Description
1. Principle of Electrode Wetting
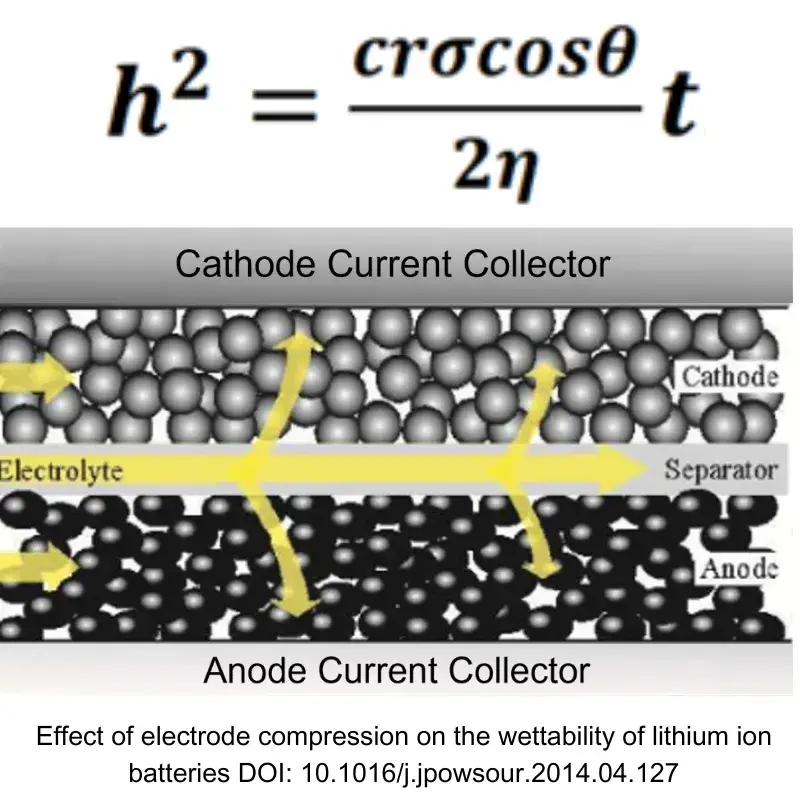
The Lucas–Washburn Equation is commonly used to describe the dynamic of liquid absorption in electrode pores, as represented by the equation below:
- r represents the radius of the capillary (m),
- σ represents the surface tension of the imbibition fluid (N/m),
- η represents the viscosity of the imbibition fluid (Pa*s),
- θ represents the contact angle of the wet phase (°),
- h represents the liquid suction height (m),
- t represents the liquid suction time,
- cr represents a fixed value, called the formal radius.
2. Applications
-
Electrolyte performance evaluation
-
Electrode consistency assessment
-
Material / electrode surface-treatment process optimization
-
Battery performance prediction
-
Production process improvement
-
