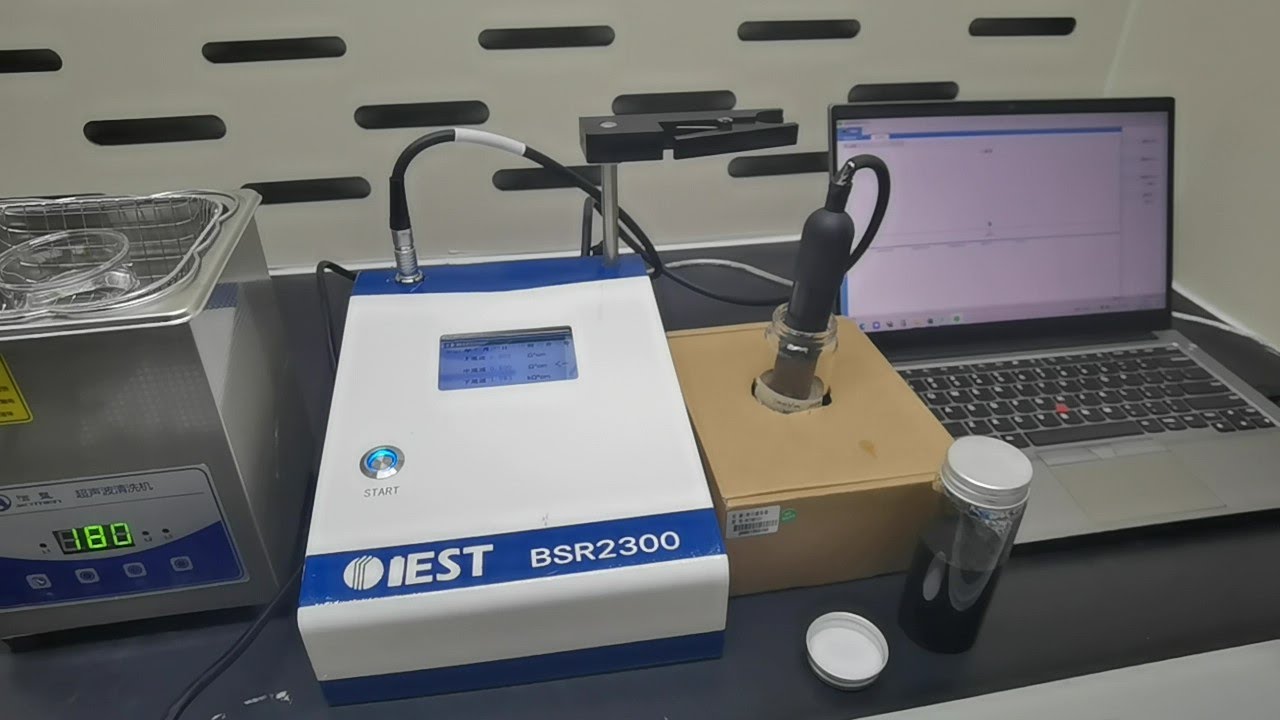
Description
1. The Significance of Slurry Resistivity
Battery Slurry serve as critical intermediates in lithium-ion battery production, where their homogeneity and stability critically determine final cell consistency and electrochemical performance. Current monitoring methods relying solely on viscosity parameters fail to accurately assess electrical homogeneity and stability. Crucially, slurry conductivity exhibits significant correlations with formulation parameters including:
-
Conductive additive type/content
-
Binder type/content
-
Solid loading
During standing periods post-mixing, slurries may undergo gelation and sedimentation, causing measurable conductivity variations. Thus, conductivity monitoring provides a robust method for characterizing slurry electrical homogeneity and stability.
