Description
1. Principle of Battery Cell Swelling
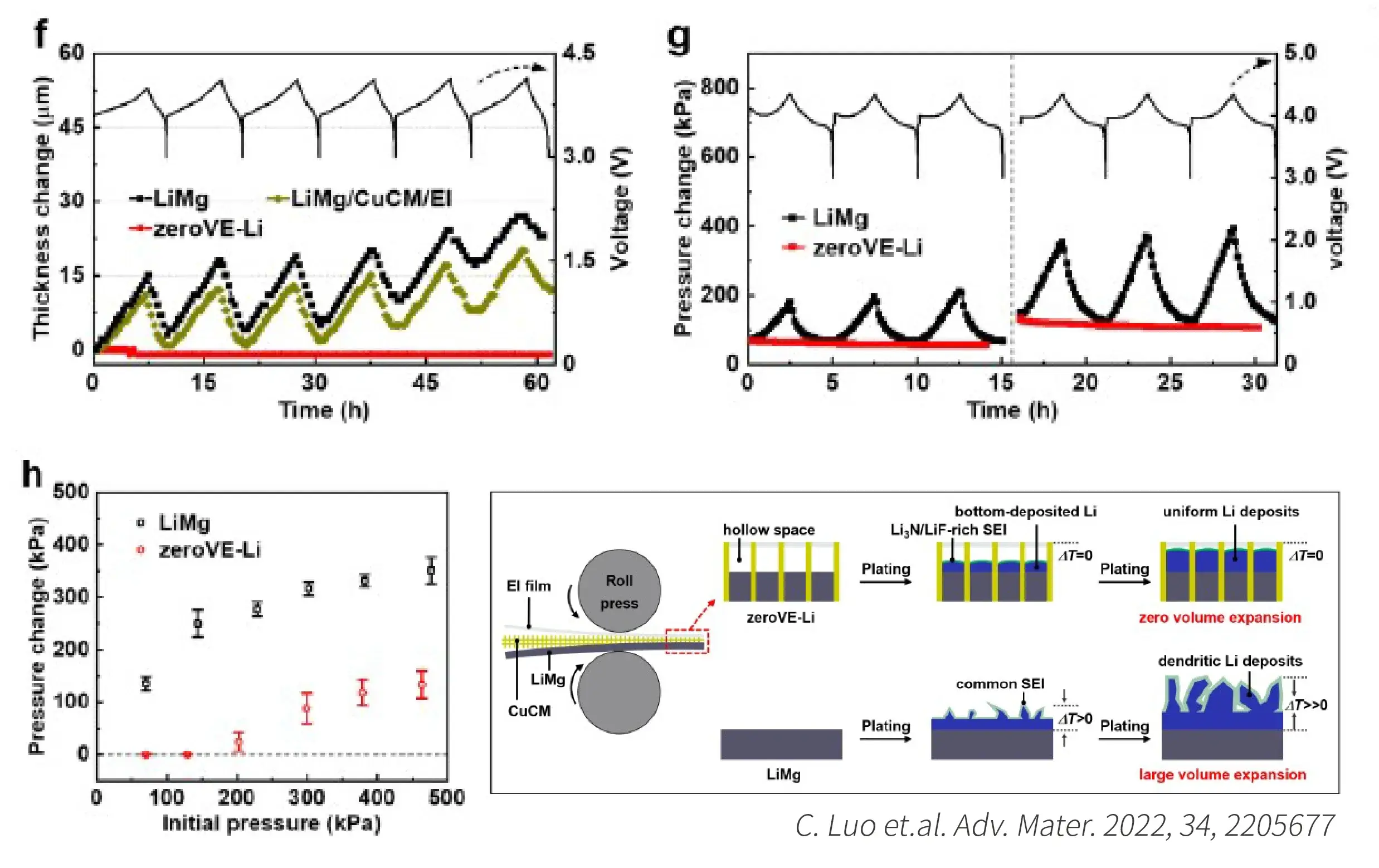
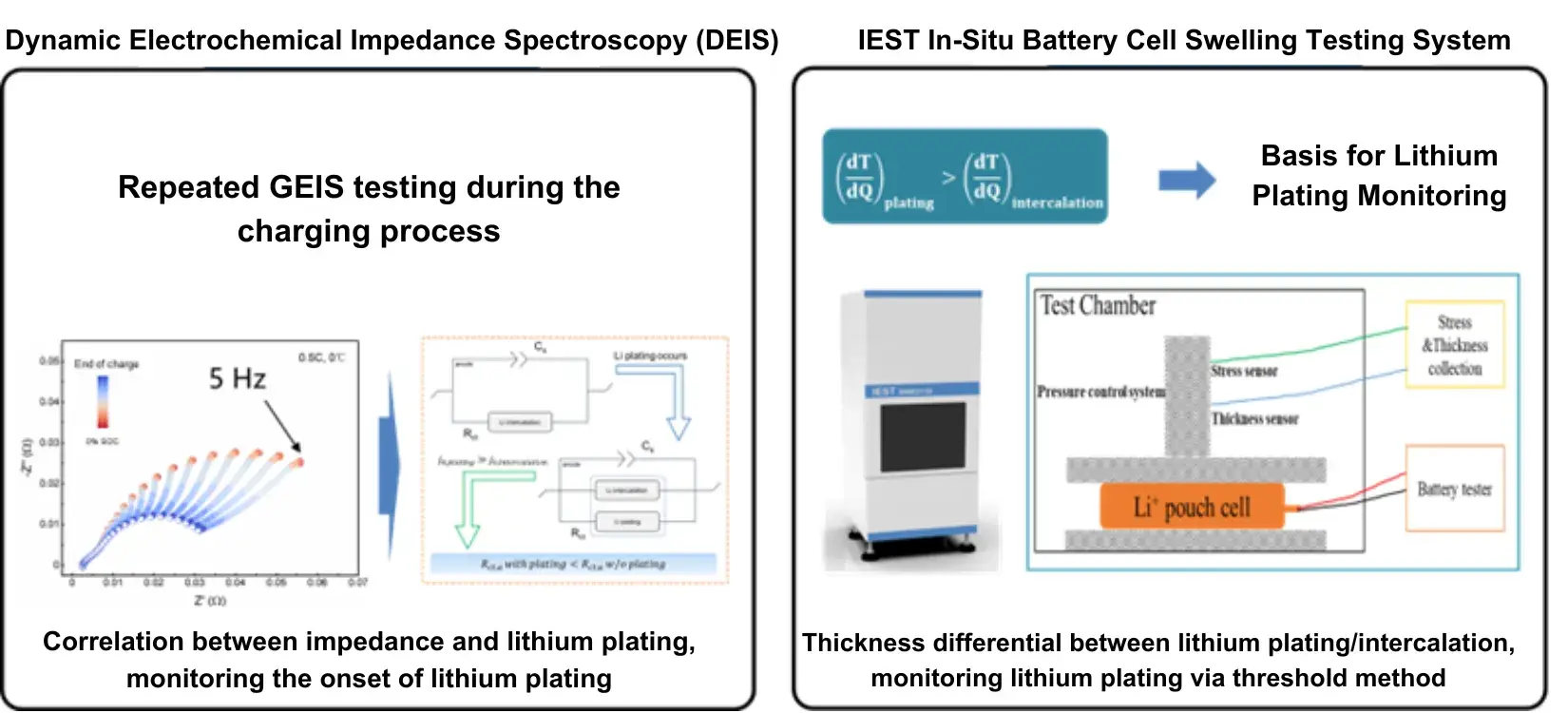
On the other hand, the lithium plating also can cause the expansion of LIBs. Thus, how to identify the lithium plating window under different charging rate and temperature by the expansion behavior of LIBs is very helpful for the developments of the fast charging technology, sectional charging technology and other charging strategies.
2. Traditional Methods for Swelling Evaluation
- Disassemble different—condition cells and measure the thickness of the cell and electrodes by micrometer;
- Li plating window judgment: Through the disassembly of full charged cell to judge the lithium precipitation on electrode surface by visual inspection;
- Destructive Test: It is a cell consuming destructive test, and there is a higher safety risk and higher operation cost because the dry environment and professional people are required;
- Non in-site Test: Only the thickness data on several specific states can be acquired, the swelling behavior of cells cannot be described systemically; Big Deviation for lithium plating window assessment: Not every lithium plating SOC and potential in different rate can be quantified.

3. IEST Creative Swelling Solutions
- In-situ swelling analysis system: Combined with the highly stable automatic platform and the high-precision thickness and mechanical sensors, it can achieve long-term stability and accurately detect the expansion thickness and the expansion force under different conditions.
- Multi-function test modes: the constant pressure and constant gap test modes can be realized for the cell, and the performance of the cell under different stress conditions can be evaluated.