Research & development(R&D)
3. Electrolyte Wetting Characterization Solutions
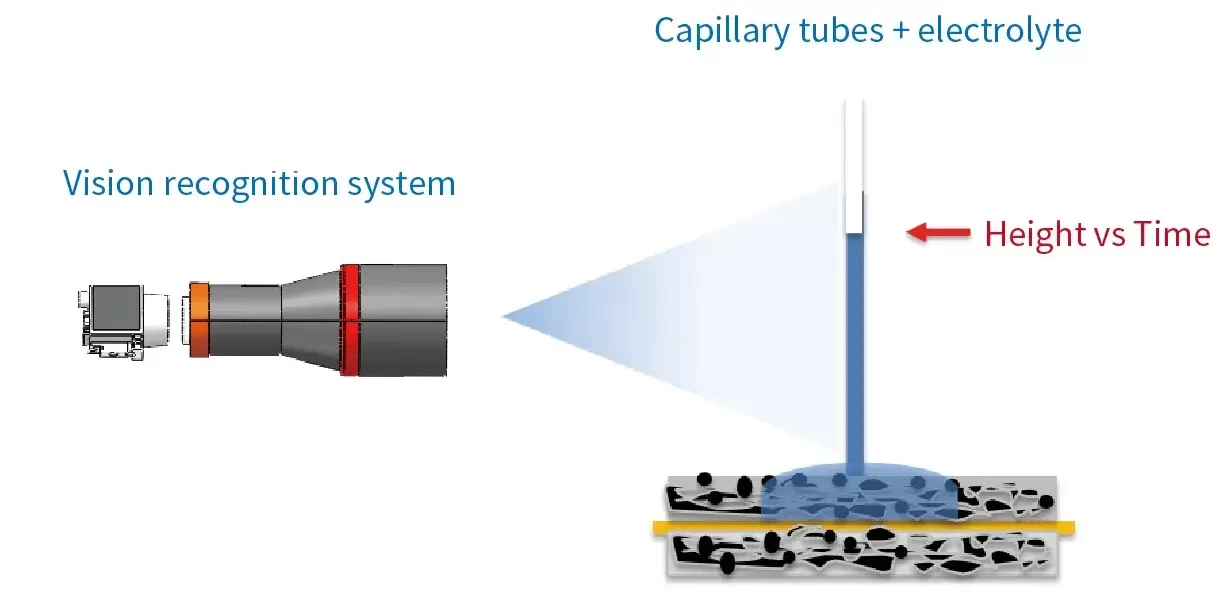
3.1 Capillary Wetting System: EWS Series – Simulation & electrode uniformity
Key Features:
- Equipped with a high-precision vision acquisition system, ensuring stable and efficient test repeatability.
- Enables in-situ real-time characterization of the electrolyte wetting rate for lithium-ion battery anode electrodes.
- Applicable Samples: anode electrode
- The greater the compacticion of the electrode, the lower the porosity, resulting in poorer electrolyte wetting.
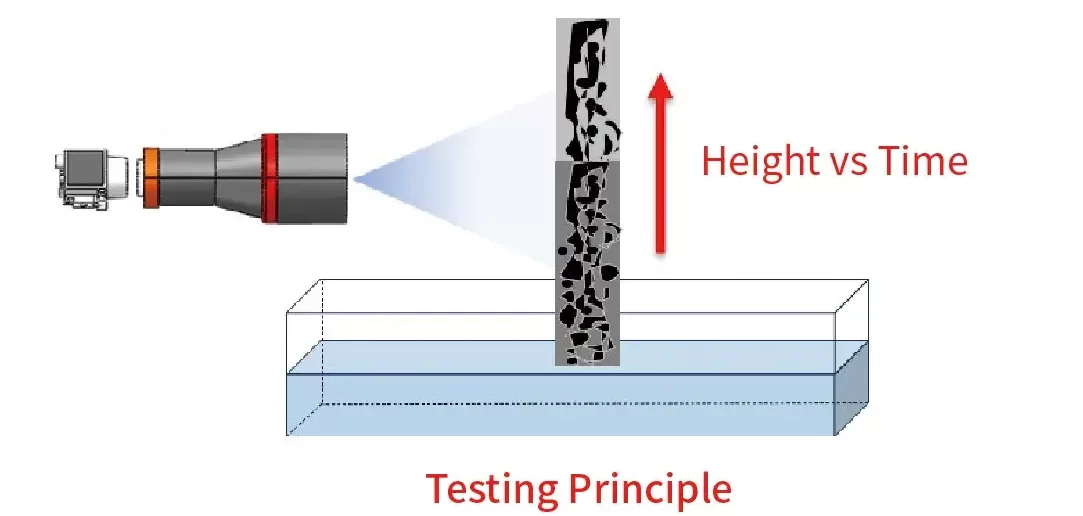
3.2 Height Wetting System: CHT Series – Electrode uniformity & process stability
Key Features:
- Equipped with a high-precision vision acquisition system, ensuring stable and efficient test repeatability.