Implementing battery slurry conductivity tracking enables:
- Material evaluation: Assessing impacts of active materials, conductive additives, binders, and solid content on electrochemical performance
- Process control: Detecting anomalies during mixing to prevent defective material flow-down, thereby reducing time/cost waste in downstream processes
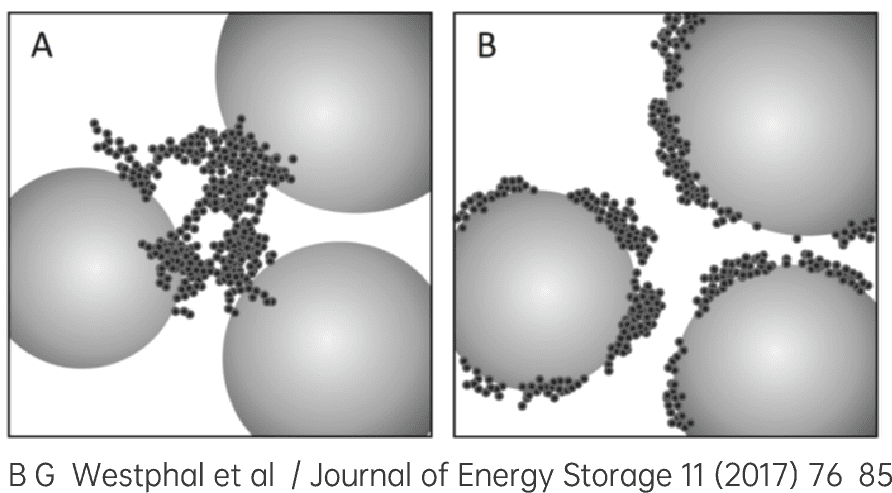
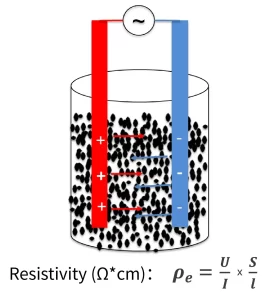
2. Battery Slurry Resistivity Test Principle
Test steps: Putting a certain volume of slurry (~80mL) into the measuring glass, inserting a clean electrode pen, start the software, start to test the changes in the slurry resistivity at the three pairs of electrodes over time and save it in the file.
