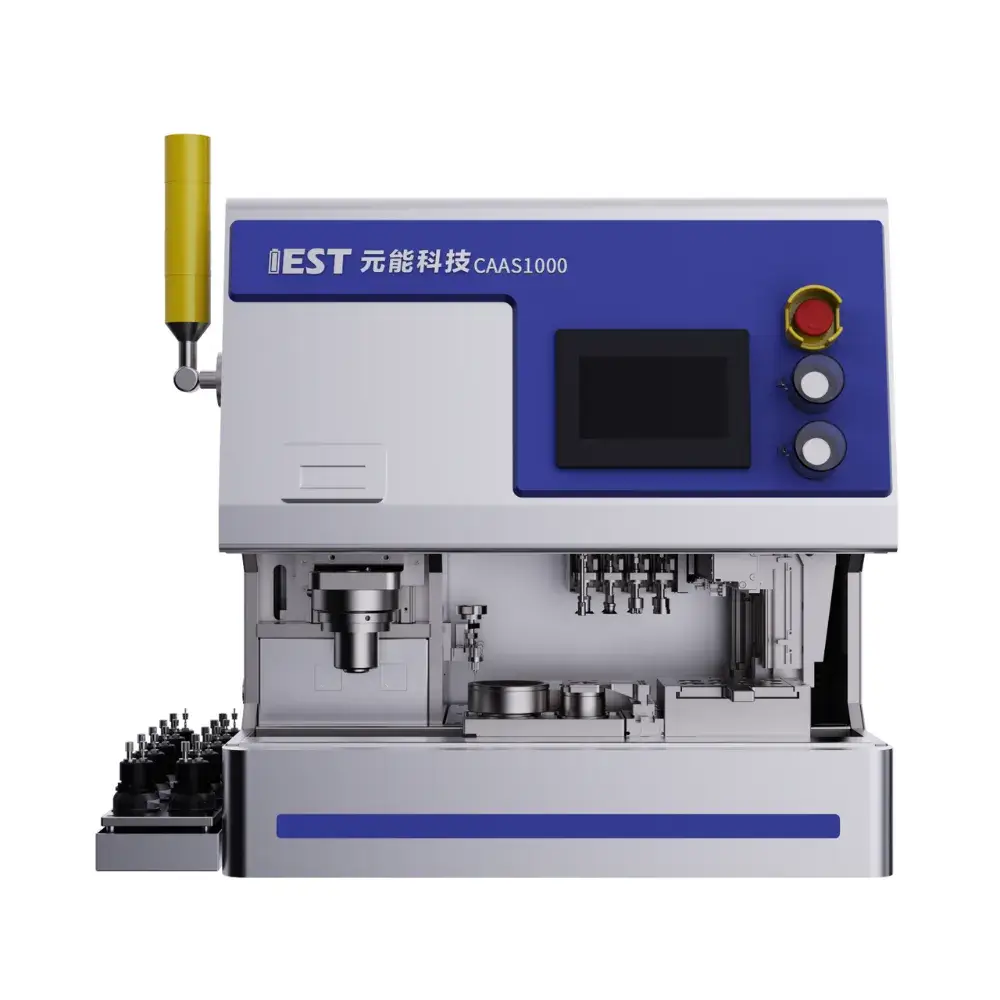
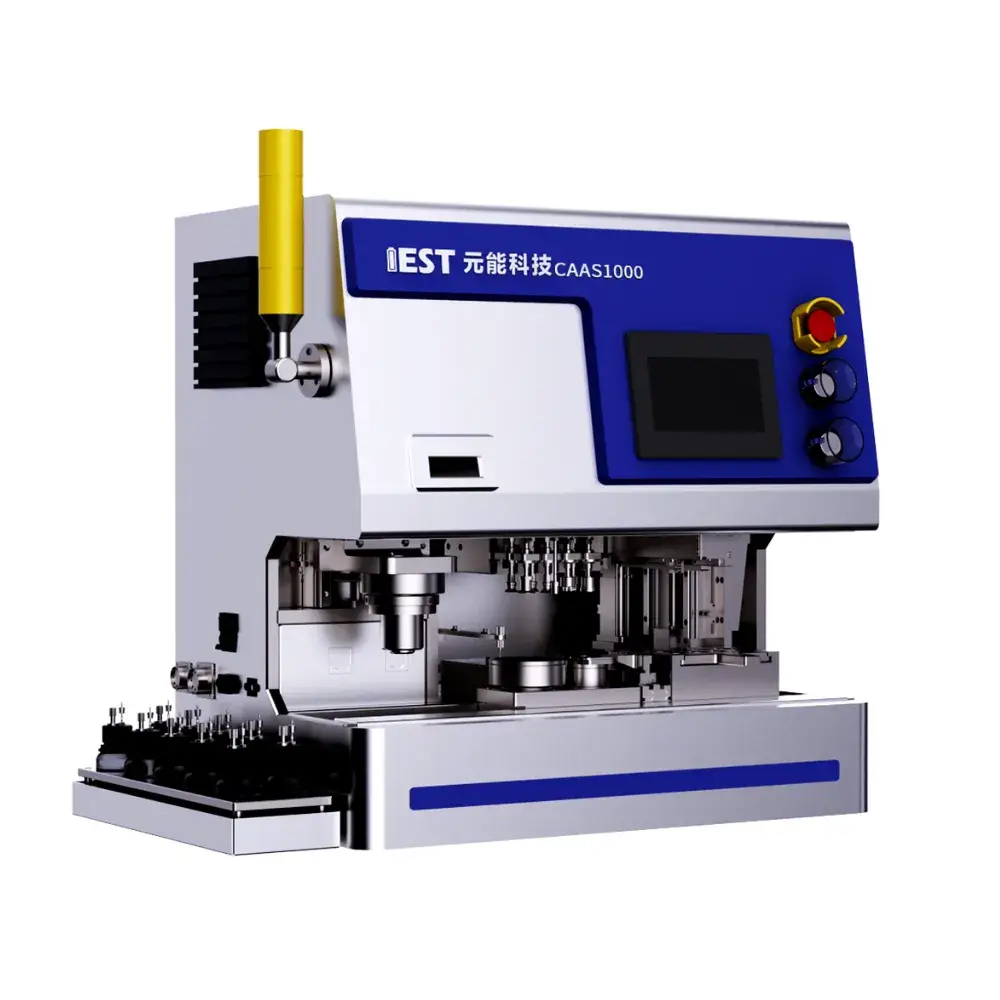
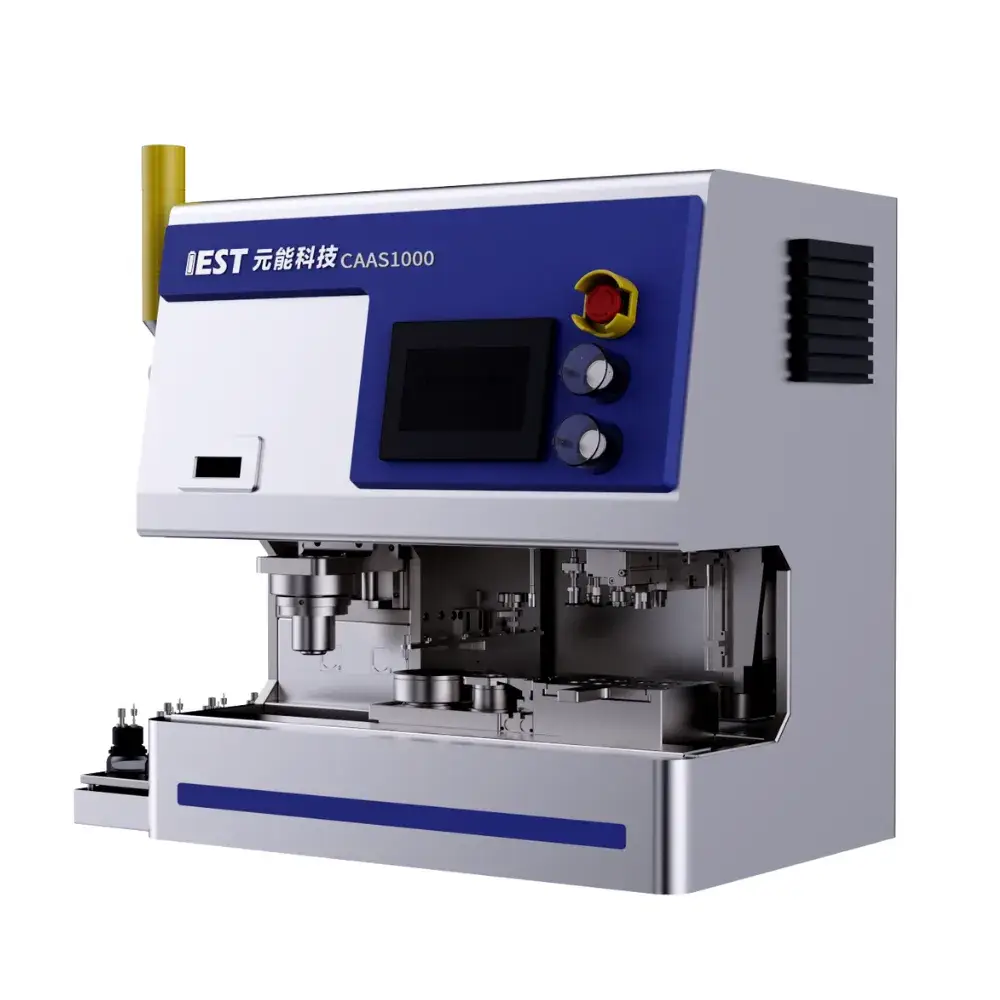
Description
1. Introduction
1.1 The Significance of Coin Cells
As the new energy industry continues to evolve, the development and testing of new materials are essential. In addition to evaluating conventional physical and chemical properties (such as particle size, BET surface area, XRD, SEM, etc.), it is even more important to conduct preliminary electrochemical performance testing and evaluation of materials and products fabricated with new processes. As a critical step in new-energy R&D, coin cell assembly quality directly determines the accuracy of material performance assessments.