- Enables in-situ real-time characterization of the electrolyte wetting rate for lithium-ion battery anode electrodes.
- Applicable samples: Anode electrodes
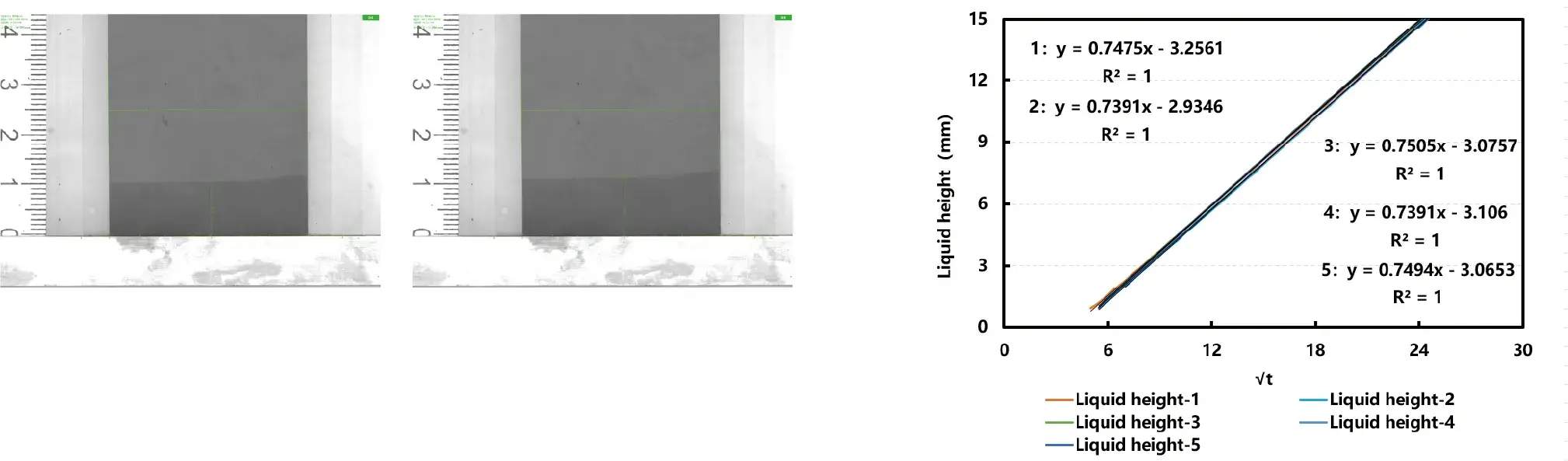
- Supports simultaneous testing of three parallel samples, demonstrating good consistency in electrolyte wetting.
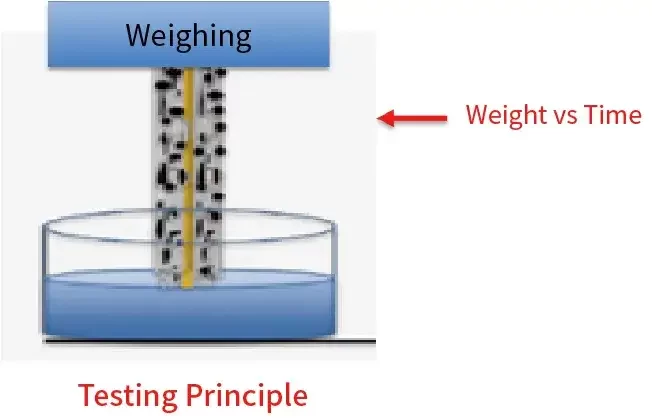
3.3 Weight Wetting System: ETS Series
3.3.1 ETS-1000 – Evaluate Jelly Roll(JR) Wetting Time for Dry Cells
Key Features:
- Equipped with a high-precision vision acquisition system, ensuring stable and efficient test repeatability.