Test parameters: Resistivity, Temperature, Time
Calculation formula:
Features:
-
Applicable for conductivity assessment and formulation optimization of lithium/sodium battery slurries and conductive additive slurries.
-
Independent voltage/current paths eliminate induction interference on voltage measurements, enhancing resistivity detection accuracy.
-
10-mm diameter disk electrodes ensure maximum sample contact area, minimizing measurement errors.
-
Triple-electrode configuration measures slurry resistivity while simultaneously evaluating sedimentation behavior.
-
Real-time monitoring of resistivity changes at three vertically distributed positions tracks time-dependent slurry homogeneity.
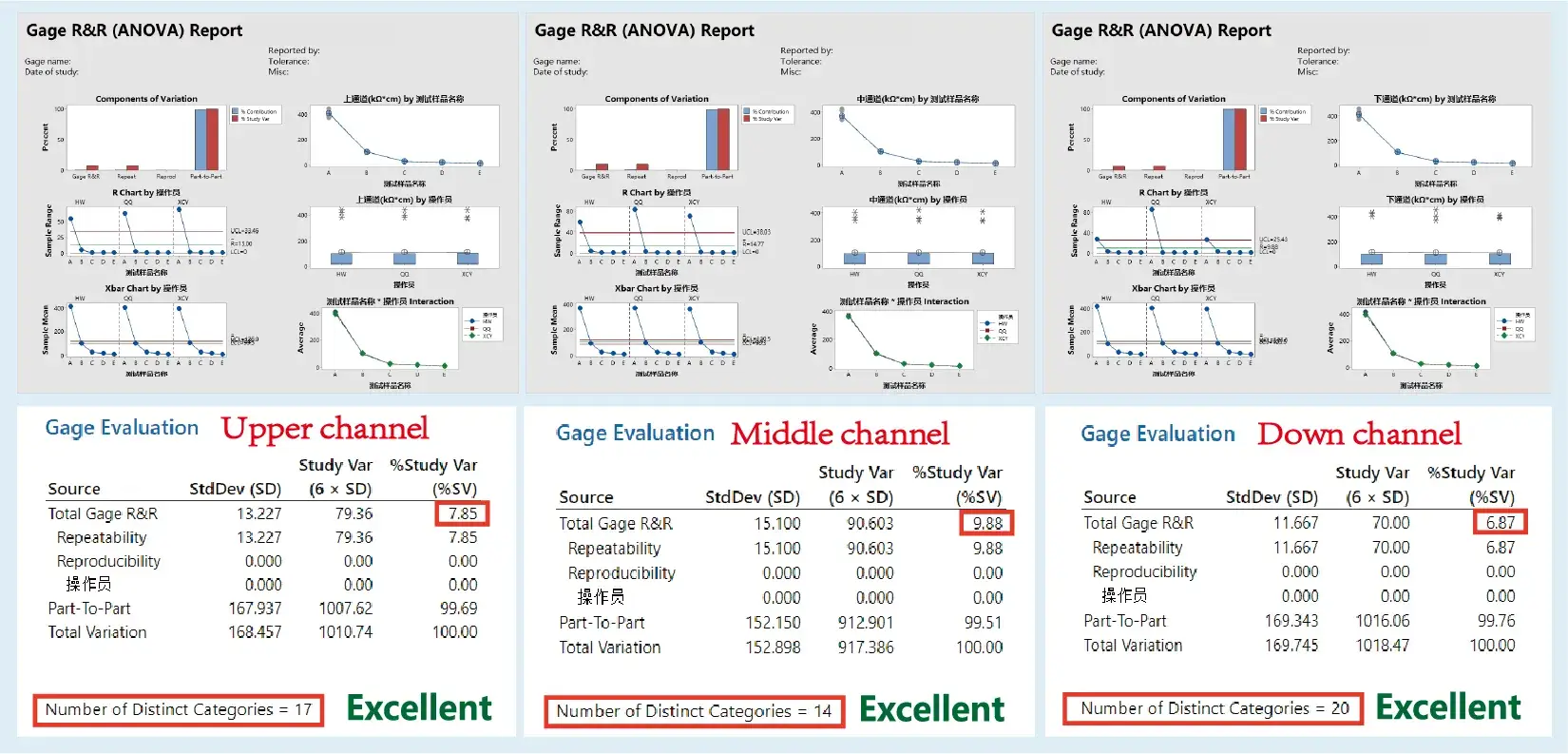
3. Slurry Resistivity Analyzer MSA
Test program: Three operators, five parallelsamples, and random testing
Test method: Sonicating the electrode pen withdeionized water for 30 seconds,and drying it with the dust-freepaper. Then five parallel sampleswas tested, and the fifth set of datawas taken for the GRR analysis
4. Applications
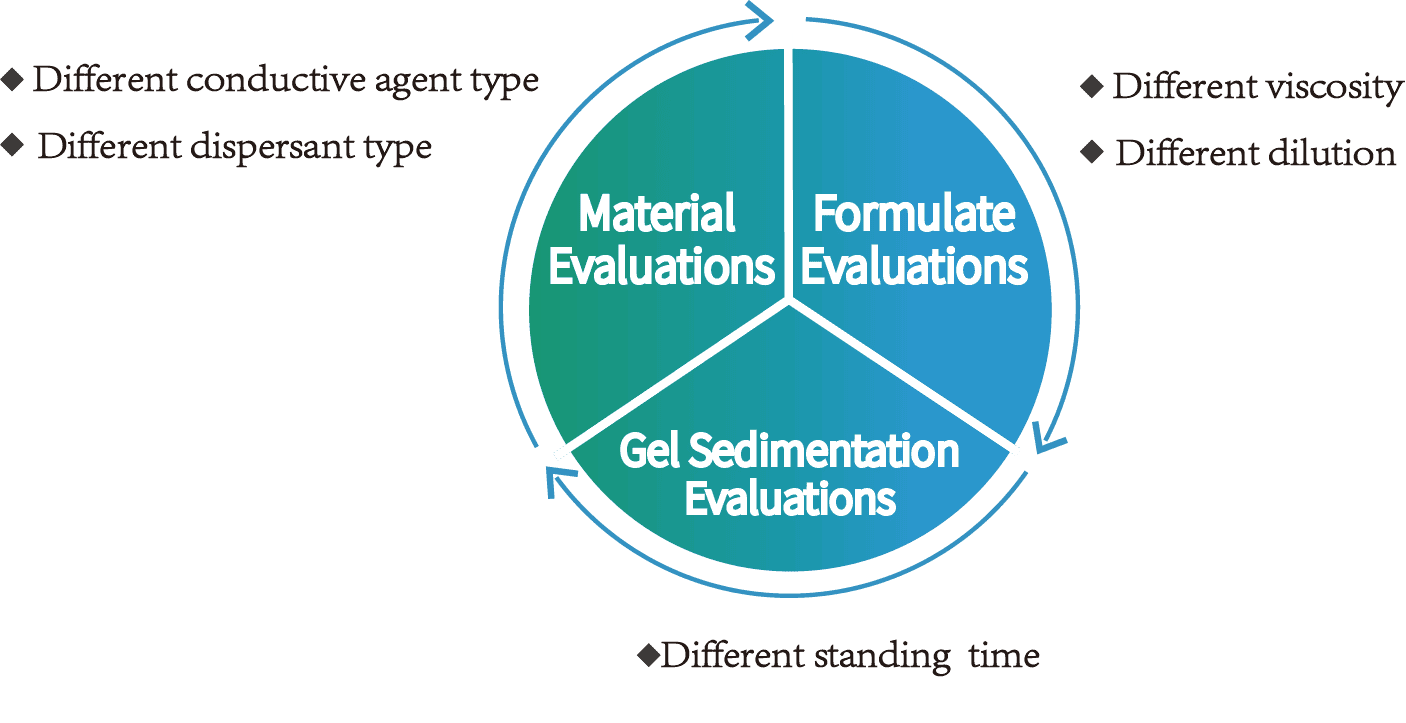
Applications
Case 1. Evaluation of Conductive Agent Slumy With Different Fommulations
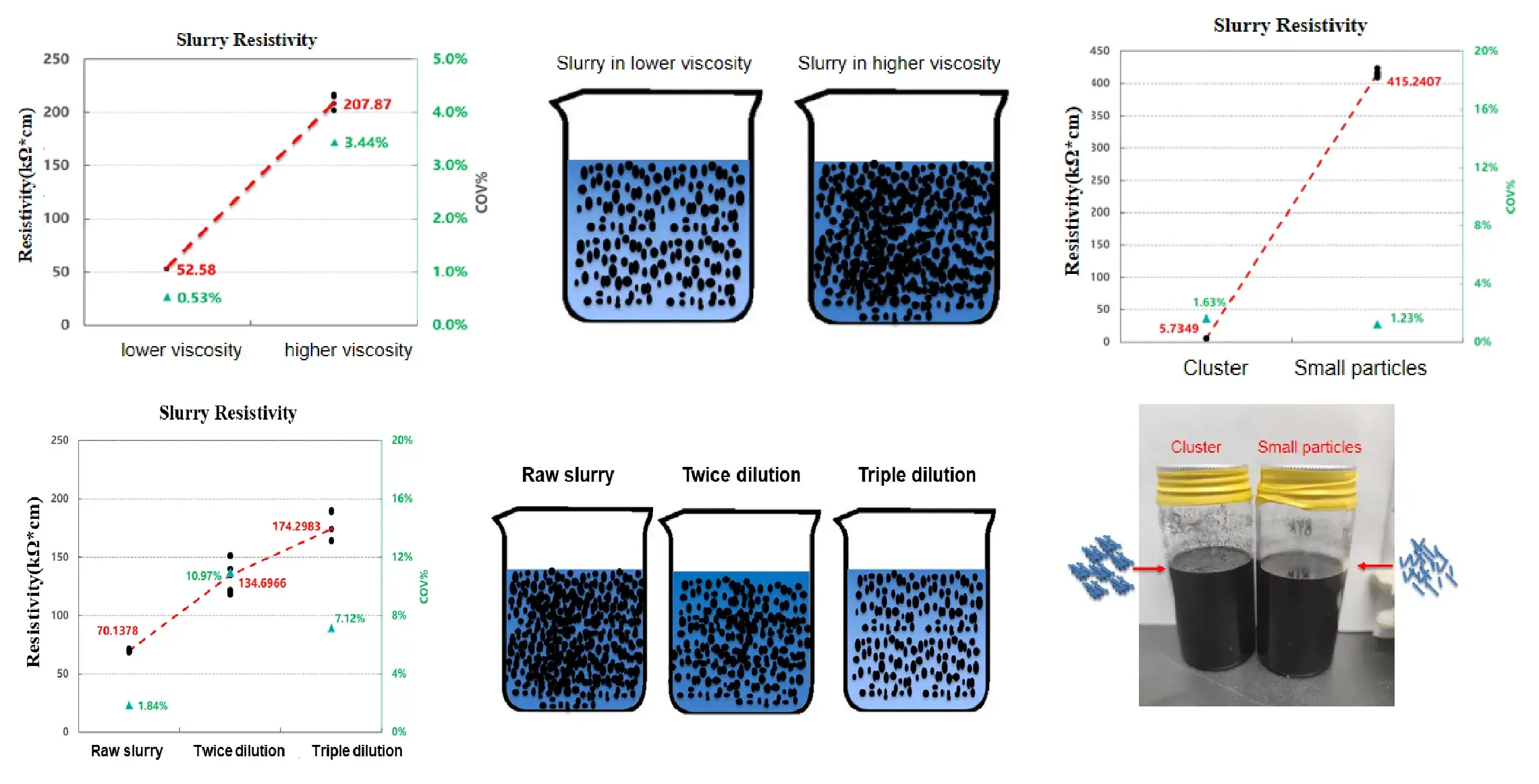
- When the viscosity, concentration and dispersant type of the conductive agent are changed, the resistivity also changes!
