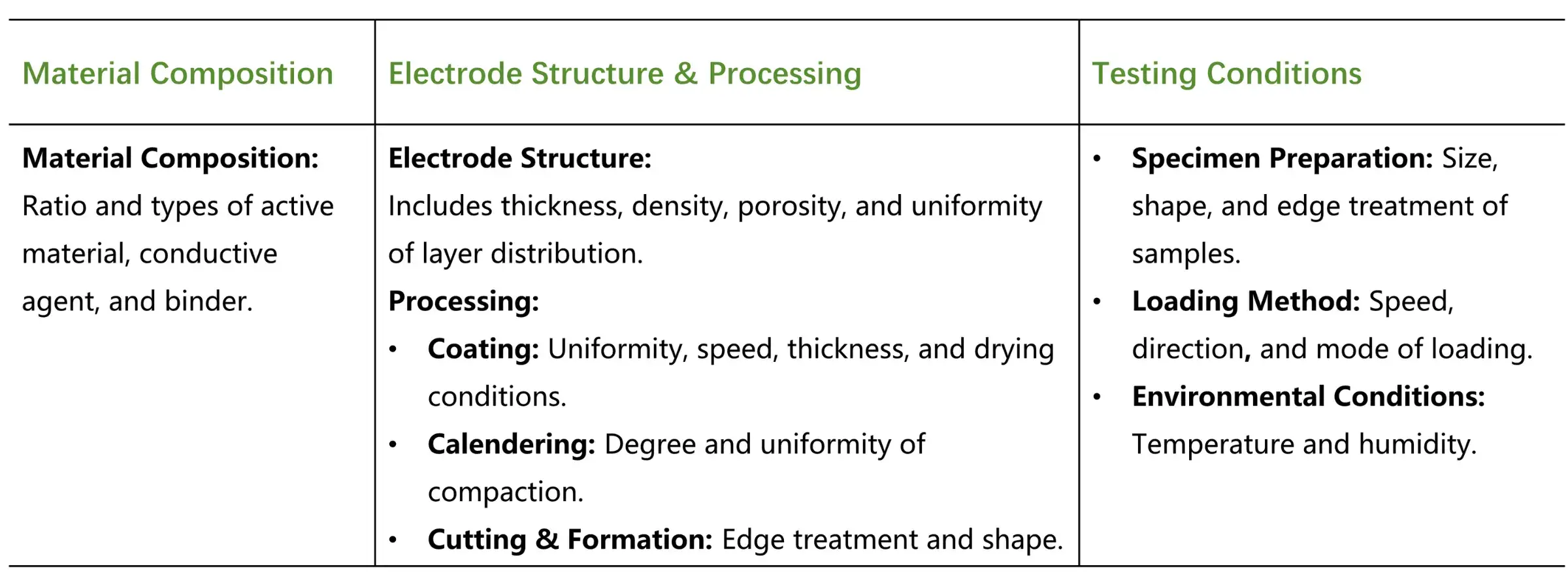
3.1 Testing influencing factors
3.2 Front-end & Back-end Performance Correlation