- Enables in-situ real-time characterization of the electrolyte wetting rate for lithium-ion battery anode electrodes.
- Applicable samples: Anode electrodes/Jelly Roll(JR) cells
- Supports simultaneous testing of three parallel samples, demonstrating good consistency in electrolyte wetting.
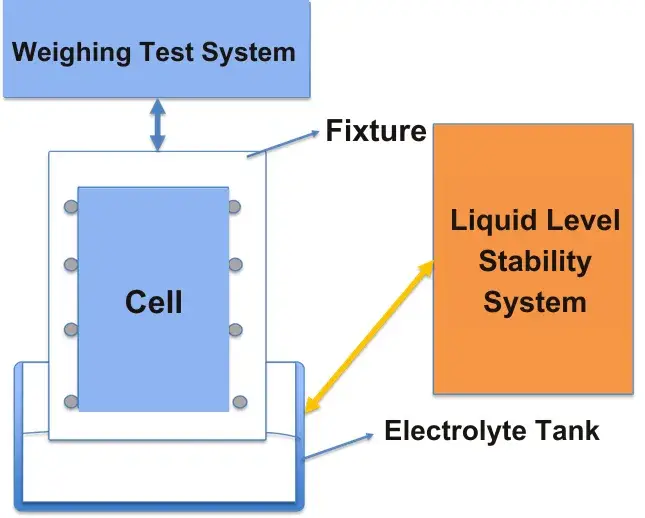
3.3.2 ETS-2000 Dry Cell JR Weight Testing System
Key Technical Features
- Weighing System: Maximum capacity 6 kg, accuracy ±0.1 g, meeting Jelly Roll (JR) test requirements;
- Liquid Level Control: Integrated electrolyte tank level control system (syringe pump + height sensor) to reduce inter-group test errors caused by liquid level fluctuations;
- Pressurized Testing: Added surface pressure fixture (pressure range: 0-0.4 MPa) with pressure film detection system for real-time monitoring of pressure variations during wetting;
- JR Resistance: Expanded channels with an internal resistance meter to externally monitor changes in JR internal resistance during wetting.
Applications
1. Capillary Wetting System-EWS Series
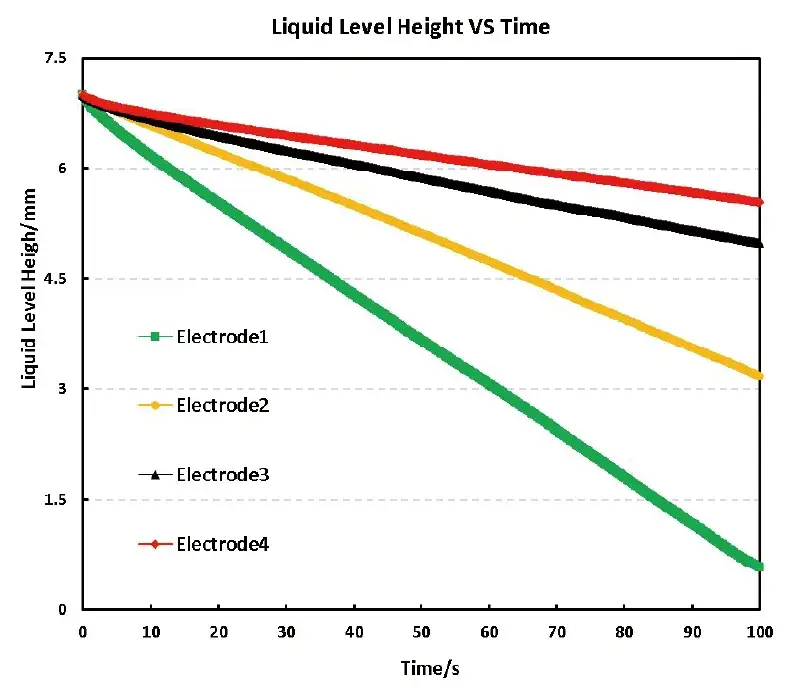
- Four different compaction densities of electrodes: 1 (1.35 g/cm³) < 2 (1.5 g/cm³) < 3 (1.6 g/cm³) < 4 (1.65 g/cm³)
- The greater the density of the electrode, the lower the porosity and the worse the electrolyte wettability.