- High precision control: The traditional fixture will generate ~70um deformation under the constant gap testing mode, which leads to the inaccurate swelling force test. However. the in-situ SWE series analysis system of IEST can control the change of the gap within ~1um by active modulation, and record the accurate swelling force during the constant gap testing mode.
4. SWE Series Instrument Schematic
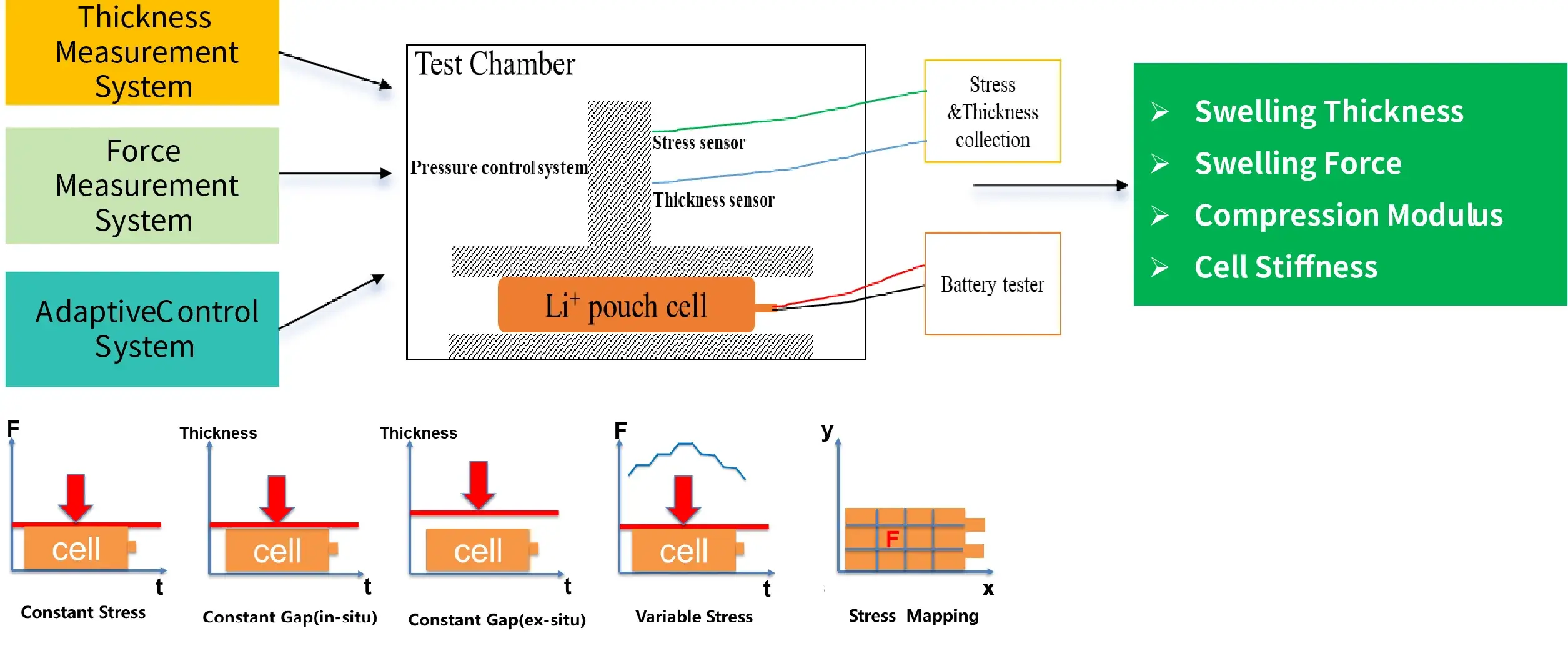
- Six Test Modes: Characterize the expansion behavior of the battery cell under different boundary conditions.
- The In-situ Swelling Analysis System Integrates: high-precision servo motor + adaptive lower-level control system + high-precision pressure sensor and thickness sensor
5. Applicable Samples

6. Applications
- Material evaluation
- Battery cell R&D
- Cell stiffness evaluation
- Swelling force distribution
- Module Simulation
- Lithium plating analysis
- Battery cell structure evaluation
- Operating condition evaluation.
Applications
1. Application Cases: Material Evaluations
1.1 Formation and charge-discharge swelling of cells with different Si/C contents
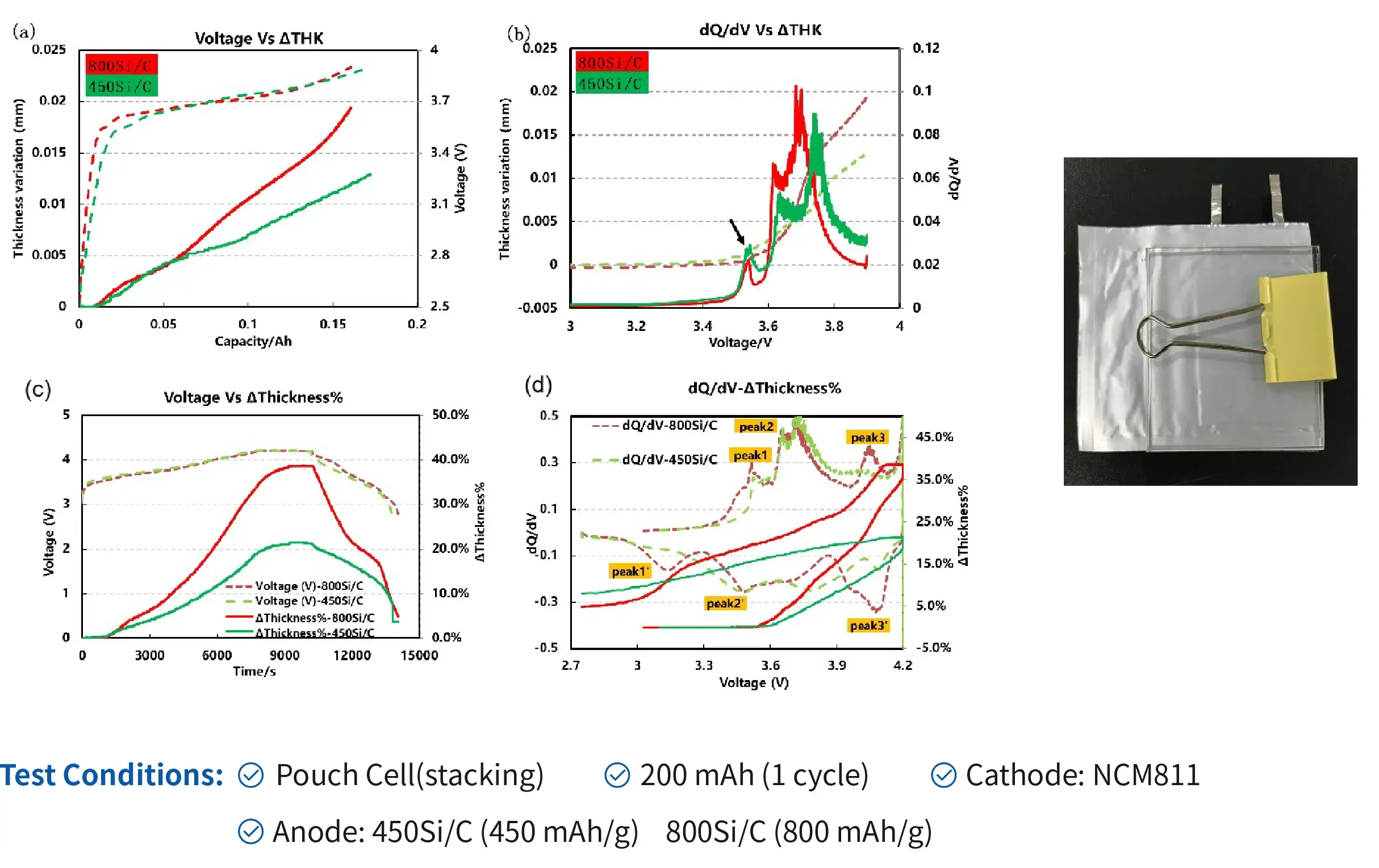
Conclusion:
- Higher silicon content in the anode leads to greater expansion caused by lithium-ion intercalation forming the LixSi alloy, and will also affect the lithium intercalation phase transition potential of graphite.
- R&D personnel should rationally regulate the silicon-to-carbon ratio and modify the structure of silicon-based materials to mitigate structural expansion.
1.2 NCM-Si/C Cell – compare the swelling differences of various modified Si/C materials;
Anode: Three types of Si/C electrodes (B, C, D) with similar capacities (approximately 5.9 mAh) but different modification methods. (Material B is a low-expansion silicon-carbon material specially modified by a Ningbo battery materials company.)