1.2 Type of Coin Cell: CR/BR
Common models are: CR2032/2430/2025/2016, etc. The first 2 digits are diameter (in mm) and the last 2 digits are thickness (in 0.1 mm).
2. The Structure of Coin Cell
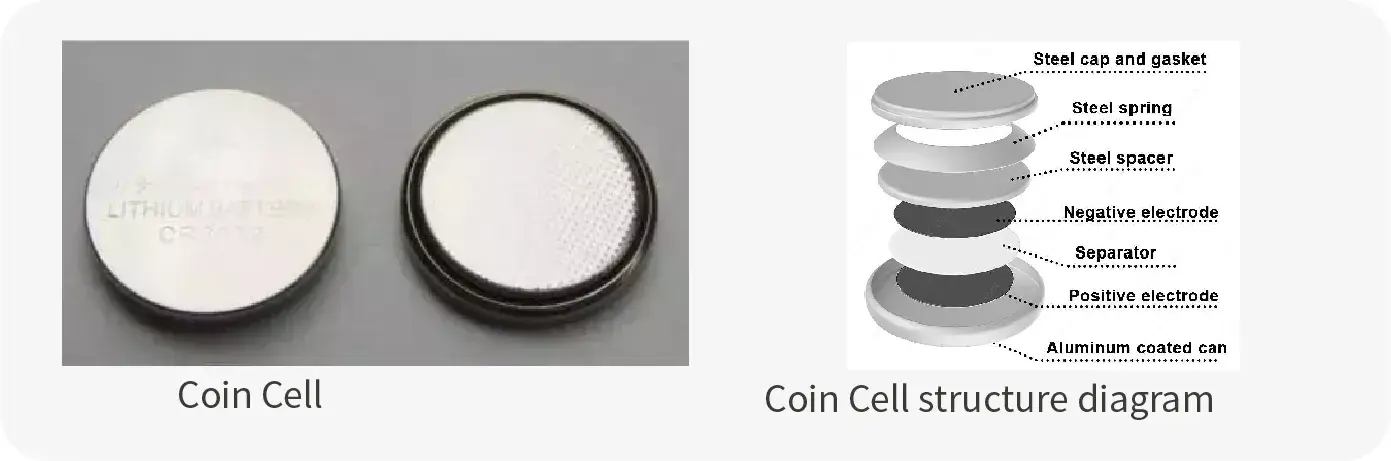

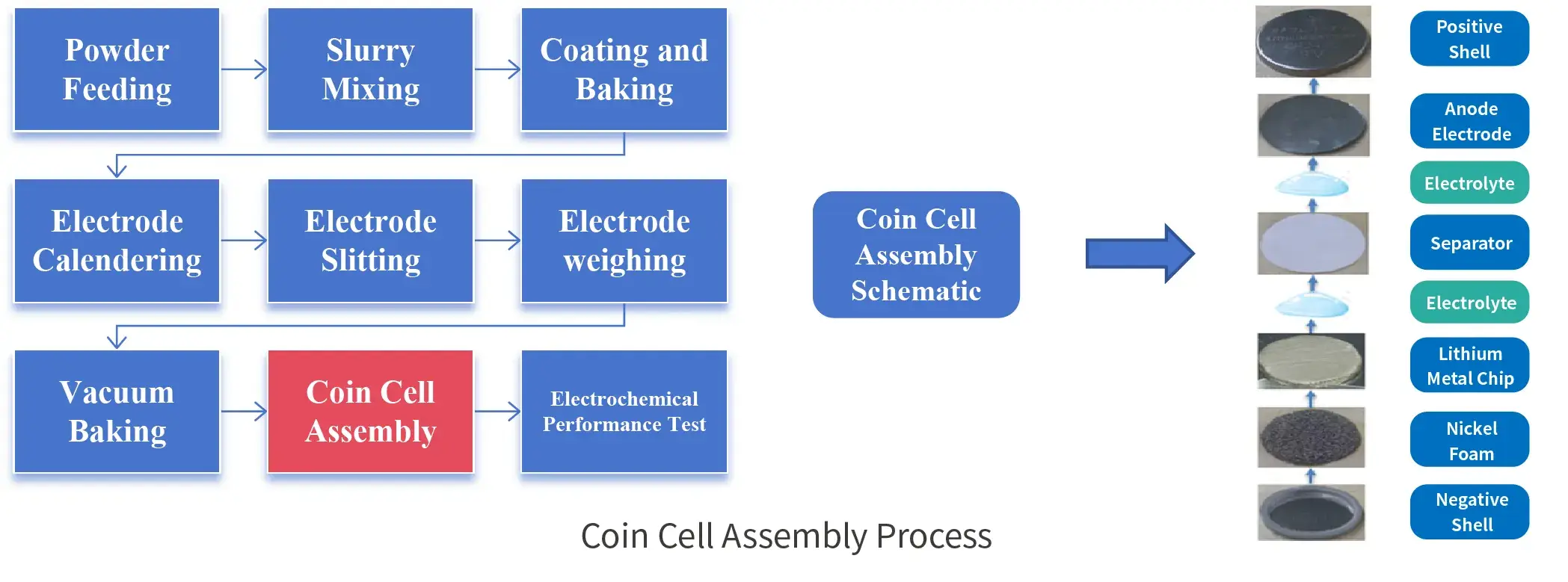
3. Coin Cell Assembly Process
Although the structure of coin cell is relatively simple compared to full cells, the preparation process is the same, which requires slurry coating at the powder end, rolling, punching and weighing of the electrode, coin cell assembly, and finally electrical performance testing.
4. Product Introduction: Next-Gen Coin Cell Assembly Machine For Lab-scale
The Lab-scale automated coin-cell assembly machine (CAAS) integrates automatic electrolyte injection, automatic sealing, a CCD positioning system, and multi-station vacuum suction grippers, enabling quick and convenient switching between coin cell assembly specifications. Assembly throughput is customizable from 1 to 10 units per batch. It reduces labor costs, ensures dimensional consistency, and minimizes repeated testing. Suitable for small batch assembly of lithium/sodium-ion coin cells.
5. Features:
5.1 Compact design
Dimensions are engineered to perfectly fit single-workstation standard glovebox specifications.
5.2 Comprehensive functionality
Integrates modules such as automatic electrolyte injection, automatic sealing, and a CCD vision system, etc.
5.3 High-speed Assembly
Approximately 2 mins/cell
5.4 High-Throughput Assembly
Up to 10 coin cells per batch, flexibly adapting to different needs.
5.5 Flexible configuration
Supports various common coin cell models such as CR2032, CR2025, CR2016, etc.
5.6 Wide range of cell types
Capable of rapidly assembling half-cells, full-cells, and symmetric cells.