- Subsequent process control can establish resistivity specifications for slurries at fixed viscosity levels, enabling real-time monitoring of slurry process stability.
Case 2. Concentration-Viscosity-Resistivity Correlation
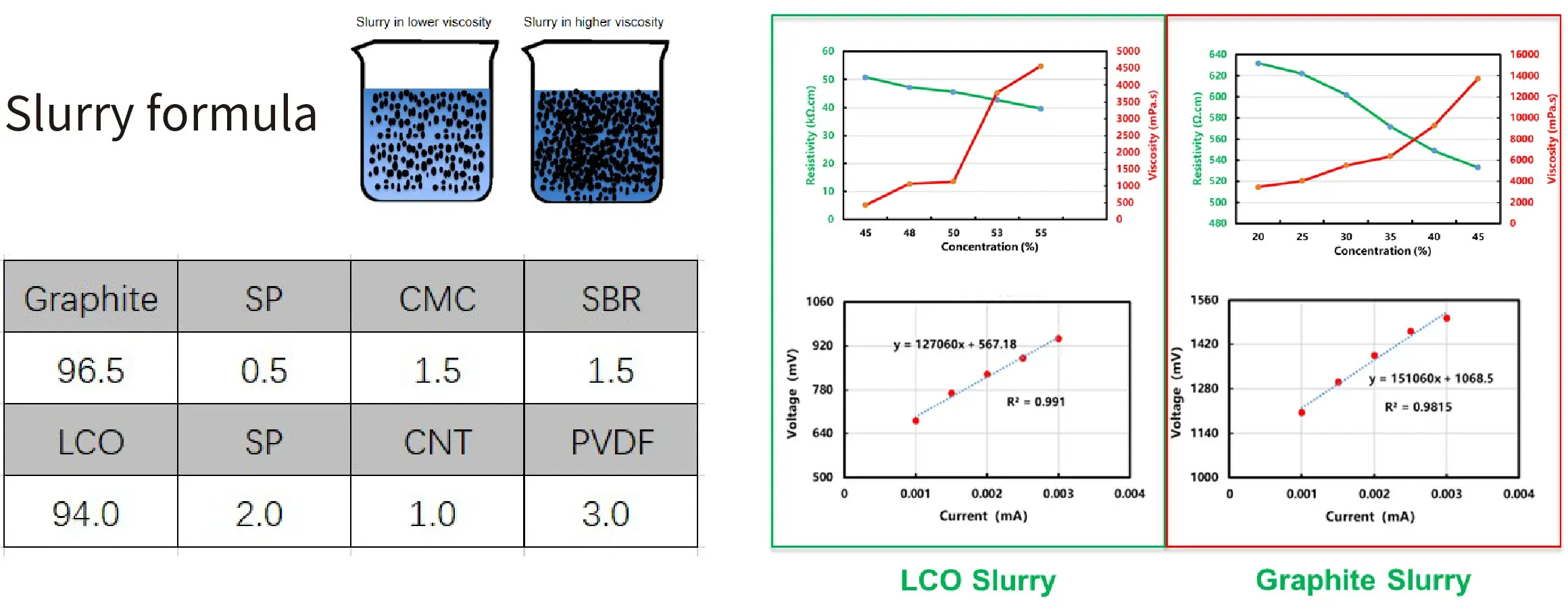
- The resistivity of the slurry decreases with the increase of the concentration, and the change of the viscosity is also inversely proportional to the relationship;
- The I-V curve test of these two types of slurries basically conforms to Ohm’s law, and the current and voltage have a linear relationship, indicating that the slurries are mainly electronic conductors;