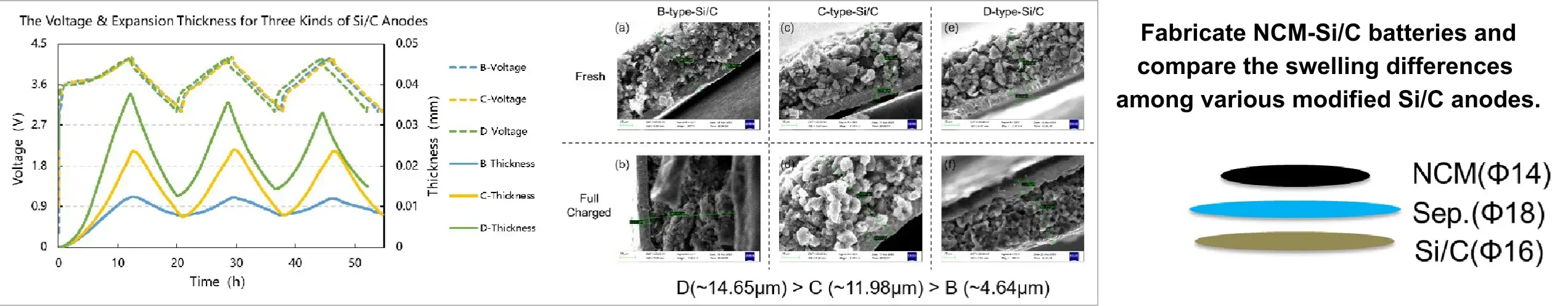
Conclusion:
- When paired with identical cathode materials, comparative swelling analysis revealed that the specially modified Si/C material (B) exhibited minimal thickness expansion.
- The swelling thickness trends aligned statistically with cross-sectional SEM measurements
1.3 Cycle swelling of cells with different binders
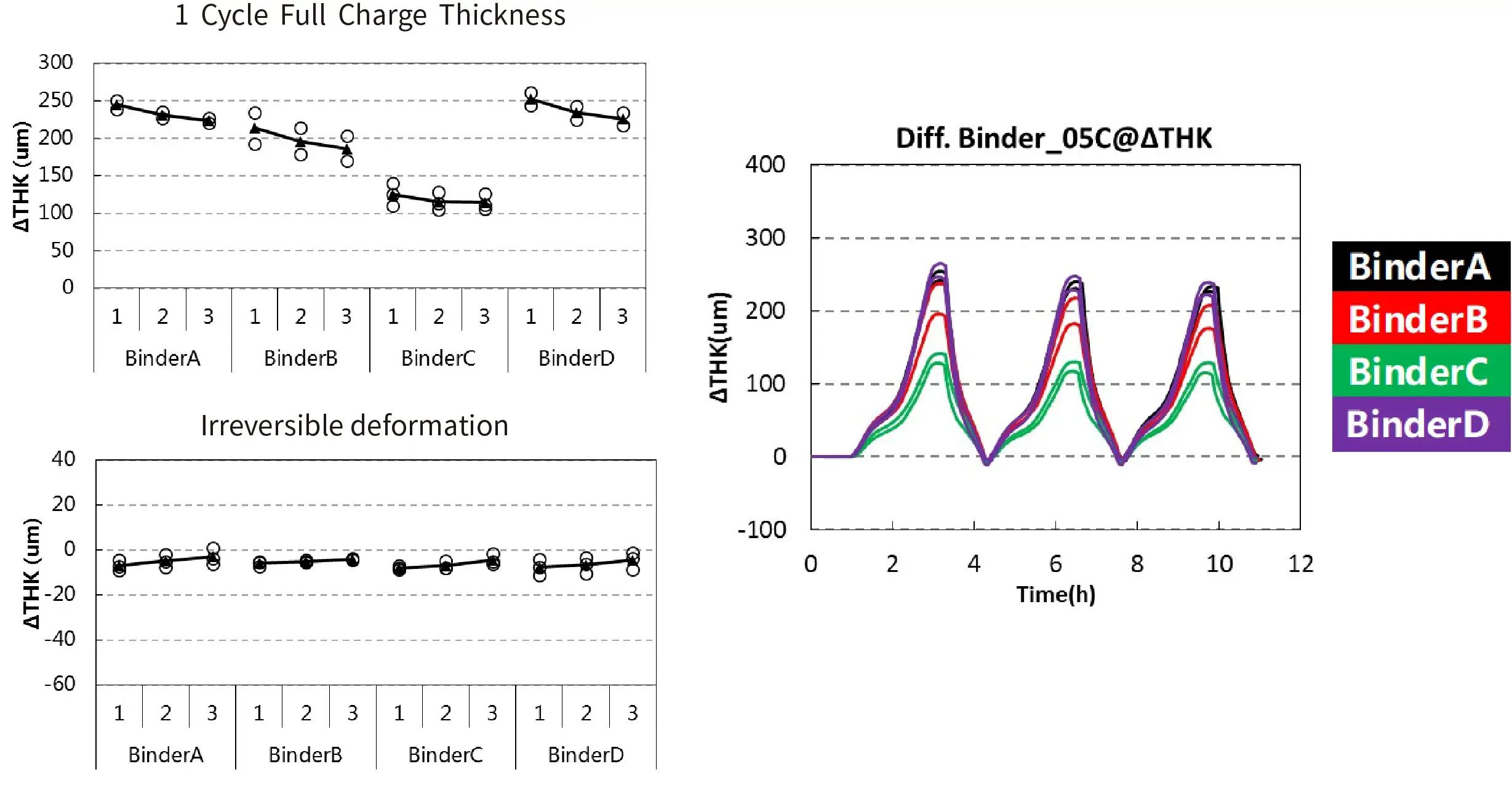
Conclusion:
- Comparison of battery cells swelling with four different binder materials: The irreversible swelling levels are comparable, with the main difference observed in the single-cycle full-charge swelling thickness. Binder C demonstrates the best swelling suppression performance.
- This approach serves can be used for evaluation and screening of different binder materials.
1.4 Lithium Metal Anodes with Distinct Modification Approaches
Conclusion:
- Modified lithium metal anodes significantly suppress volume expansion during cycling.
2. Application Cases: Non-Destructive Lithium Plating Analysis
2.1 Lithium plating under different C-rate
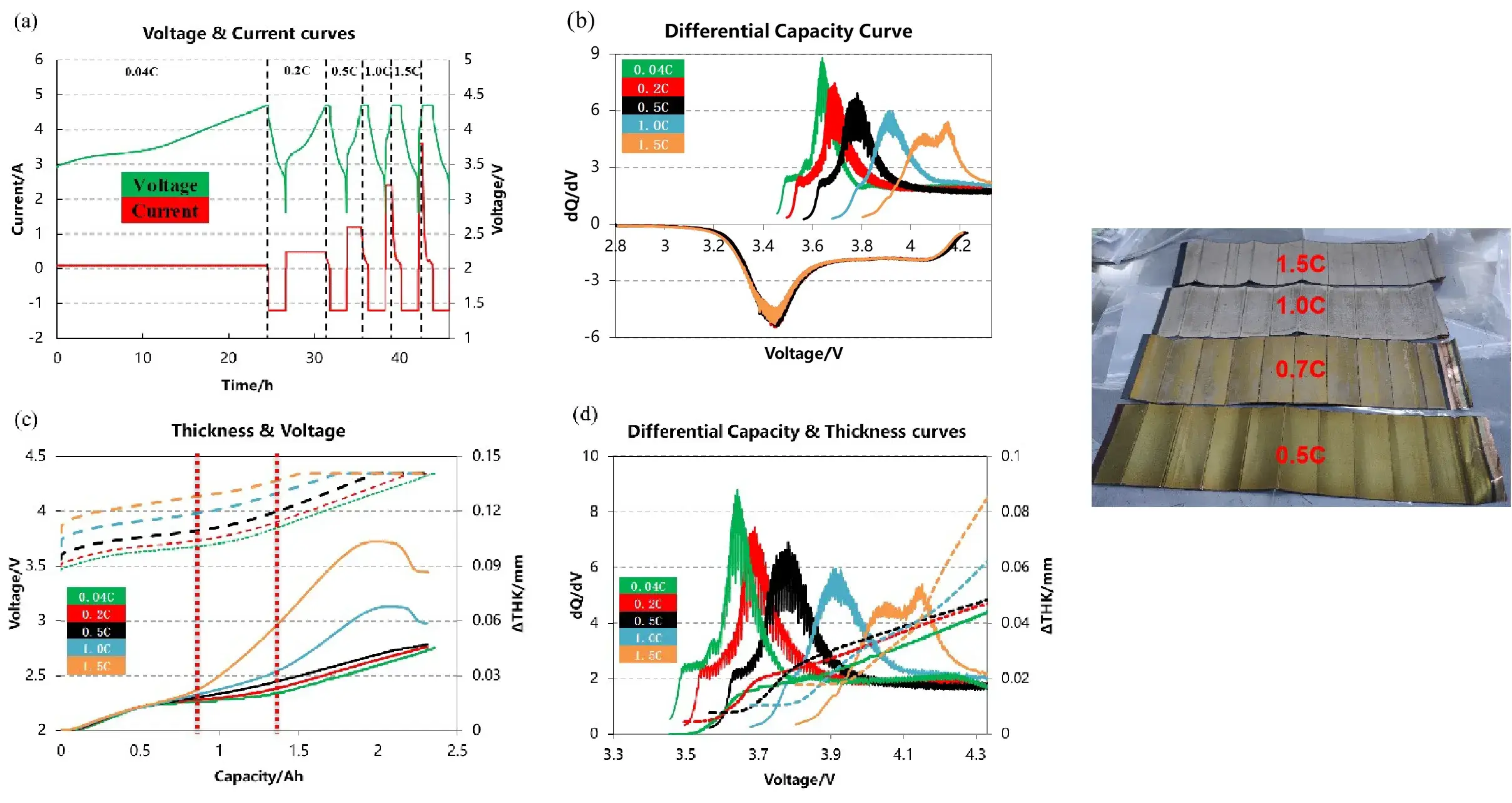
- Testing Method: In-situ testing of the cell’s thickness curve at different charging C-rates.