6. Coin Cell Assembly Machine Features

Applications
Case 1: Curling Issue of Single-Sided Electrodes after Calendering and Punching
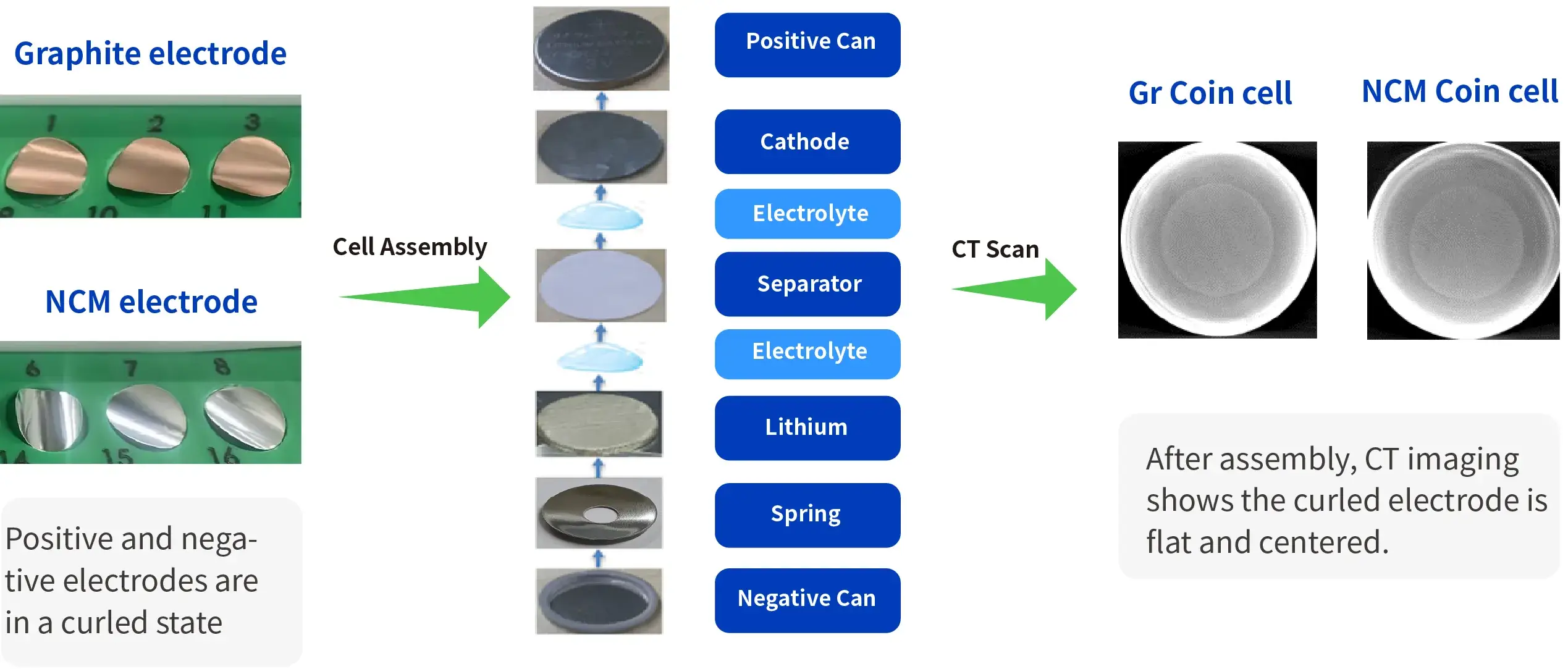
- Our special suction cup can ensure that the curled electrode is sucked evenly and flatly.
- Our visual positioning system can avoid the placement position deviation caused by the curling of the electrodes.
- The positive electrode shell is pressed down horizontally to flatten the curled electrode that contacts the electrolyte.