2. Weight Wetting System-ETS Series

- Trimming three sets of anode electrode from the same batch (65*70mm)
3. Height Wetting System-CHT Series
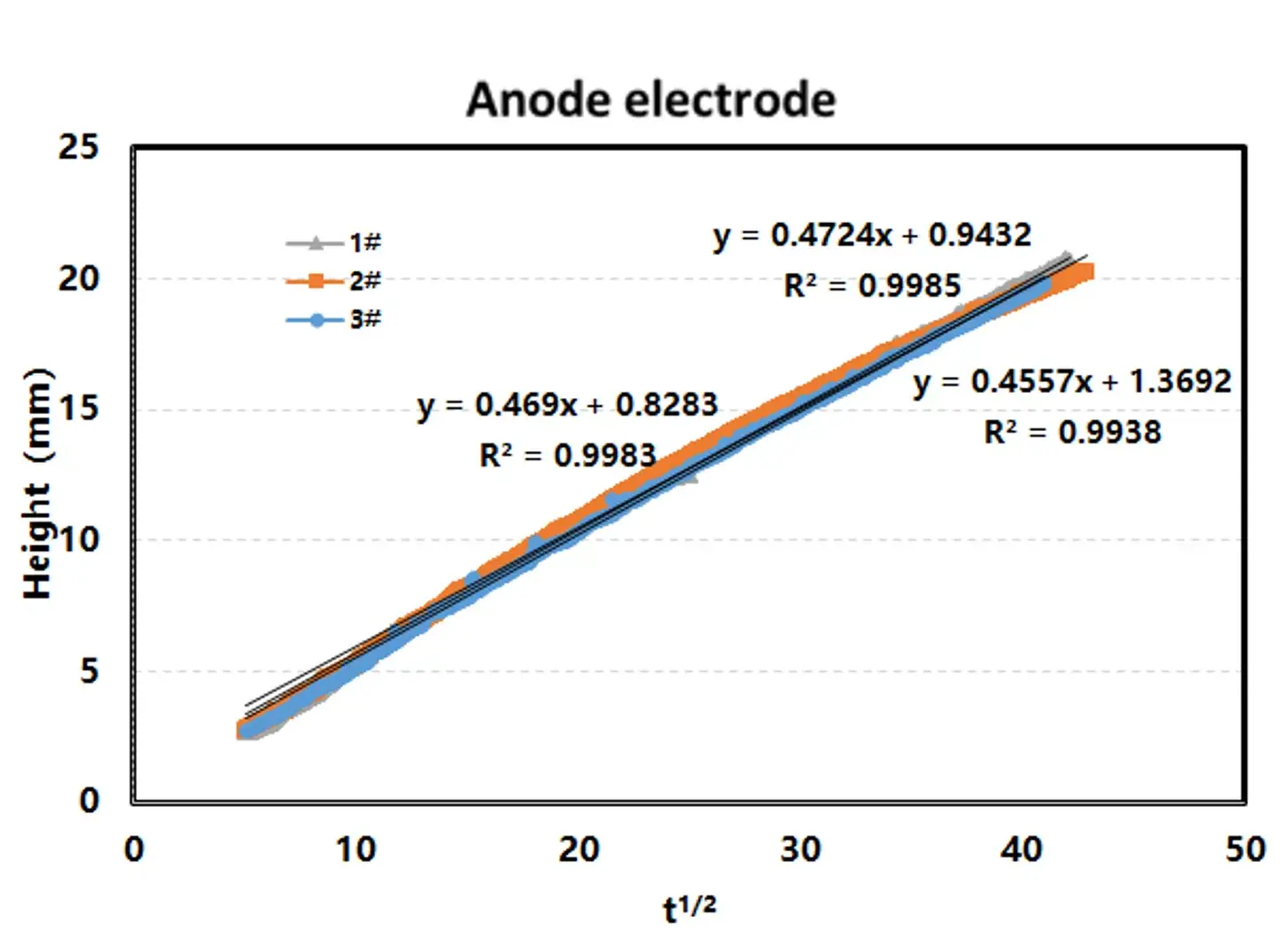
- The slopes of the 3 tested electrodes are consistent with each other, so is the wetting consistency of their electrolytes.