2.2 Lithium plating under different tempreture
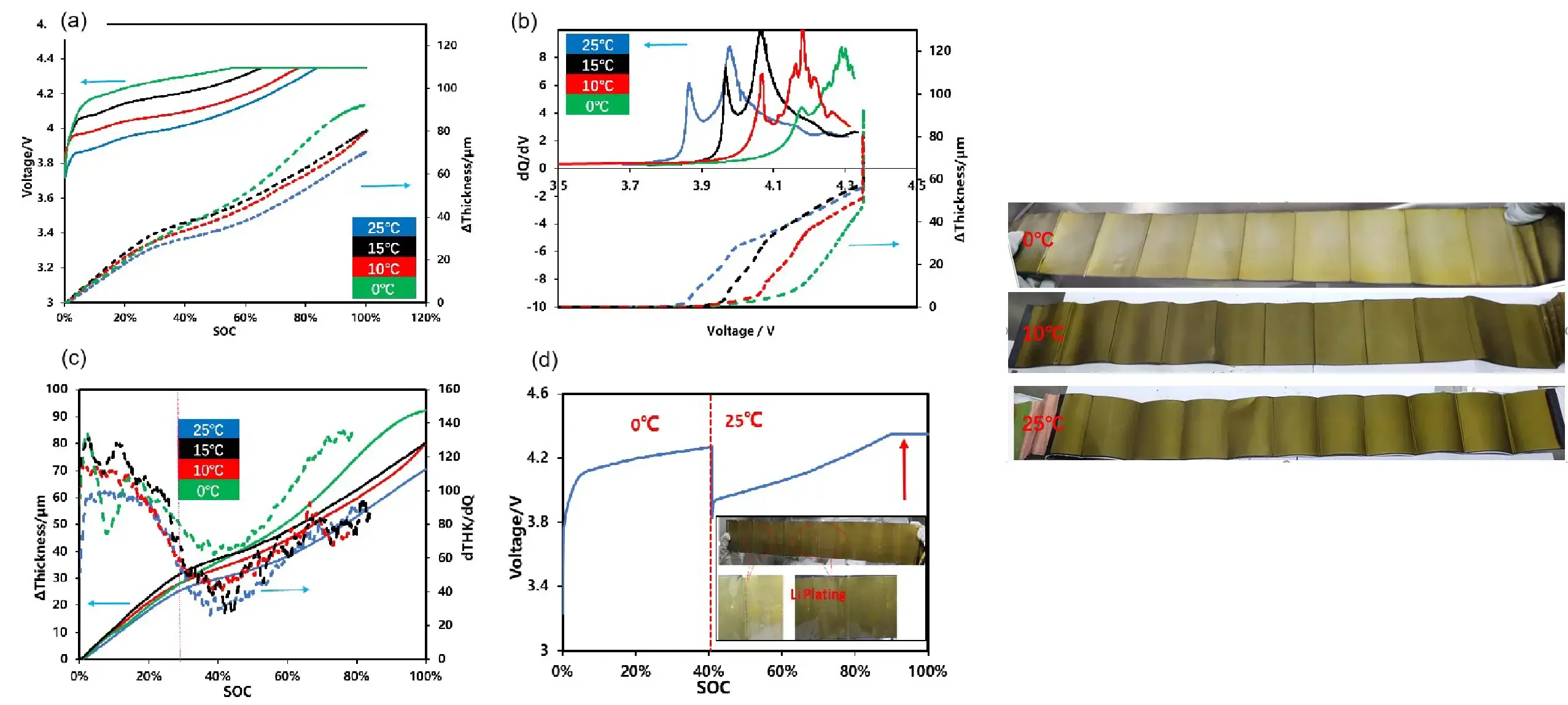
- Testing Method: In-situ testing of the cell’s thickness curve at different temperatures.
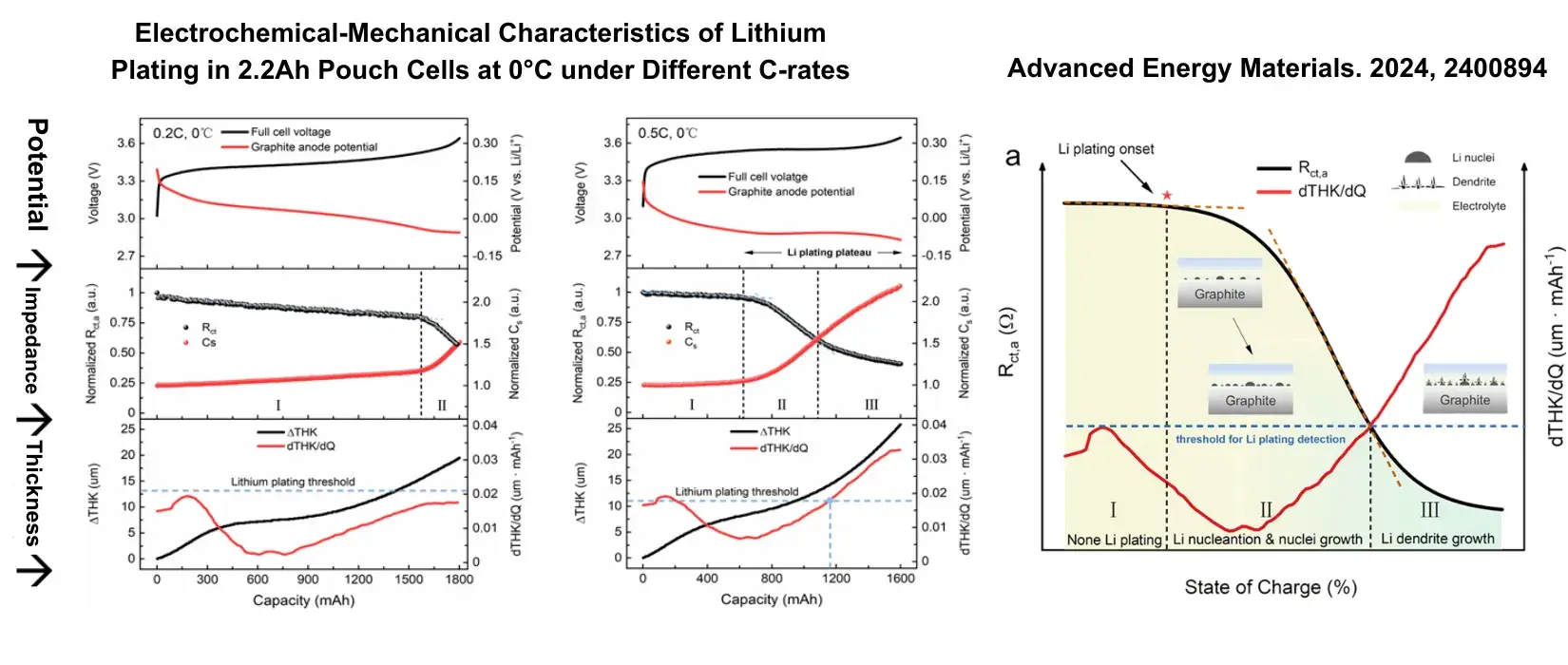
2.3 Analysis of the Three-Stage Lithium Plating Process on Graphite Surface in Pouch Cells
Conclusion:
- By correlating changes in the anode charge transfer resistance (Rct,a) using the impedance method, the onset of lithium plating nucleation can be monitored.