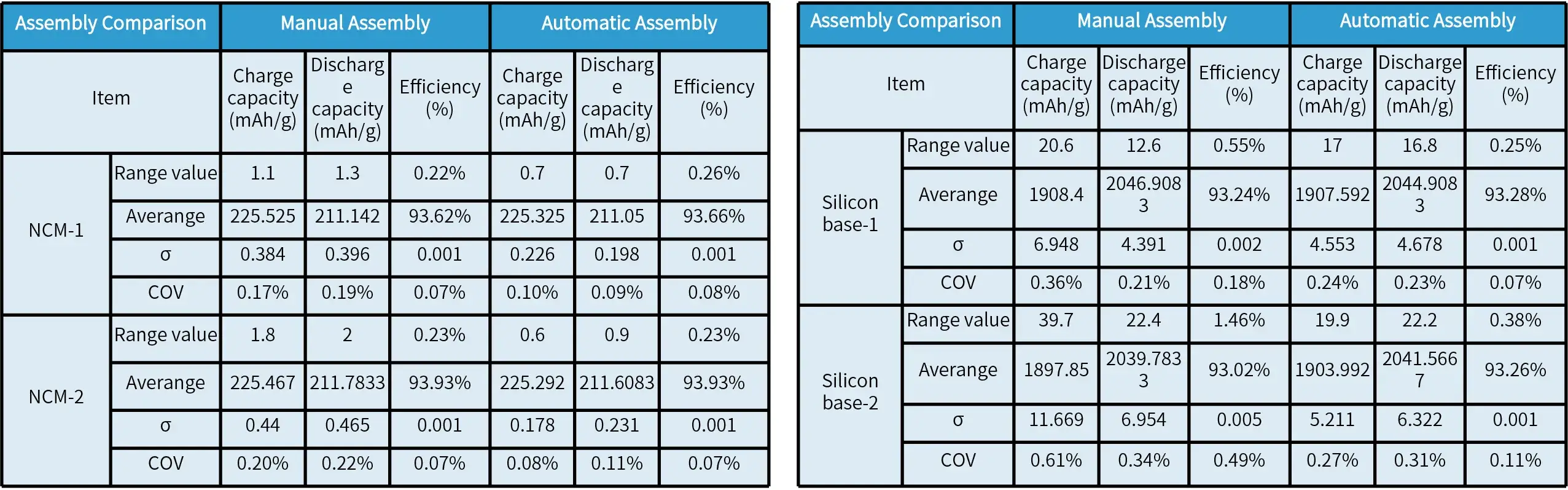
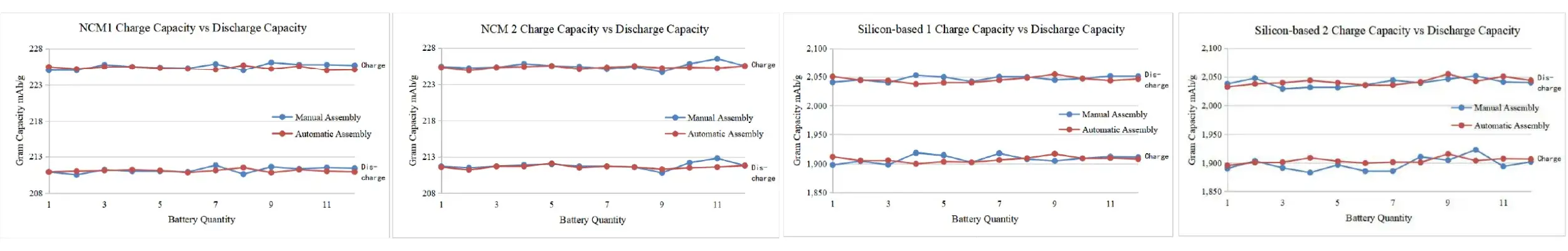
Case 2: Comparison of Manual & Automatic Assembly
Summary:
-
The range of charge/discharge specific capacity for NCM with automatic assembly is 0.6~0.9 mAh/g (σ ≈ 0.25), while with manual assembly it is 1~2 mAh/g (σ ≈ 0.4).
-
The range of charge/discharge specific capacity for Si-based materials with automatic assembly is 15~20 mAh/g (σ ≈ 4~6), while with manual assembly it is 20~40 mAh/g (σ ≈ 5~10).
-
The average coin cell specific capacity is similar between automatic and manual assembly, but the data stability of automatic assembly is superior to that of manual assembly.