Case 3. Sedimentation Performance Evaluation of Battery Slurries
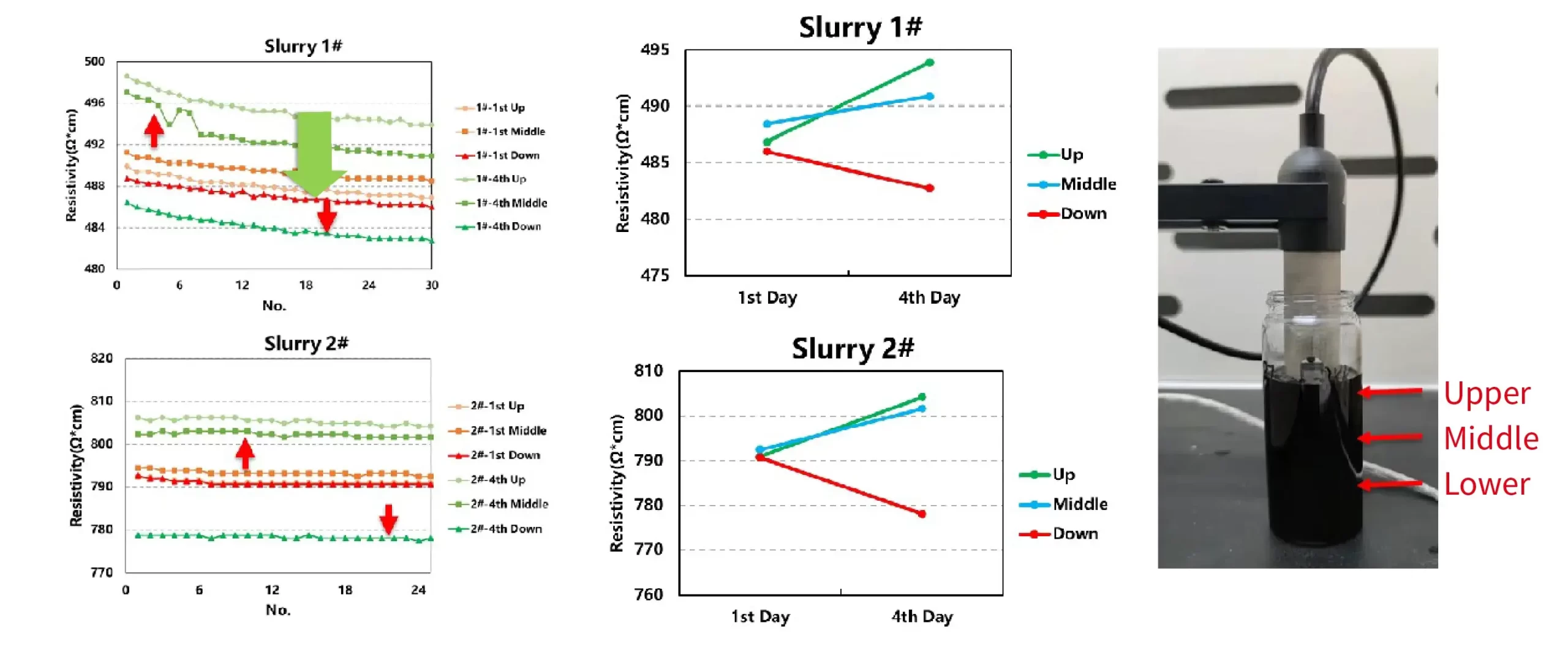
- On the first and fourth day of testing, the resistivity of the upper and middle channels increased, while the resistivity of the lower channel decreased, indicating that after four days of shelving, the slurry shows obvious settlement.
- Subsequently, a shelving period can be formulated for a certain of slurry according to the change of the resistivity to ensure the uniformity of the slurry!
Video