3. Application Cases: Cell Structure
3.1 Multi-layer jelly rolls vs. Single-layer stacked cells
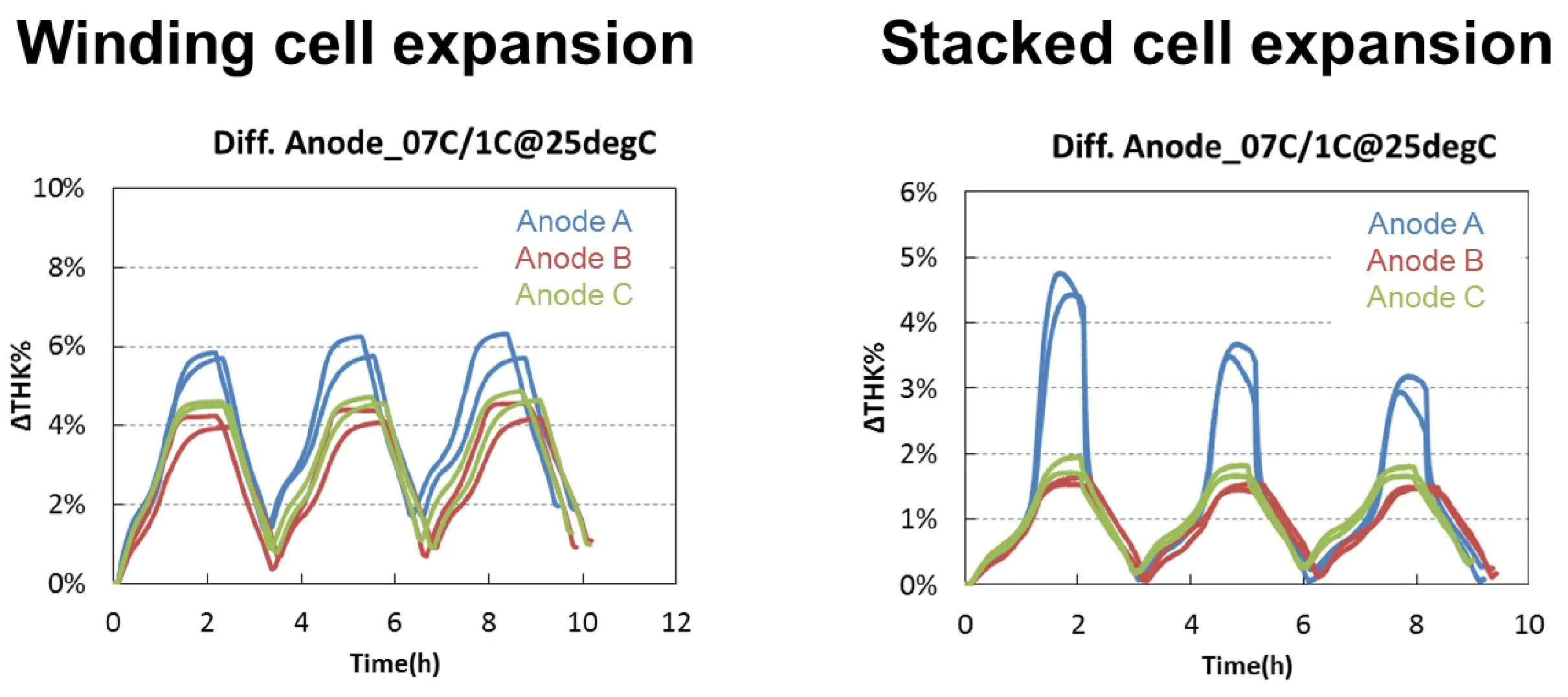
Conclusion:
- Two models are used to evaluate the swelling of different anode cells, and the comparison law is basically the same as A> C> B.
- Because the two sides of the winding are bound, the crimping stress caused by the lateral swelling accumulates in the middle, so that the thickness increases with the cycle, and the four sides of the lamination are not bound, so the crimp stress of the group A pole piece with larger lateral swelling is released during the cycle, and the thickness decreases with the cycle. (Single-sided anode).
- In-situ Cell Swelling Testing System can be used to deeply analyze the influence of process on stress and strain.
3.2 Swelling stiffness VS Compression stiffness under constant pressure
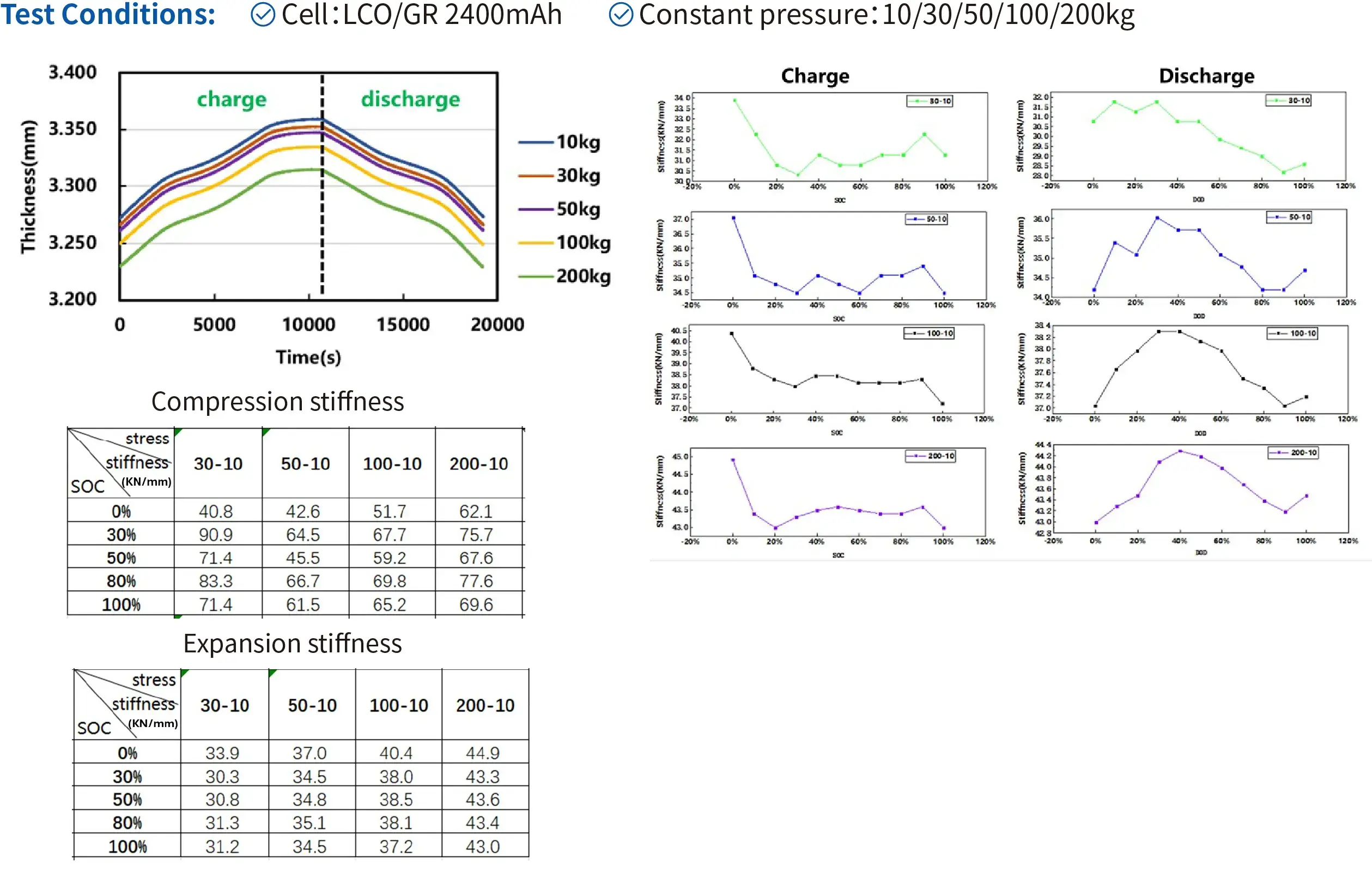
Conclusion:
- The swelling stiffness changes regularly with charging and discharging.
- The difference between swelling stiffness and compression stiffness is obvious.