Case 3: Automatic Coin Cell Assembly of LFP Cathodes
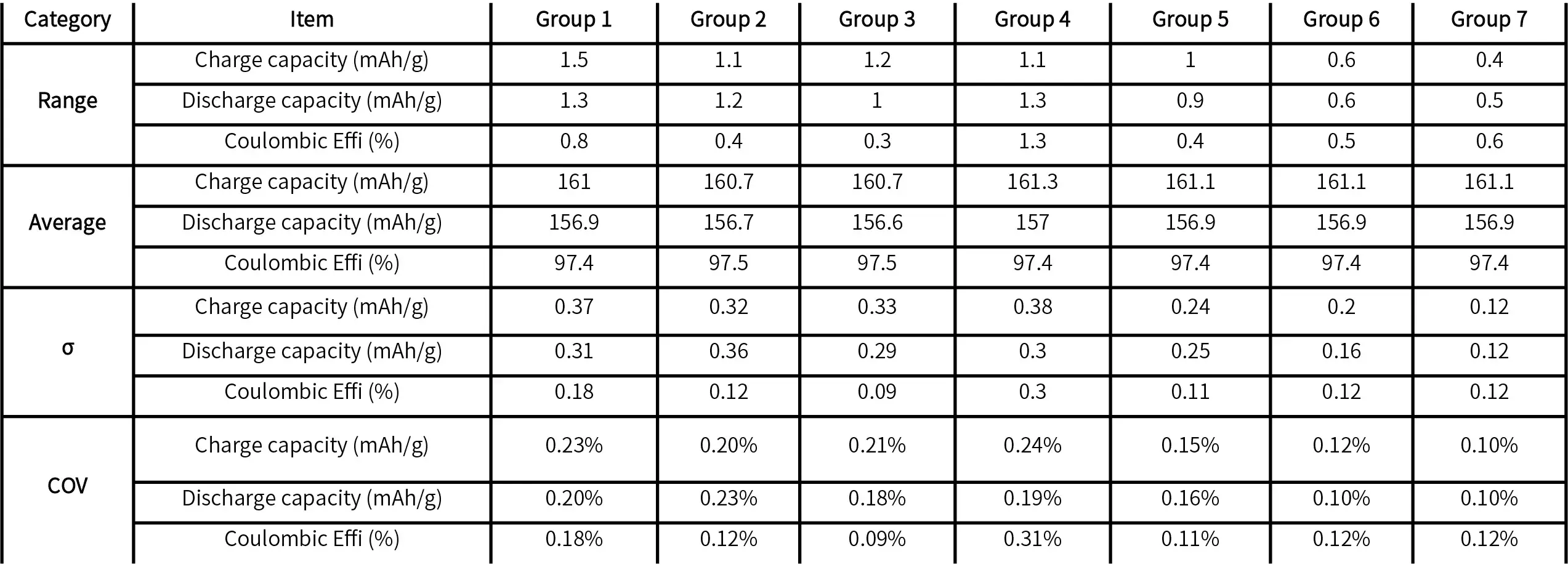
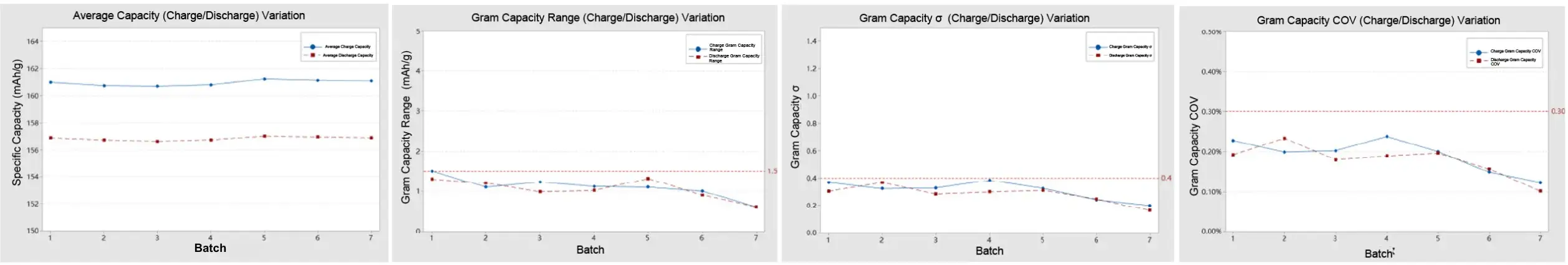
-
The standard deviation (σ) for the charge/discharge specific capacity of each group is less than 0.4.
- The range for the charge/discharge specific capacity of each group is less than 1.5 mAh/g.
- The coefficient of variation (COV) for the charge/discharge specific capacity of each group is less than 0.3%.