Video
Specifications
Capillary Wetting System-EWS Series
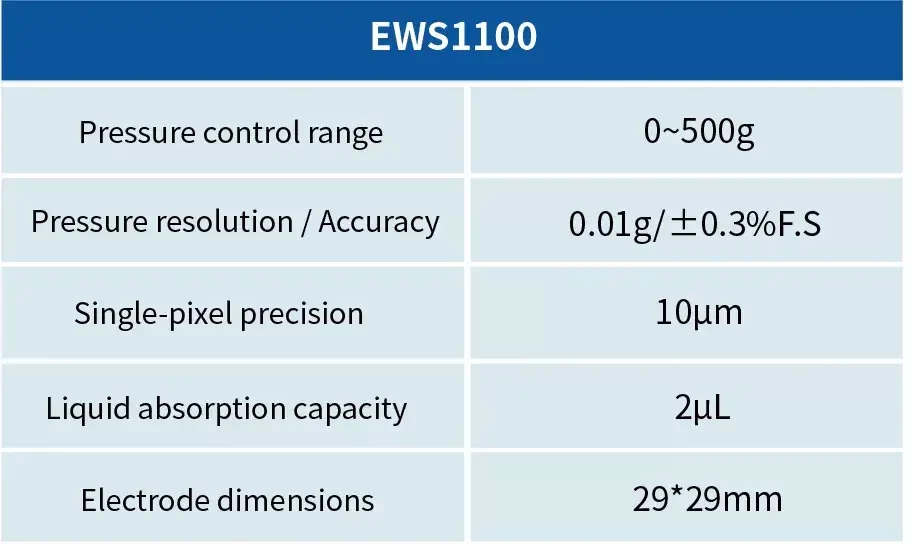
Weight Wetting System-ETS Series
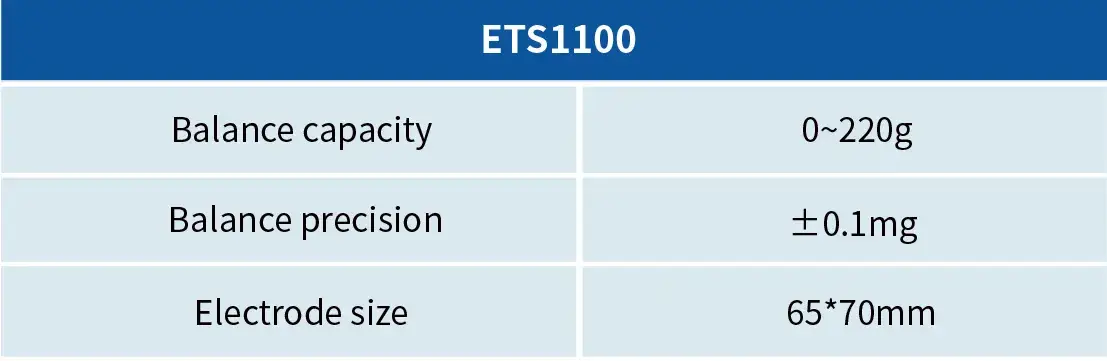
Height Wetting System-CHT Series