4. Application Cases: Operating Condition Evaluation
4.1 Swelling of prismatic cells under different stress
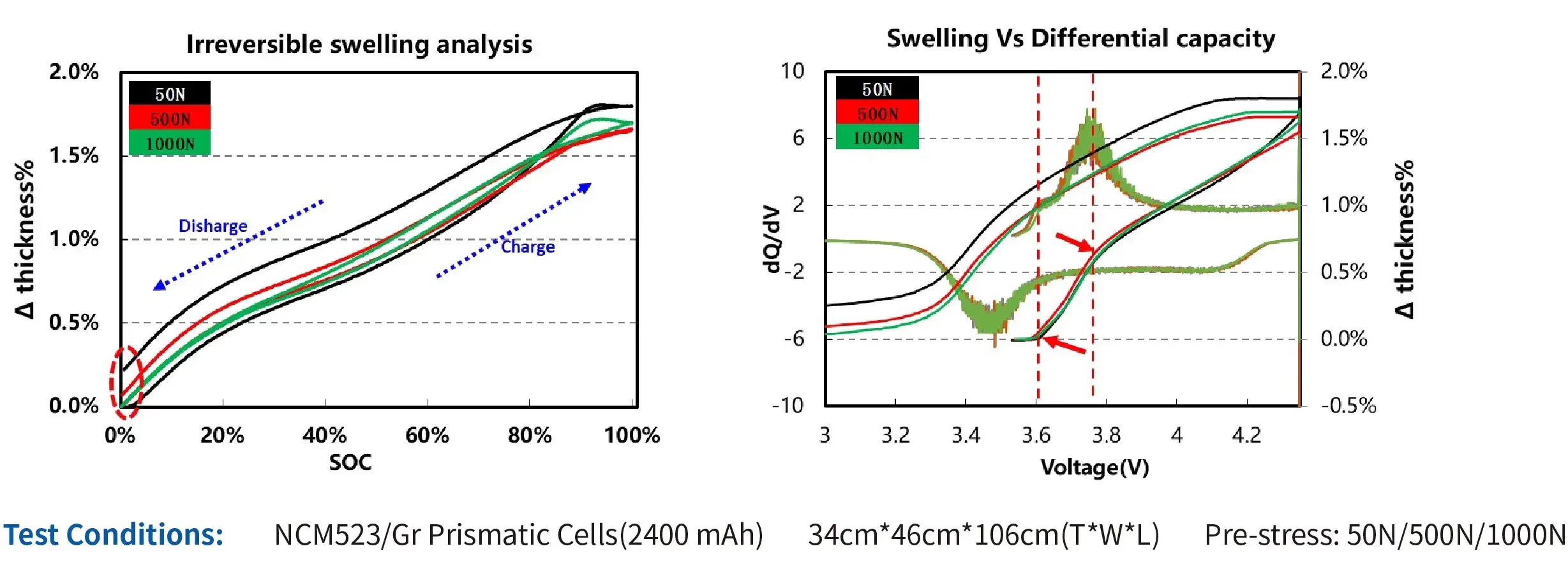
Conclusion:
- The proportion of irreversible swelling of the cells can be reduced by increasing the pre-stress.
- During the charge process, the 2 inflection points of the swelling curve correspond to the 2 peaks of the diferential capacity curve, indicating that the swelling of the cell is related to the phase transition of lithium intercalation & deintercalation.
4.2 Swelling of prismatic cells under different temperature
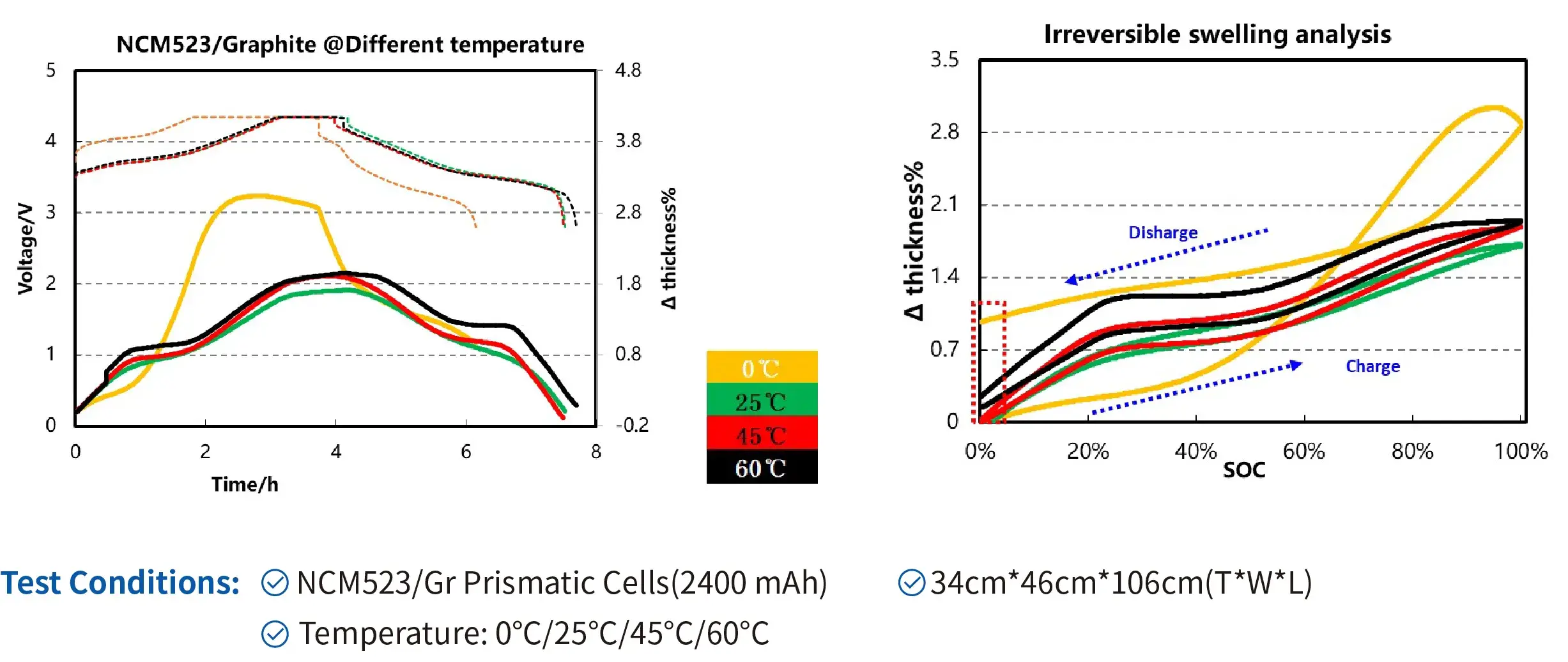
Conclusion:
- The irreversible swelling of the cells increases in both cases when the temperature increases from 25℃ to 60℃, as well as decreases from 25℃ to 0℃. However, the causes of such swelling under high-temperature and low-temperature conditions may differ.
4.3 Swelling of prismatic cells under different charge rate
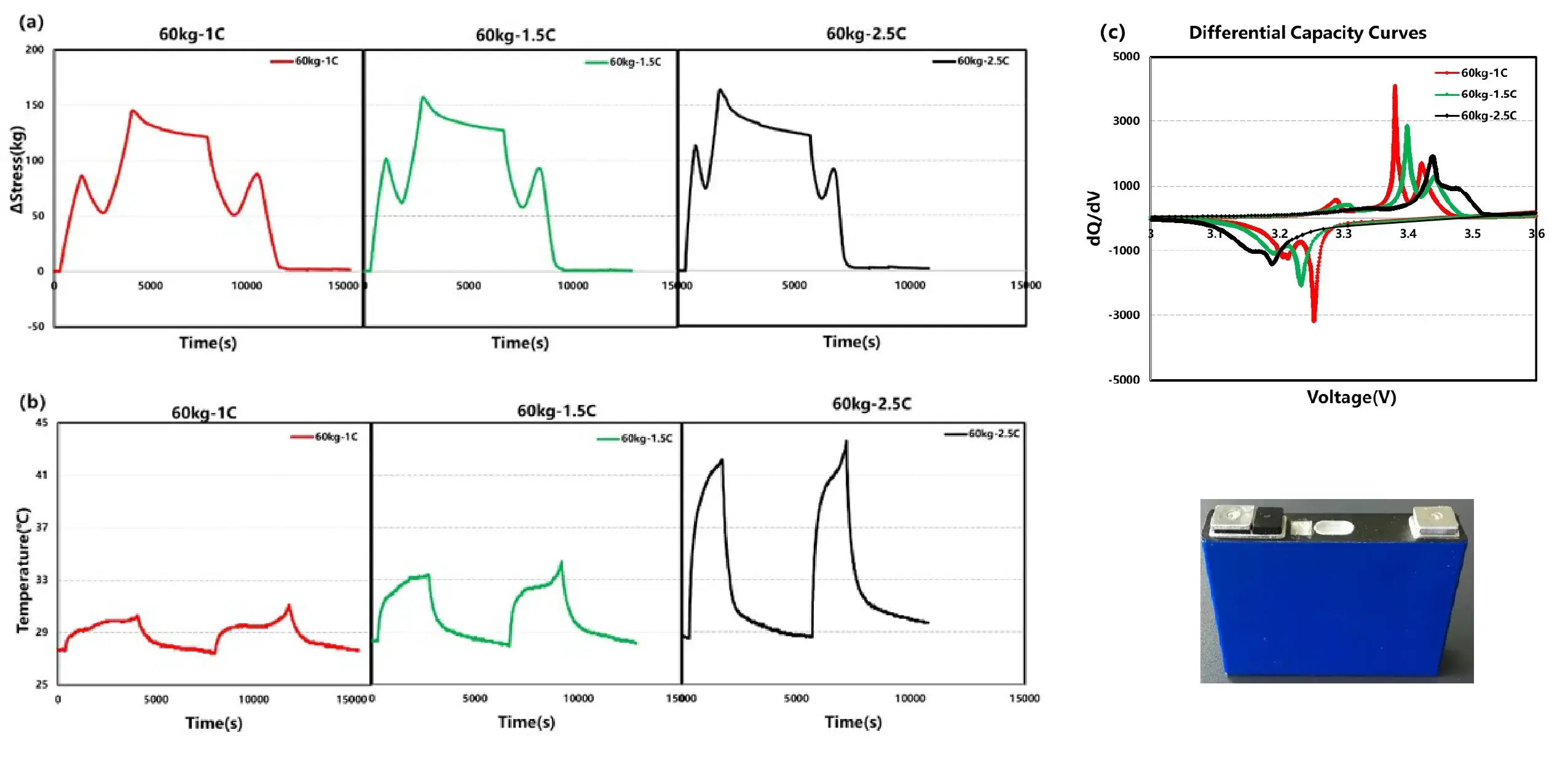
Conclusion:
- LEP/Graphite 40Ah Prismatic Cell
- As the charge rate increases, the cell’s temperature rise progressively intensifies. This trend predicts that exceeding certain C-rate thresholds may trigger excessive temperature elevation and potential thermal runaway.