Case 4: Automatic Coin Cell Assembly of Graphite Anodes
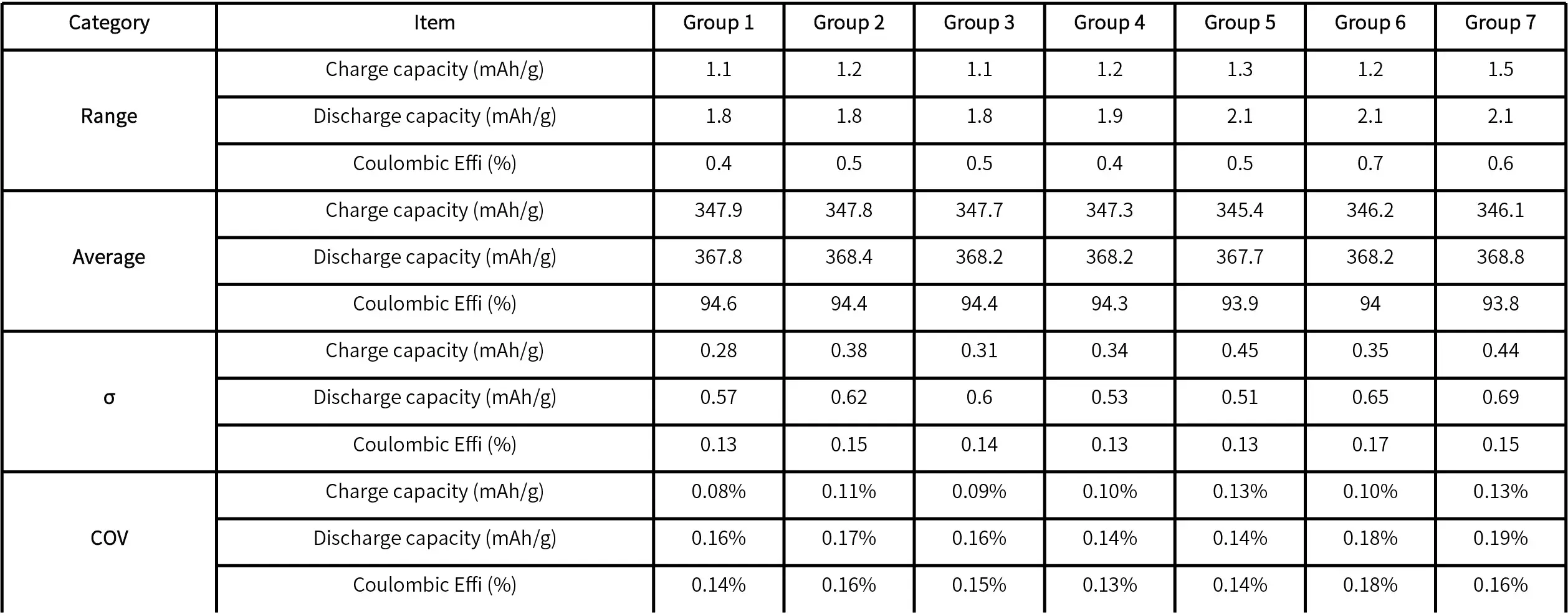
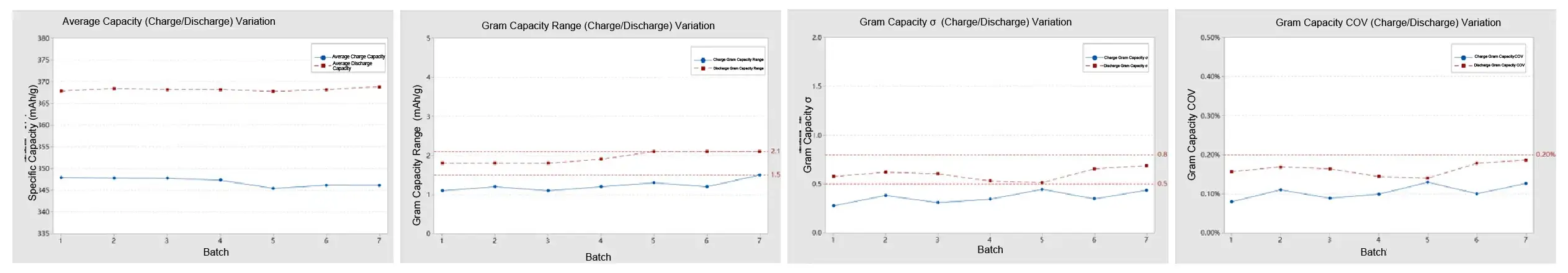
- The standard deviation (σ) for the discharge specific capacity in each group is less than 0.8, and for the chargespecific capacity, it is less than 0.5.
- The range for the discharge specific capacity in each group is less than 2.1 mAh/g, and for the charge specificcapacity, it is less than 1.5mAh/g.
- The coefficient of variation (COV) for both charge and discharge specific capacity in each group is less than 0.2%.
Specifications
Video