4.4 Swelling of prismatic cells under different pre-stress
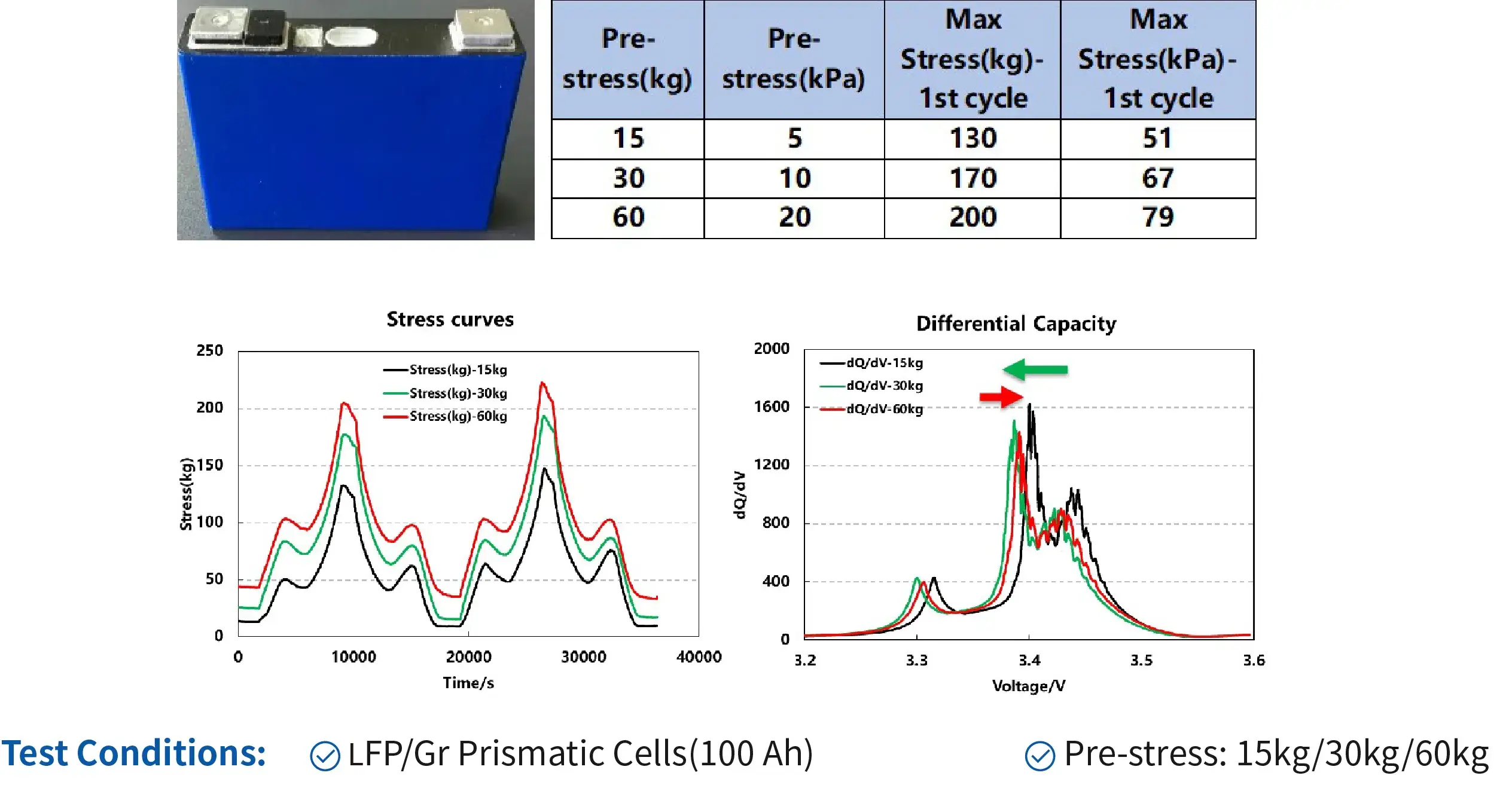
Conclusion:
- As preload increases, the initial cell gap progressively decreases, while swelling force variation during charge/discharge cycles intensifies. This enables derivation of the relationship between initial preload and maximum swelling force, providing critical guidance for battery module design.
- Concurrently, charge polarization initially decreases then increases with higher preload. This indicates that for this prismatic hard-case cell, an optimal preload around 30kg enhances rate capability.
4.5 Thickness and stress changes during charge and discharge
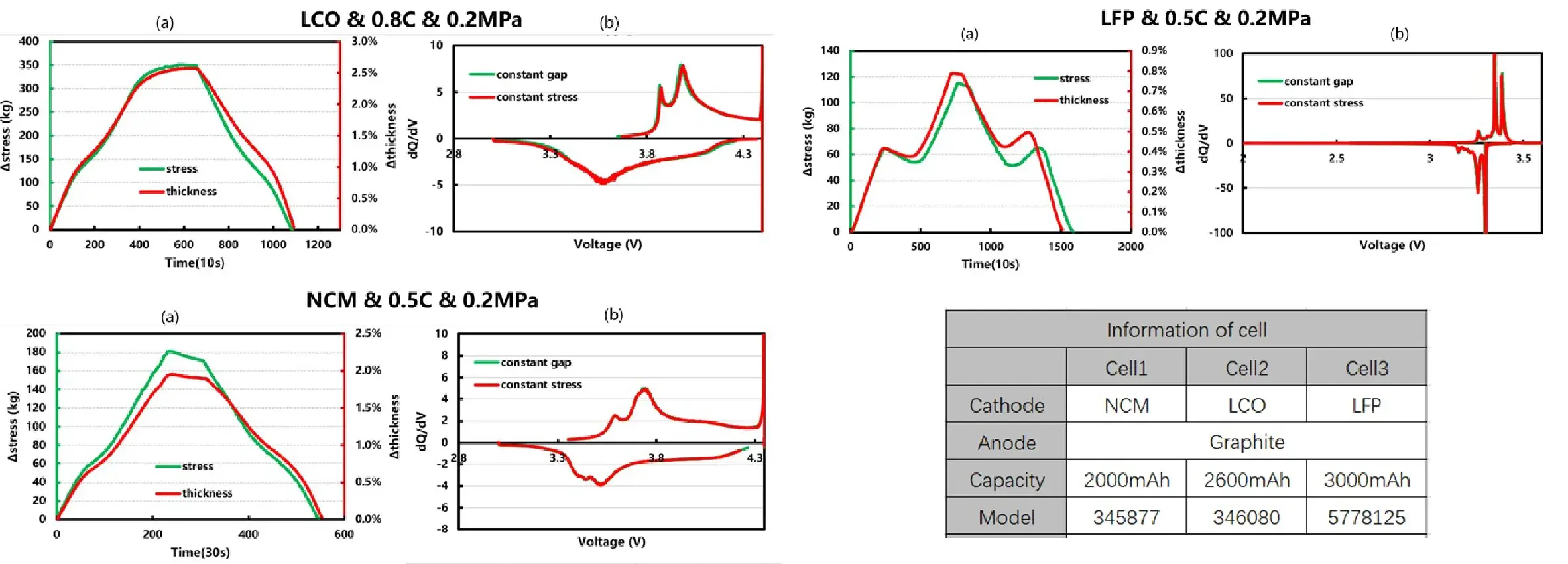
Conclusion:
- LFP-based cells exhibit a distinctive voltage hump during charge/discharge cycles, whereas LCO and NCM systems show no such phenomenon. Additionally, NCM cells demonstrate a mild reduction in swelling during the constant-voltage charging phase.
- These differential swelling behaviors serve a dual purpose: they provide lithium-ion battery researchers with an in-situ characterization method for swelling performance, while simultaneously offering mechanistic insights and benchmark data for studying expansion characteristics in specific cathode systems.
4.6 Cyclic Swelling Analysis
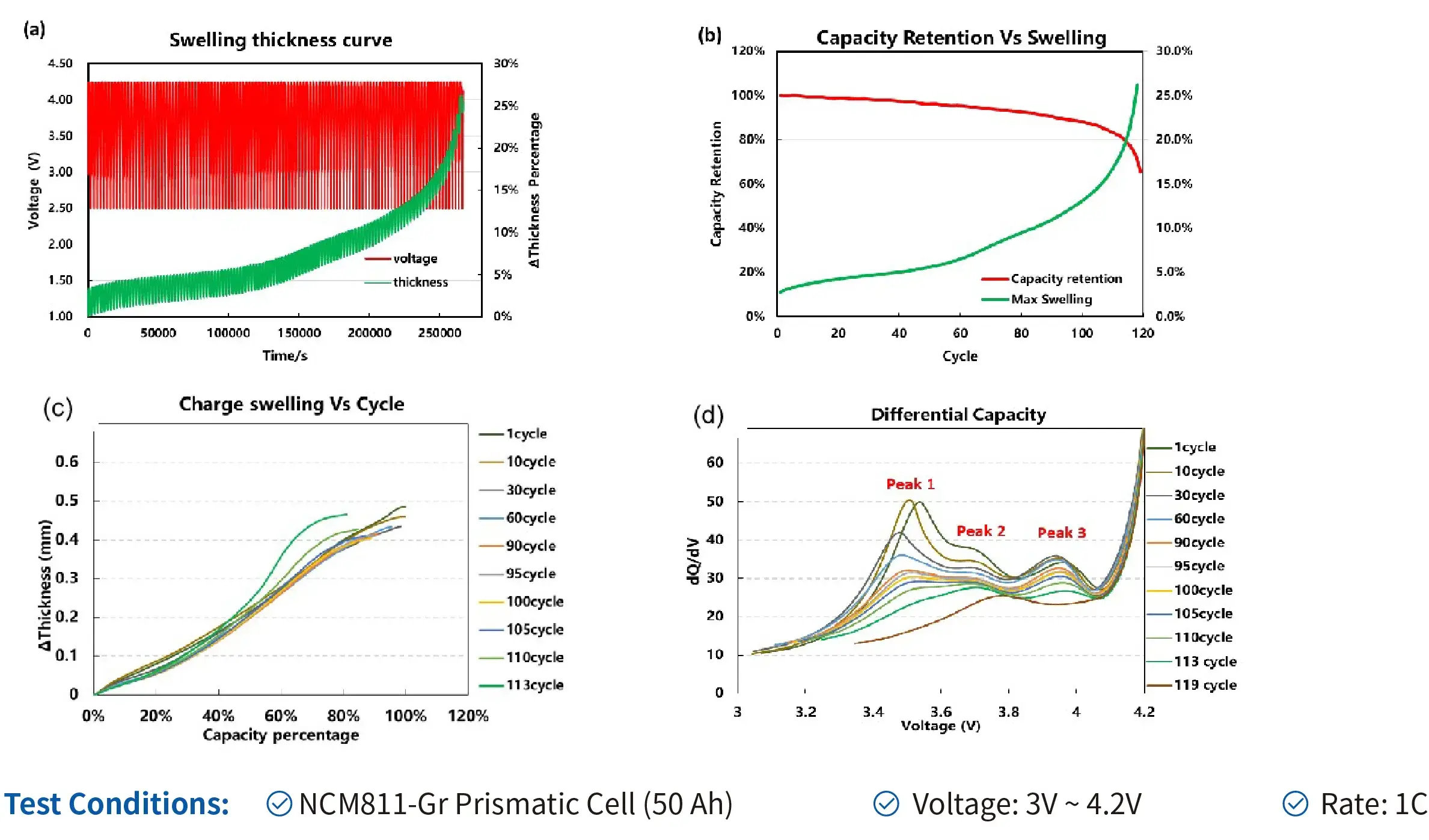
Conclusion:
- Investigating the correlation between capacity fade and thickness expansion in NCM cells during long-term cycling. Through comprehensive analysis of cell swelling thickness and electrochemical data, we infer that the cycling degradation mechanisms include electrode mechanical degradation, lithium plating, and parasitic side reactions.
4.7 Constant stress test analysis
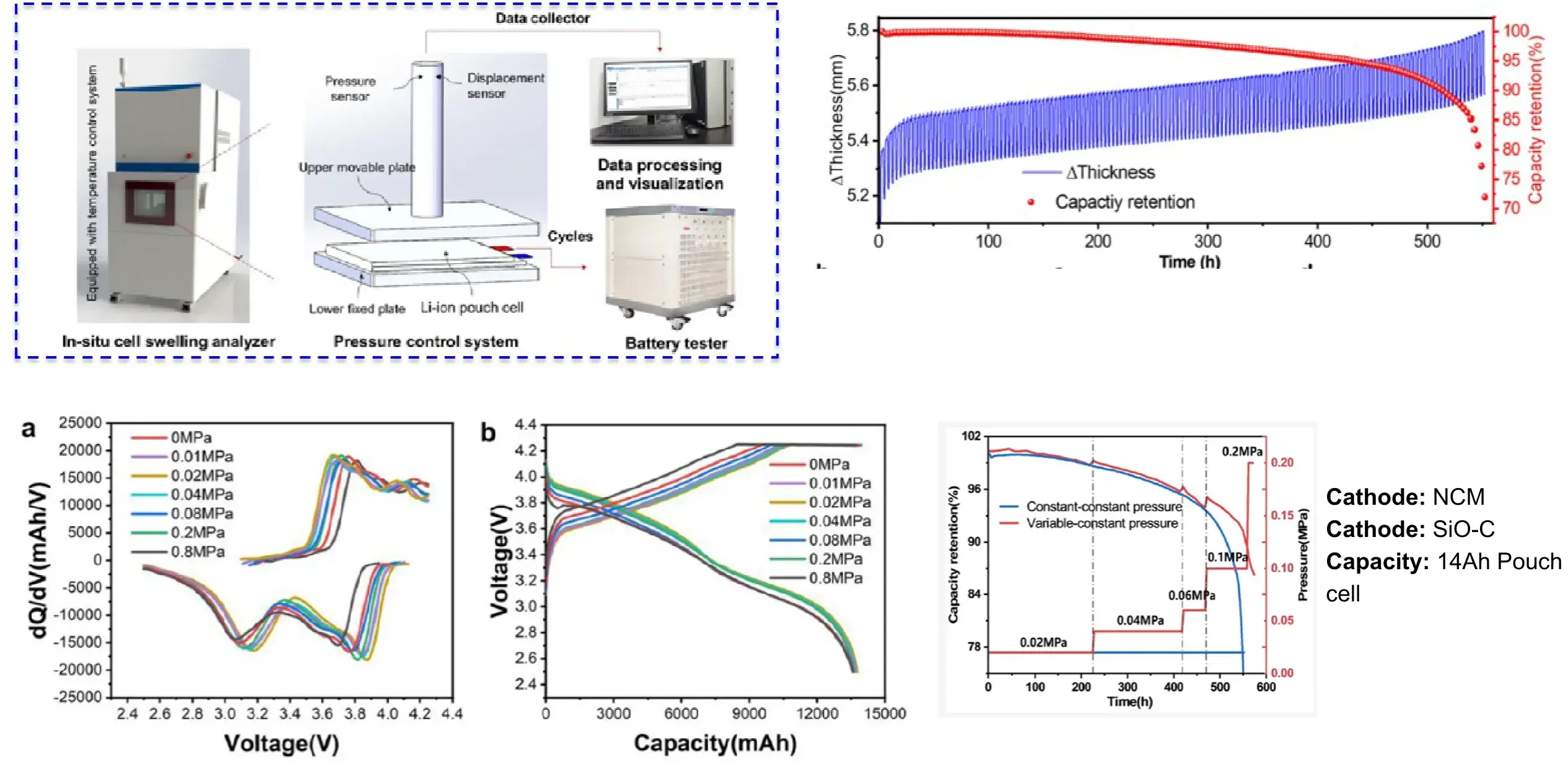
Conclusion:
- Optimal external pressure mitigates cell polarization during cycling. Implementing stepwise external pressure throughout battery operation significantly extends cycle life.
- These findings establish an effective strategy for capacity enhancement in lithium-ion batteries featuring silicon-dominant anodes, providing critical guidance for pack engineering design.
Video